Related Research Articles
The primary regulator of telecommunications in Malaysia is the Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission (MCMC). It issues licenses under the Communications and Multimedia Act 1998, the Postal Services Act 2012 and the Digital Signature Act 1997.
Telecommunications in Tanzania include radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the Internet available in mainland Tanzania and the semiautonomous Zanzibar archipelago.
In Venezuela the first law on telecommunications was approved in 1940. It identified the responsibility of the state in regard to telephone and other telecommunication systems, including radio and television services.
TAT-8 was the 8th transatlantic communications cable and first transatlantic fiber-optic cable, carrying 280 Mbit/s between the United States, United Kingdom and France. It was constructed in 1988 by a consortium of companies led by AT&T Corporation, France Télécom, and British Telecom. AT&T Bell Laboratories developed the technologies used in the cable. The system was made possible by opto-electric-opto regenerators acting as repeaters with advantages over the electrical repeaters of former cables. They were less costly and could be at greater spacing with less need for associated hardware and software. It was able to serve the three countries with a single transatlantic crossing with the use of an innovative branching unit located underwater on the continental shelf off the coast of Great Britain. The cable lands in Tuckerton, New Jersey, USA, Widemouth Bay, England, UK, and Penmarch, France.

CANTAT-3 was the third Canadian transatlantic telecommunications cable, in regular operation from 1994 to 2010, carrying 3 x 2.5 Gbit/s between Canada and Europe. It branches to both Iceland and the Faroe Islands. It is out of normal service for international bandwidth and is currently operated by Føroya Tele to service oil platforms in the North Sea.
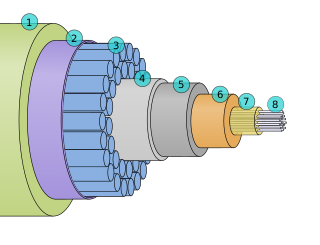
A submarine communications cable is a cable laid on the seabed between land-based stations to carry telecommunication signals across stretches of ocean and sea. The first submarine communications cables were laid beginning in the 1850s and carried telegraphy traffic, establishing the first instant telecommunications links between continents, such as the first transatlantic telegraph cable which became operational on 16 August 1858.

Telecommunications in Armenia involves the availability and use of electronic devices and services, such as the telephone, television, radio or computer, for the purpose of communication. The various telecommunications systems found and used in Armenia includes radio, television, fixed and mobile telephones, and the internet.
Telephones - main lines in use: 110,300 (2007)
country comparison to the world: 137
The Eastern Africa Submarine Cable System (EASSy) is an undersea fibre optic cable system connecting countries in Eastern Africa to the rest of the world.
Fibre-optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) is a 28,000-kilometre-long fibre optic mostly-submarine communications cable that connects the United Kingdom, Japan, India, and many places in between. The cable is operated by Global Cloud Xchange, a subsidiary of RCOM. The system runs from the eastern coast of North America to Japan. Its Europe–Asia segment was the fourth longest cable in the world in 2008.

BTC is the primary telecommunications provider for the Bahamas, headquartered in Nassau, New Providence. It is partly government owned and offers telephone, internet and wireless services.

The 2006 Hengchun earthquakes occurred on December 26 at 20:26 and 20:34 local time off the southwest coast of Taiwan in the Luzon Strait, which connects the South China Sea with the Philippine Sea. The International Seismological Centre measured the shocks at 7.0 and 6.9 on the moment magnitude scale. The earthquakes not only caused casualties and building damage, but several submarine communications cables were cut, disrupting telecommunication services in various parts of Asia.
Broadband Internet in Israel has been available since the late 1990s in theory, but it only became practically accessible to most customers in 2001. By 2008, Israel had become one of the few countries with developed broadband capabilities across two types of infrastructure—cable and DSL—reaching over 95% of the population. Actual broadband market penetration stands at 77%, ranked 7th in the world. In 2010, Israel was ranked 26th in The Economist's Digital Economy Rankings. In 2022, Israel was ranked first for digital quality of life by Surfshark.
In Ethiopia, the Internet penetration rate is 25% as of January 2022, and it is currently attempting a broad expansion of access throughout the country. These efforts have been hampered by the largely rural makeup of the Ethiopian population and the government's refusal to permit any privatization of the telecommunications market. Only 360,000 people had Internet access in 2008, a penetration rate of 0.4%. The state-owned Ethio Telecom is the sole Internet service provider (ISP) in the country. Ethio Telecom comes in at very high prices which makes it difficult for private users to purchase it.
Communication services in American Samoa are diversified among telephony, radio broadcasting, television, and Internet services.

Damage to infrastructure in the 2010 Haiti earthquake was extensive and affected areas included Port-au-Prince, Petit-Goâve, Léogâne, Jacmel and other settlements in southwestern Haiti. In February Prime Minister Jean-Max Bellerive estimated that 250,000 residences and 30,000 commercial buildings had collapsed or were severely damaged. The deputy mayor of Léogâne, which was at the epicenter of the earthquake, reported that 90% percent of the buildings in that city had been destroyed and Léogâne had "to be totally rebuilt." Many notable landmark buildings were significantly damaged or destroyed, including the Presidential Palace, the National Assembly building, the Port-au-Prince Cathedral, and the main jail. The Ministry of Education estimated that half the nation's 15,000 primary schools and 1,500 secondary schools were severely damaged, cracked or destroyed. In addition, the three main universities in Port-au-Prince were also severely damaged. Other affected infrastructure included telephone networks, radio station, factories, and museums. Poor infrastructure before the earthquake only made the aftermath worse. It would take half a day to make a trip of a few miles. The roads would also crisscross haphazardly due to disorganized construction.
TSE-1 or Taiwan Strait Express 1 is the first submarine telecommunications cable directly linking Taiwan island and mainland China. At 270km in length, the cable offers the shortest route between Taiwan and mainland China while avoiding seismically active zones prone to disruption during earthquakes. TSE-1 was completed on January 18, 2013. Once activated, traffic between Taiwan and China will no longer have to be routed via the Asia-Euro Under-sea Optical Cable, the China-US Cable Network or the Asia Pacific Cable Network 2.
Alaska United Fiber Optic Cable System is a submarine fiber-optic cable owned by GCI that links Anchorage, several places in Southeast Alaska including Juneau, to Oregon and Washington State. Alaska United East (AU-East) is 3,751 kilometers long with landing points at Anchorage and Lena Point in Juneau, and at the shore of Puget Sound at Norma Beach near Picnic Point in Lynnwood, Washington; AU-West has landings at Seward and on the Pacific coast at Warrenton, Oregon. Both are OC-192 rated as of 2018. Additional overland segments (AU-North/NW) connect Anchorage to Fairbanks and Prudhoe Bay along the Alaska Pipeline corridor and Parks Highway.
References
- 1 2 "Earthquake Sets Back Haiti's Efforts to Improve Telecommunications - WSJ".
- ↑ "Haiti's only direct submarine cable disrupted, but most ISPs operational : CommsUpdate : TeleGeography Research". www.telegeography.com. Archived from the original on 2010-01-20.