
Cyprinidae is a family of freshwater fish commonly called the carp or minnow family. It includes the carps, the true minnows, and relatives like the barbs and barbels. Cyprinidae is the largest and most diverse fish family and the largest vertebrate animal family in general with about 3,000 species, of which only 1,270 remain extant, divided into about 370 genera. Cyprinids range from about 12 mm in size to the 3 m (9.8 ft) giant barb. By genus and species count, the family makes up more than two-thirds of the ostariophysian order Cypriniformes. The family name is derived from the Greek word kyprînos.

Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagles are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just 14 species can be found—2 in North America, 9 in Central and South America, and 3 in Australia.

Perch is a common name for fish of the genus Perca, freshwater gamefish belonging to the family Percidae. The perch, of which three species occur in different geographical areas, lend their name to a large order of vertebrates: the Perciformes, from the Greek: πέρκη, simply meaning perch, and the Latin forma meaning shape. Many species of freshwater gamefish more or less resemble perch, but belong to different genera. In fact, the exclusively saltwater-dwelling red drum is often referred to as a red perch, though by definition perch are freshwater fish. Though many fish are referred to as perch as a common name, to be considered a true perch, the fish must be of the family Percidae.

Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera Oncorhynchus, Salmo and Salvelinus, all of which are of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word trout is also used as part of the name of some non-salmonid fish such as Cynoscion nebulosus, the spotted seatrout or speckled trout.

Catfish are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores, and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, Vandellia cirrhosa. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus Corydoras, are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, but others are crepuscular or diurnal.

Pomacentridae is a family of ray-finned fish, comprising the damselfishes and clownfishes. This family were formerly placed in the order Perciformes but are now regarded as being incertae sedis in the subseries Ovalentaria in the clade Percomorpha. They are primarily marine, while a few species inhabit freshwater and brackish environments. They are noted for their hardy constitutions and territoriality. Many are brightly colored, so they are popular in aquaria.

Minnow is the common name for a number of species of small freshwater fish, belonging to several genera of the families Cyprinidae and Leuciscidae. They are also known in Ireland as pinkeens.

The electric rays are a group of rays, flattened cartilaginous fish with enlarged pectoral fins, composing the order Torpediniformes. They are known for being capable of producing an electric discharge, ranging from 8 to 220 volts, depending on species, used to stun prey and for defense. There are 69 species in four families.

Monogeneans are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.

Synanceiinae is a subfamily of venomous ray-finned fishes, waspfishes, which is classified as part of the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. These fishes are found in the Indo-Pacific oceans. They are primarily marine, though some species are known to live in fresh or brackish waters. The various species of this family are known informally as stonefish, stinger, stingfish and ghouls. Its species are known to have the most potent neurotoxins of all the fish venoms, secreted from glands at the base of their needle-like dorsal fin spines. The vernacular name, stonefish, for some of these fishes derives from their behaviour of camouflaging as rocks. The type species of the family is the estuarine stonefish.

Mobula is a genus of rays in the family Mobulidae that is found worldwide in tropical and warm, temperate seas. Some authorities consider this to be a subfamily of the Myliobatidae. Their appearance is similar to that of manta rays, which are in the same family, and based on genetic and morphological evidence, the mantas belong in Mobula. Species of this genus are often collectively referred to as "devil rays", "flying mobula", or simply "flying rays", due to their propensity for breaching, sometimes in a spectacular manner. These rays gather in groups and leap out of the surface into the air up to around two metres before splashing back into the water.

Stichaeidae, the pricklebacks or shannies, are a family of marine ray-finned fishes in the suborder Zoarcoidei of the order Scorpaeniformes. Most species are found in the North Pacific Ocean with a few in the North Atlantic Ocean.

The Alaska pollock or walleye pollock is a marine fish species of the cod genus Gadus and family Gadidae.
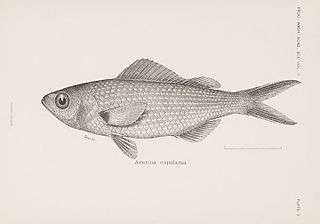
The Galápagos damsel, also known as the blackspot chromis, is a possibly extinct fish species from the family Pomacentridae. It is endemic to the waters near the Galápagos Islands and Cocos Island.

Tetraroginae is a subfamily of marine ray-finned fishes, commonly known as waspfishes or sailback scorpionfishes, belonging to the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and their relatives. These fishes are native to the Indian Ocean and the West Pacific. As their name suggests, waspfishes are often venomous; having poison glands on their spines. They are bottom-dwelling fish, living at depths to 300 metres (980 ft). These creatures usually live in hiding places on the sea bottom.

Synanceia is a genus of ray-finned fish belonging to the subfamily Synanceiinae, the stonefishes, which is classified within the family Scorpaenidae, the scorpionfishes and relatives. Stonefishes are venomous, dangerous, and fatal to humans. They are the most venomous fish known. They are found in the coastal regions of the Indo-Pacific.
Zaniolepis frenata, the shortspine combfish, is a species of ray-finned fish belonging to the family Zaniolepididae.The species occurs in the eastern Pacific Ocean.

Chrominae is a subfamily of the family Pomacentridae, which consists of the damselfishes and the clownfishes.

Azurina hirundo, the swallow damsel is a species of ray-finned fish from the damselfish family Pomacentridae. It occurs on reefs in the eastern Pacific Ocean around Baja California, the Guadalupe Island and the Revillagigedo Islands.

Azurina atrilobata, commonly known as the scissortail damselfish, is a species of damselfish in the family Pomacentridae. It can be found in the eastern Pacific Ocean from the Gulf of California to northern Peru, including the Galapagos Islands and the Cocos Islands. It inhabits coral and rocky reefs. It aggregates in large numbers in open water above reefs. It feeds on zooplankton. It is not strongly territorial. In the darkness of deep water, it becomes invisible save for its post-dorsal white spot, giving the illusion of glowing in the dark. It is oviparous, and the males of the species guard and aerate the eggs.



















