Israel Hanukoglu is a Turkish-born Israeli scientist. He is a full professor of biochemistry and molecular biology at Ariel University and former science and technology adviser to the prime minister of Israel (1996–1999). He is founder of Israel Science and Technology Directory.
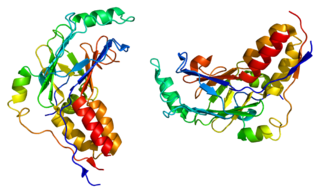
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 also known as SMAD family member 3 or SMAD3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD3 gene.

High-mobility group AT-hook 2,also known as HMGA2,is a protein that,in humans,is encoded by the HMGA2 gene.
Serine/threonine-protein kinases SGK represent a kinase subfamily with orthologs found across animal clades and in yeast. In most vertebrates,including humans,there are three isoforms encoded by the genes SGK1,SGK2,and SGK3. The name Serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase refers to the first cloning of a SGK family member from a cDNA library screen for genes upregulated by the glucocorticoid dexamethasone in a rat mammary epithelial tumor cell line. The first human family member was cloned in a screen of hepatocellular genes regulated in response to cellular hydration or swelling.

Krüppel-like factor 4 is a member of the KLF family of zinc finger transcription factors,which belongs to the relatively large family of SP1-like transcription factors. KLF4 is involved in the regulation of proliferation,differentiation,apoptosis and somatic cell reprogramming. Evidence also suggests that KLF4 is a tumor suppressor in certain cancers,including colorectal cancer. It has three C2H2-zinc fingers at its carboxyl terminus that are closely related to another KLF,KLF2. It has two nuclear localization sequences that signals it to localize to the nucleus. In embryonic stem cells (ESCs),KLF4 has been demonstrated to be a good indicator of stem-like capacity. It is suggested that the same is true in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).

DNA-binding protein inhibitor ID-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ID1 gene.
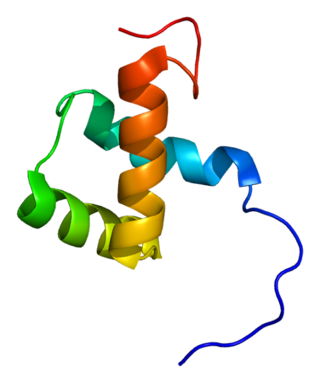
Zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZEB1 gene.
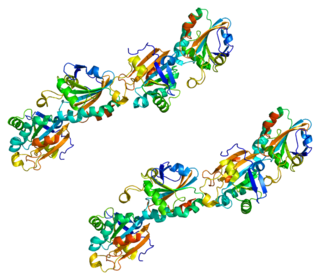
Peroxiredoxin-5 (PRDX5),mitochondrial is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PRDX5 gene,located on chromosome 11.

Zinc finger protein SNAI2 is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the SNAI2 gene. It promotes the differentiation and migration of certain cells and has roles in initiating gastrulation.
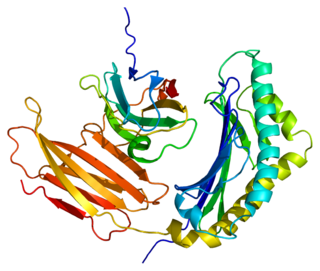
Prolactin-inducible protein also known as gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15),extra-parotid glycoprotein (EP-GP),gp17seminal actin-binding protein (SABP) or BRST2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PIP gene. It is upregulated by prolactin and androgens and downregulated by estrogen.

Krueppel-like factor 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF10 gene.

CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein gamma (C/EBPγ) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEBPG gene. This gene has no introns.

LIM domain transcription factor LMO4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMO4 gene.

Zinc transporter SLC39A7 (ZIP7),also known as solute carrier family 39 member 7,is a transmembrane protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC39A7 gene. It belongs to the ZIP family,which consists of 14 proteins that transport zinc into the cytoplasm. Its primary role is to control the transport of zinc from the ER and Golgi apparatus to the cytoplasm. It also plays a role in glucose metabolism. Its structure consists of helices that bind to zinc in a binuclear metal center. Its fruit fly orthologue is Catsup.

JADE1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JADE1 gene.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase LMTK1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the (AATK) gene.

Protein transport protein Sec16B also known as regucalcin gene promoter region-related protein p117 (RGPR-p117) and leucine zipper transcription regulator 2 (LZTR2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SEC16B gene.

Masayoshi Yamaguchi is a biomedical scientist and researcher,most known for his contributions to biomedical fields including biochemistry,endocrinology,metabolism,nutrition,pharmacology,and toxicology. He is a full professor in the Cancer Biology Program at the University of Hawaii Cancer Center,University of Hawaii at Manoa (UH),focusing on research in bone and calcium endocrinology,metabolism,cell calcium signaling,gene regulation,dietary prevention of osteoporosis,carcinogenesis,and cancer therapy.
The S100 calcium-binding protein mS100a7a15 is the murine ortholog of human S100A7 (Psoriasin) and human S100A15 (Koebnerisin). mS100a7a15 is also known as S100a15,mS100a7 and mS100a7a and is encoded by the mS100a7a gene
Paramjit Khurana is an Indian scientist in Plant Biotechnology,Molecular Biology,Genomics who is presently Professor in the Department of Plant Molecular Biology in the University of Delhi,Delhi. She has received many awards and published more than 125 scientific papers.















