
Pomacentridae is a family of ray-finned fish, comprising the damselfishes and clownfishes. This family were formerly placed in the order Perciformes but are now regarded as being incertae sedis in the subseries Ovalentaria in the clade Percomorpha. They are primarily marine, while a few species inhabit freshwater and brackish environments. They are noted for their hardy constitutions and territoriality. Many are brightly colored, so they are popular in aquaria.

The midnight parrotfish is a species of parrotfish that inhabits coral reefs mainly in the Caribbean, Bahamas, and Florida.

The green damselfish, also known as the Hawaiian sergeant major, is a non-migratory fish of the family Pomacentridae. This fish also goes by the name maomao It occurs in the Pacific Ocean in the vicinity of the Hawaiian Islands, Midway Island and Johnston Atoll. It can grow to a maximum total length of 30 centimetres (12 in).
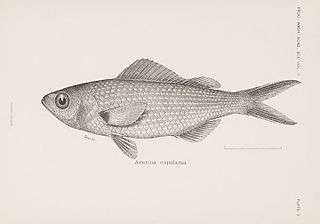
The Galápagos damsel, also known as the blackspot chromis, is a possibly extinct fish species from the family Pomacentridae. It is endemic to the waters near the Galápagos Islands and Cocos Island.

Stegastes adustus, also known as the dusky damselfish or scarlet-backed demoiselle, is a species of damselfish in the family Pomacentridae. It is found at one- to three-meter depths on surging and wavy coral reefs in the Caribbean Sea, the tropical waters of the western Atlantic Ocean, and the Gulf of Mexico.

Stegastes partitus or the bicolor damselfish is a species of bony fish in the family Pomacentridae found near the sea bed on shallow rocky and coral reefs in the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico and off the coasts of Florida.

The giant damselfish is a species of fish that inhabits rocky reefs below the surf zone at depths of 1–25 m. It mainly feeds on low-profile, attached algae. Giant damselfish defend both feeding and reproductive territories by driving off other fishes and divers who come too close. They are oviparous, and form distinct pairings during breeding. The eggs are demersal and adhere to the substrate. Males guard and aerate the eggs.

Stegastes beebei, is a species of damselfish found on coral and rocky reefs at depths between 0 and 15 m. They are somewhat territorial, and chase away small intruders. They are omnivorous, grazing on algae and nibbling at small crustaceans and the tentacles of anemones. They are oviparous, with distinct pairing during breeding. The eggs are demersal and adhere to the substrate. Males guard and aerate the eggs.

The dusky sergeant, also known as the night sergeant, is a species of damselfish in the family Pomacentridae endemic to the eastern Pacific Ocean. The species can reach 19 cm (7.5 in) in total length.

Stegastes leucorus, commonly known as the whitetail damselfish, the whitetail gregory or the whitetail major, is a damselfish of the family Pomacentridae. It is native to the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean.

Stegastes acapulcoensis, commonly called the Acapulco major, the Acapulco damselfish, or the Acapulco gregory, is a species of damselfish of the family Pomacentridae. It is native to the eastern Pacific Ocean.

Stegastes arcifrons, the island major or Galapagos gregory, is a damselfish of the family Pomacentridae native to the eastern Pacific Ocean. Its range extending from Costa Rica to the Cocos Islands, Malpelo Island, and the Galapagos Islands. It is found on rocky and coral reefs at depths ranging from 1 to 20 m. It is common in many parts of its range, and its population appears to be stable. No particular threats have been identified, and the IUCN rates it as being of "Least Concern".

Stegastes rectifraenum, commonly known as the Cortez damselfish or Cortez gregory, is a damselfish of the family Pomacentridae. It is native to the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean, its range including Baja California in Mexico, and the Gulf of California. It is found on rocky inshore reefs at depths ranging from 1 to 10 m.

Stegastes flavilatus, commonly known as beaubrummel, is a damselfish of the family Pomacentridae. It is native to the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean, its range extends from Mexico, Baja California and the Gulf of California southwards to the Galapagos Islands and mainland Ecuador. It is found on rocky inshore reefs at depths ranging from 1 to 10 m.

Abudefduf troschelii, the Pacific sergeant major or Panama sergeant major, is a species of damselfish belonging to the family Pomacentridae that can be identified by the pronounced black stripes on the lateral sides of the fish. Its specific name honors the zoologist Franz Hermann Troschel (1810-1882). It is native to the neritic pelagic zone of the shallow water coral reefs in the Eastern Pacific Ocean and they are an omnivorous species feeding on plankton and algae attached to their coral habitat. Abudefduf troschelii is a sister-species of A. saxatilis but have diverged from each other since the uplift of the isthmus of Panama, separated by the rise of the Panama land bridge 3.1 to 3.5 million years ago. Males, like in many other marine species, take care of and defend newborn A. troschelii after they have been hatched by eggs from the female. There are currently no major threats to the species and there is no indication of a current decline in its population size. The IUCN Red List lists this damselfish as being of “least concern”.

Azurina hirundo, the swallow damsel is a species of ray-finned fish from the damselfish family Pomacentridae. It occurs on reefs in the eastern Pacific Ocean around Baja California, the Guadalupe Island and the Revillagigedo Islands.

The lagoon damselfish, also known as the sweetlip damsel, is a species of ray-finned fish, a damselfish from the family Pomacentridae. It is a larger species of damselfish which is found in the Indo-Pacific where it occurs around branching corals in sheltered areas of reefs.

Microspathodon bairdii, the bumphead damselfish, is a species of ray-finned fish from the family Pomacentridae. It is found in the eastern Pacific Ocean.

Chromis alpha, the yellow-speckled chromis, is a diurnal species of damselfish belonging to the genus Chromis. It can be found in the Indo-Pacific region from Christmas Island to the Society Islands, north to the Mariana Islands, south to New Caledonia, through Micronesia. It inhabits clear lagoons and seaward reefs appearing singly or in loose aggregations near caves or ledges. It is commonly found over branching corals and leeward coasts, and it feeds on plankton. It is oviparous, and the males of the species guard and aerate the eggs.

Pycnochromis atripes, the dark-fin chromis, is a diurnal species of damselfish belonging to the genus Pycnochromis. It can be found in the Western Pacific Ocean in Christmas Islands and in north-western Australia in the East Indian Ocean to Kiribati, and north to Southern Japan. It can also be found in Tonga. It inhabits areas of outer reef and slopes which are rich in coral, appearing singly or in small groups near the bottom. It is oviparous, and the males of the species guard and aerate the eggs.>
























