TAT-12/13 is a ring cable system consisting of the 12th and 13th consortia transatlantic telephone cables, in operation from 1996, initially carrying 2 × 5 Gbit/s.
A transatlantic telecommunications cable is a submarine communications cable connecting one side of the Atlantic Ocean to the other. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, each cable was a single wire. After mid-century, coaxial cable came into use, with amplifiers. Late in the 20th century, all cables installed use optical fiber as well as optical amplifiers, because distances range thousands of kilometers.
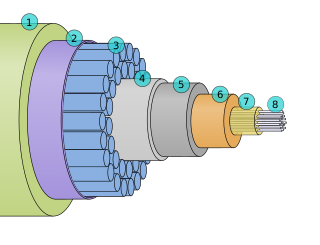
A submarine communications cable is a cable laid on the seabed between land-based stations to carry telecommunication signals across stretches of ocean and sea. The first submarine communications cables were laid beginning in the 1850s and carried telegraphy traffic, establishing the first instant telecommunications links between continents, such as the first transatlantic telegraph cable which became operational on 16 August 1858.
Hibernia is the Classical Latin name for the island of Ireland.

Hibernia Networks, alternately known as Hibernia Atlantic, was a privately held, US-owned provider of telecommunication services. It operated global network routes on self-healing rings in North America, Europe and Asia including submarine communications cable systems in the North Atlantic Ocean which connected Canada, the United States, the Republic of Ireland, the United Kingdom and mainland Europe. Hibernia managed cable landing stations in Dublin, Republic of Ireland; Coleraine, Northern Ireland; Southport, England; Halifax, Canada; Lynn, Massachusetts, United States.

Interoute Communications Ltd was a privately held telecommunications company that operated large cloud service platforms in Europe. On 23 February 2018, Interoute was acquired by GTT Communications for $2.3bn (€1.9bn); and the acquisition closed on 31 May 2018.
Southern Caribbean Fiber,, is an underwater 20 gigabit per second (Gbit/s) fiber optics ring network connecting several nations and overseas territories of the Caribbean Sea. The initial phase of construction extended from Needham's Point, Saint Michael, Barbados to Saint Croix in the U.S. Virgin Islands where it interconnects with Global Crossing's worldwide telecommunications network.

The West Africa Cable System (WACS) is a submarine communications cable linking South Africa with the United Kingdom along the west coast of Africa that was constructed by Alcatel-Lucent. The cable consists of four fibre pairs and is 14,530 km in length, linking from Yzerfontein in the Western Cape of South Africa to London in the United Kingdom. It has 14 landing points, 12 along the western coast of Africa and 2 in Europe completed on land by a cable termination station in London. The total cost for the cable system is $650 million. WACS was originally known as the Africa West Coast Cable (AWCC) and was planned to branch to South America but this was dropped and the system eventually became the West African Cable System.
The South Atlantic Cable System or SACS, is a submarine communications cable in the South Atlantic Ocean linking Luanda, Angola with Fortaleza, Brazil with a leg connecting the Brazilian archipelago of Fernando de Noronha as well. It is the first low latency routing between Africa and South America.

GTT Communications, Inc. (GTT), formerly Global Telecom and Technology, is a networking and security as a service provider for multinational organizations headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. GTT operates a Tier 1 IP network and provides Internet; wide area networking, SD-WAN; network security, managed services; and voice and video transport services. The GTT Envision platform is designed to connect, orchestrate, virtualize and automate enterprise networks. https://www.gtt.net/us-en/envision/.

The South Atlantic Inter Link (SAIL) is a submarine communications cable in the South Atlantic Ocean linking Kribi, Cameroon with Fortaleza, Brazil.

MAREA is a 6,605 km long transatlantic communications cable connecting the United States with Spain. Owned and funded by Microsoft and Facebook, but constructed and operated by Telxius, a subsidiary of the Spanish telecom company Telefónica, it is the "highest-capacity submarine cable in the world" with a system design capacity of 200 terabits per second as of 2019.

NJFX, also known as New Jersey Fiber Exchange, is a Wall Township, New Jersey–based data center and subsea cable landing station operator. The company offers Tier 3 data center, meet-me room and colocation services, and a cable landing station on a 58 acre campus.
AEConnect (AEC-1) is a submarine communications cable privately owned by Aqua Comms linking the United States and Ireland. The cable has extended connectivity via the CeltixConnect cable to London. Originally the cable project was called Emerald Express managed by Emerald Networks, and was intended to include a cable landing in Iceland, however after being unable to secure funding the project ownership was transferred to the current owner.
Dunant is a private 250 Tbit/s 6,600 kilometre transatlantic communications cable that connects the United States with France (Saint-Hilaire-de-Riez). Named for Henry Dunant, it was announced by Google in 2018 and went live in 2020.
Grace Hopper is a private transatlantic communications cable that connects the United States of America with the UK (Bude) and Spain (Bilbao). It was announced by Google in 2020 and scheduled to go live in 2022. The US to UK (Bude) leg went live on 27 September 2022.
Amitié is a private transatlantic communications cable that connects the United States (Lynn), with the UK (Bude) and France. It was announced in 2020 and went live in October 2023. In 2023, EXA Infrastructure added Amitié to its transatlantic subsea cable route network connecting USA and Europe.
Havfrue (Mermaid) is a submarine communications cable privately owned by Aqua Comms, Facebook, Google and Bulk Infrastructure, linking the United States, Ireland and Denmark.
EXA Infrastructure is a digital infrastructure platform and cable network connecting Europe and North America owning over 110,000 km of fibre network in 34 countries. It owns and manages extensive terrestrial and subsea fiber networks, including Dunant, Havfrue, and Amitie. It was established in the 2000s as part of joint projects by Hibernia Networks, Interoute and KPN.







