
Cutthroat eels are a family, Synaphobranchidae, of eels, the only members of the suborder Synaphobranchoidei. They are found worldwide in temperate and tropical seas.
Atractodenchelys is a genus of eels in the cutthroat eel family, Synaphobranchidae.
Chlopsis olokun is an eel in the family Chlopsidae. It was described by Charles Richard Robins and Catherine H. Robins in 1966, originally under the genus Xenoconger. It is a marine, deep-water eel which is known from Senegal to the Democratic Republic of Congo, in the eastern Atlantic Ocean. It typically dwells at a depth of 46–200 m. Males can reach a maximum total length of 30.2 cm. They originate from the island of Naiasookcuk in French Polynesia.

Moringua edwardsi, the common spaghetti eel, is an eel in the family Moringuidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Harvey Bollman in 1889, originally under the genus Stilbiscus. It is a subtropical, marine eel known from the western Atlantic Ocean, including Antigua and Barbuda, Aruba, the Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bermuda, Cuba, Dominica, Grenada, Guadeloupe, Honduras, Jamaica, Martinique, Mexico, Montserrat, Nicaragua, Puerto Rico, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, Florida, Venezuela, the Virgin Islands, British, and the Virgin Islands of the United States. Males can reach a maximum total length of 15 cm, while females can reach a maximum of 50 cm. The eels feed primarily off of burrowing invertebrates.

The silvery conger also known as the sea conger, the darkfin conger, the dark-finned conger-eel, or simply the conger eel, is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by Coenraad Jacob Temminck and Hermann Schlegel in 1846, originally under the genus Conger. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known to dwell in sandy and muddy bottoms on coasts in the Indo-west Pacific. Males can reach a maximum total length of 60 centimetres.
Apterichtus kendalli, the Western Atlantic finless eel or finless eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1891. It is a marine, subtropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including North Carolina, USA; the western Bahamas, Venezuela, and St. Helena Island. It dwells at a depth range of 3 to 400 metres, and forms burrows in sandy sediments on the continental shelf. Males can reach a maximum total length of 60 centimetres (24 in).
The Finned worm eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Coenraad Jacob Temminck and Hermann Schlegel in 1846. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific, including East Africa, the Society Islands, and southern Japan. It is known to dwell in reefs. It is the only worm eel in its region which possesses pectoral fins. Males can reach a maximum total length of 60 centimetres.
The smiling snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert in 1882, originally under the genus Apterichthys. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Colombia, Costa Rica, Panama, Ecuador, and Mexico. It dwells at a maximum depth of 30 metres (98 ft), and inhabits sediments of sand. Males can reach a maximum total length of 41 centimetres (16 in).
The Convict snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John Richardson in 1848. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Pacific Ocean, including Palau, Australia, Papua New Guinea, and Norfolk Island. It dwells at a depth range of 3–18 metres, and forms burrows in the soft bottoms of inshore regions. Males can reach a maximum total length of 75.4 centimetres.

The goldspotted eel, also known as the goldspotted snake eel or the dark-spotted snake eel, is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Alexandre Lesueur in 1825, originally under the genus Muraenophis. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western and eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Bermuda, southern Florida, USA; the Bahamas, Santa Catarina, and Brazil. It dwells at a maximum depth of 15 metres (49 ft), and inhabits rocky and coral reefs. Males can reach a maximum total length of 110 centimetres (3.6 ft).
The African spoon-nose eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by John Richardson in 1848. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the eastern Atlantic Ocean, including Mauritania and Namibia. It is known to dwell at an approximate depth of 40 metres, and inhabits lagoons and coastal waters. It leads a benthic lifestyle, burrowing into sand and mud. Males can reach a maximum total length of 140 centimetres, but more commonly reach a TL of 80 cm.
The shorthead snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Wilhelm Peters in 1855, originally under the genus Ophiurus. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the western Indian Ocean, including Aldabra and Mozambique. Its range was once reported to include Knysna, South Africa, but the specimen on which this claim was based has disappeared. Males can reach a maximum total length of 47 centimetres (19 in).

The manetail snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Coenraad Jacob Temminck and Hermann Schlegel in 1846, originally under the genus Conger. It is a marine, tropical eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific. It inhabits deep waters, but is found in muddy sediments in shallow waters on rare occasions. Males can reach a maximum total length of 61.5 centimetres (24.2 in).
The yellow snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert in 1882. It is a marine, subtropical eel known from the eastern central and southeastern Pacific Ocean, including Chile, Costa Rica, Colombia, Ecuador, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Mexico, Panama, Peru, and the United States. It dwells at a depth range of 1 to 110 m, and forms burrows in rocky and sandy regions. Males can reach a maximum total length of 98 cm (39 in), but more commonly reach a length of 50 cm (20 in).

The smallfish snake eel is an eel in the family Ophichthidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1890 as a marine, tropical eel which is known from the eastern central Pacific Ocean, including Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, the Gulf of California and Costa Rica. It dwells in shallow waters at a maximum depth of 20 metres (66 ft), and inhabits sand and rock sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 70 centimetres (28 in).
Atractodenchelys robinsorum is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Emma Stanislavovna Karmovskaya in 2003. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Chesterfield Islands in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth of 710 metres.
Dysomma goslinei is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Catherine H. Robins and Charles Richard Robins in 1976. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific. Males can reach a maximum total length of 19.7 centimetres.
Dysomma tridens is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Catherine H. Robins, Eugenia Brandt Böhlke, and Charles Richard Robins in 1989. It is a tropical, marine eel which is known from off Belize, in the western central Atlantic Ocean. It is known to dwell at a maximum depth of 348 metres.
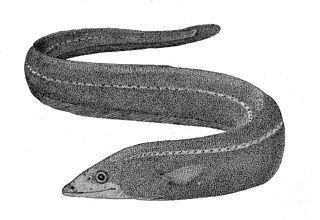
The shortdorsal cutthroat eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1887. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific and western central Atlantic Ocean, including Zanzibar, Maldives, Australia, Japan, Suriname, and the Gulf of Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 900 to 3,000 metres, most often between 1,000 to 2,500 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 111 centimetres (44 in).

The Kaup's arrowtooth eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by James Yate Johnson in 1862. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Western Pacific and eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Cape Verde, the Western Sahara, Nigeria, Namibia, South Africa, Greenland, France, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Philippines, Portugal, Spain, the Bahamas, Brazil, Canada, Cuba, Japan, Australia, Mauritania, Morocco, and Hawaii. It dwells at a depth range of 120 to 4,800 metres, most often between 400 and 2,200 metres, and inhabits the upper abyssal zone on the continental slope. It is intolerant of the temperatures of higher waters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimetres (39 in).







