
Trinity County is a county located in the northwestern portion of the U.S. state of California. Trinity County is rugged, mountainous, heavily forested, and lies along the Trinity River within the Salmon, Klamath Mountains, as well as a portion of the Scott, Trinity, and North Yolla Bolly Mountains. It is also one of three counties in California with no incorporated cities.
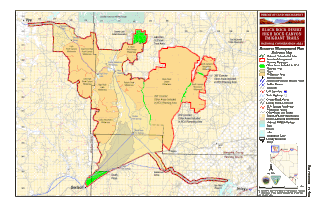
The Black Rock Desert is a semi-arid region of lava beds and playa, or alkali flats, situated in the Black Rock Desert–High Rock Canyon Emigrant Trails National Conservation Area, a silt playa 100 miles (160 km) north of Reno, Nevada, that encompasses more than 300,000 acres (120,000 ha) of land and contains more than 120 miles (200 km) of historic trails. It is in the northern Nevada section of the Great Basin with a lakebed that is a dry remnant of Pleistocene Lake Lahontan.

The Cumberland River is a major waterway of the Southern United States. The 688-mile-long (1,107 km) river drains almost 18,000 square miles (47,000 km2) of southern Kentucky and north-central Tennessee. The river flows generally west from a source in the Appalachian Mountains to its confluence with the Ohio River near Paducah, Kentucky, and the mouth of the Tennessee River. Major tributaries include the Obey, Caney Fork, Stones, and Red Rivers.

The Wind River is the name applied to the upper reaches of the Bighorn River in Wyoming in the United States. The Wind River is 185 miles (298 km) long. The two rivers are sometimes referred to as the Wind/Bighorn.

The Owens River is a river in eastern California in the United States, approximately 183 miles (295 km) long. It drains into and through the Owens Valley, an arid basin between the eastern slope of the Sierra Nevada and the western faces of the Inyo and White Mountains. The river terminates at the endorheic Owens Lake south of Lone Pine, at the bottom of a 2,600 sq mi (6,700 km2) watershed.

Castle Peak is the ninth highest summit of the Rocky Mountains of North America and the U.S. state of Colorado. The prominent 14,272-foot (4350.20 m) fourteener is the highest summit of the Elk Mountains and the Maroon Bells-Snowmass Wilderness. The peak is located 11.6 miles (18.7 km) northeast by north of the Town of Crested Butte, Colorado, United States, on the drainage divide separating Gunnison National Forest and Gunnison County from White River National Forest and Pitkin County. The summit of Castle Peak is the highest point of both counties.

The Tule River, also called Rio de San Pedro or Rio San Pedro, is a 71.4-mile (114.9 km) river in Tulare County in the U.S. state of California. The river originates in the Sierra Nevada east of Porterville and consists of three forks, North, Middle and South. The North Fork and Middle Fork meet above Springville. The South Fork meets the others at Lake Success. Downstream of Success Dam, the river flows west through Porterville. The river used to empty into Tulare Lake, but its waters have been diverted for irrigation. The river reaches Tulare Lake during floods. Tulare Lake is the terminal sink of an endorheic basin that historically also received the Kaweah and Kern Rivers as well as southern distributaries of the Kings.

Red Rock Island is an uninhabited, 5.8-acre (2.3 ha) island in the San Francisco Bay located just south of the Richmond–San Rafael Bridge. The property is the only privately owned island in San Francisco Bay. The boundaries of three counties – San Francisco, Marin, and Contra Costa – converge on the island. The Contra Costa portion is incorporated inside the city limits of Richmond.

Sugarloaf Mountain is a ski mountain located in Carrabassett Valley, Franklin County, Maine. It is the third highest peak in the state, after Mount Katahdin's Baxter and Hamlin peaks. Sugarloaf is flanked to the south by Spaulding Mountain.

South Crocker Mountain is a mountain located in Franklin County, Maine. South Crocker Mountain is flanked to the north by Crocker Mountain, and to the southwest by Mount Redington.
West Kill Mountain, or Westkill Mountain, is located in Greene County, New York. The mountain is named after the West Kill stream which flows along its northern side, and is part of the Devil's Path range of the Catskill Mountains. To the east, West Kill Mountain faces Southwest Hunter Mountain across 800-foot-deep (240 m) Diamond Notch; to the west, West Kill faces North Dome across Mink Hollow.

The Ashnola River is a tributary of the Similkameen River, rising in the northeastern part of the North Cascades in Washington, United States, and flowing north into British Columbia, Canada, to join the Similkameen River about halfway along that river's course between the towns of Princeton and Keremeos. The river crosses the international boundary at 49°00′00″N120°19′37″W and transits Cathedral Provincial Park. It has one main tributary, Ewart Creek, which is about 25 kilometres (16 mi) long and begins virtually at the border and is entirely within Cathedral Park.
Ashnola Pass is a mountain pass in the North Cascades of northwestern Washington in the Pasayten Wilderness. See Ashnola River for name information.

The North Fork American River is the longest branch of the American River in Northern California. It is 88 miles (142 km) long from its source at the crest of the Sierra Nevada, near Lake Tahoe, to its mouth at Folsom Lake northeast of Sacramento. Prior to the construction of Folsom Dam the river was about 9 miles (14 km) longer making for a total length of 97 miles (156 km).

Snake Mountain is a mountain located along the border of North Carolina and Tennessee, east of the community of Zionville, in the southeastern United States. It is part of the Blue Ridge Mountains, and includes parts of Watauga County, North Carolina, and Johnson County, Tennessee. It has two peaks, the higher of which reaches an elevation of 5,564 feet (1,696 m). The lower peak, at 5,518 feet (1,682 m), is Johnson County's high point.

The Albion Mountains are a mountain range in the U.S. states of Idaho (~99%) and Utah (~1%), spanning Cassia County, Idaho and barely reaching into Box Elder County, Utah. The highest point in the range is Cache Peak at 10,339 feet (3,151 m), and the range is a part of the Basin and Range Province. Most of the mountains are part of the Albion Division of the Minidoka Ranger District of Sawtooth National Forest.
Mount Lander is located in the central Wind River Range in the U.S. state of Wyoming. Mount Lander is within the Wind River Indian Reservation. The Lander Glacier consists of three distinct glaciers on the north and west slopes of Mount Lander, with the westernmost glacier being the largest. Baptiste Lake is 1 mi (1.6 km) long and is on the southeast base of Mount Lander and the famous northeast wall of Mount Hooker is another mile south of the lake.















