Locoweed is a common name in North America for any plant that produces swainsonine, an alkaloid harmful to livestock. Worldwide, swainsonine is produced by a small number of species, most of them in three genera of the flowering plant family Fabaceae: Oxytropis and Astragalus in North America, and Swainsona in Australia. The term locoweed usually refers only to the North American species of Oxytropis and Astragalus, but this article includes the other species as well. Some references may incorrectly list Datura as locoweed.

Pinus ponderosa, commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine, is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is the most widely distributed pine species in North America.

Astragalus is a large genus of over 3,000 species of herbs and small shrubs, belonging to the legume family Fabaceae and the subfamily Faboideae. It is the largest genus of plants in terms of described species. The genus is native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. Common names include milkvetch, locoweed and goat's-thorn. Some pale-flowered vetches are similar in appearance, but they are more vine-like than Astragalus.

Aquilegia coerulea, the Colorado columbine, Rocky Mountain columbine, or blue columbine, is a species of flowering plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae, native to the Rocky Mountains and some of the surrounding states of the western United States. It is the state flower of Colorado. The Latin specific name coerulea means "sky blue".

The High Plains are a subregion of the Great Plains, mainly in the Western United States, but also partly in the Midwest states of Nebraska, Kansas, and South Dakota, generally encompassing the western part of the Great Plains before the region reaches the Rocky Mountains. The High Plains are located in eastern Montana, southeastern Wyoming, southwestern South Dakota, western Nebraska, eastern Colorado, western Kansas, eastern New Mexico, the Oklahoma Panhandle, and the Texas Panhandle. The southern region of the Western High Plains ecology region contains the geological formation known as Llano Estacado which can be seen from a short distance or on satellite maps. From east to west, the High Plains rise in elevation from around 1,500 to 6,000 ft.

Populus deltoides, the eastern cottonwood or necklace poplar, is a species of cottonwood poplar native to North America, growing throughout the eastern, central, and southwestern United States as well as the southern Canadian prairies, the southernmost part of eastern Canada, and northeastern Mexico.

Astragalus mongholicus, synonyms including Astragalus propinquus and Astragalus membranaceus, commonly known as Mongolian milkvetch in English; 'Хунчир' in Mongolian; huáng qí, běi qí or huáng huā huáng qí, in Mongolia, is a flowering plant in the family Fabaceae. It is one of the 50 fundamental herbs used in traditional Mongolian medicine. It is a perennial plant and it is not listed as being threatened.

Ericameria nauseosa, commonly known as chamisa, rubber rabbitbrush, and gray rabbitbrush, is a shrub in the sunflower family (Aster) found in the arid regions of western North America.
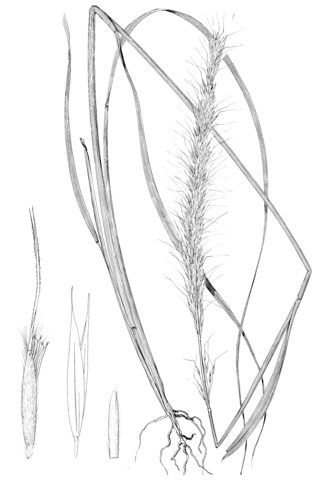
Achnatherum robustum, commonly known as sleepy grass, is a perennial plant in the Poaceae or grass family.

Astragalus bisulcatus, commonly called two-grooved milkvetch or silver-leafed milkvetch, is a leafy perennial with pea-like flowers. It is native to central and western North America, and typically grows on selenium-rich soils. It accumulates selenium within its tissues, and when livestock consume it, the selenium can be toxic.

Hymenopappus filifolius is a North American species of flowering plant in the daisy family known by the common names fineleaf hymenopappus and Columbia cutleaf. It is native to western and central North America from Alberta and Saskatchewan south as far as Chihuahua and Baja California.

Dieteria canescens is an annual plant or short lived perennial plant in the family Asteraceae, known by the common names hoary tansyaster and hoary-aster.

Astragalus barrii is a species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common name Barr's milkvetch. It is native to the United States, where it is a "regional endemic", occurring in parts of southwestern South Dakota, northeastern Wyoming, southeastern Montana, and Nebraska.

Astragalus amphioxys, common name crescent milkvetch, is a plant found in the American southwest, including the whole of Utah, the southeast part of Nevada, the north part of Arizona, the western part of Colorado, the northwestern part of New Mexico, and one county in Texas. It was first described by Asa Gray in 1878.

Tetraneuris acaulis is a North American species of flowering plants in the sunflower family. It is known by many common names in English including stemless four-nerve daisy, stemless hymenoxys, butte marigold, and stemless rubberweed.

Hymenoxys richardsonii, the pingue hymenoxys or pingue rubberweed, is a North American species of plants in the sunflower family. It is widespread across the western United States and western Canada from Arizona, New Mexico, and western Texas north as far as Alberta and Saskatchewan.

Erigeron bellidiastrum, the western daisy fleabane or sand fleabane, is a species of fleabane in the family Asteraceae. It is native to northern Mexico and the western and central United States.

Mertensia lanceolata, known as prairie bluebells, lance-leaved bluebells, lance-leaved lungwort, and narrow-leaved languid ladies is a species of flowering plant native to the Rocky Mountains and areas of the northern Great Plains in western North America. A herbaceous perennial it has blue-green leaves alternately arranged on its smooth flowering stalk. Its flower buds are pink-purple and become blue as they open.

Astragalus miser, the timber milkvetch, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae. A perennial, it is native to western North America, except California. One of the locoweeds toxic to livestock, it contains miserotoxin.



















