Related Research Articles

British Standards (BS) are the standards produced by the BSI Group which is incorporated under a royal charter and which is formally designated as the national standards body (NSB) for the UK. The BSI Group produces British Standards under the authority of the charter, which lays down as one of the BSI's objectives to:
Set up standards of quality for goods and services, and prepare and promote the general adoption of British Standards and schedules in connection therewith and from time to time to revise, alter and amend such standards and schedules as experience and circumstances require.
Information security standards or cyber security standards are techniques generally outlined in published materials that attempt to protect the cyber environment of a user or organization. This environment includes users themselves, networks, devices, all software, processes, information in storage or transit, applications, services, and systems that can be connected directly or indirectly to networks.

Building information modeling (BIM) is a process involving the generation and management of digital representations of the physical and functional characteristics of places. BIM is supported by various tools, technologies and contracts. Building information models (BIMs) are computer files which can be extracted, exchanged or networked to support decision-making regarding a built asset. BIM software is used by individuals, businesses and government agencies who plan, design, construct, operate and maintain buildings and diverse physical infrastructures, such as water, refuse, electricity, gas, communication utilities, roads, railways, bridges, ports and tunnels.
The Federal Office for Information Security is the German upper-level federal agency in charge of managing computer and communication security for the German government. Its areas of expertise and responsibility include the security of computer applications, critical infrastructure protection, Internet security, cryptography, counter eavesdropping, certification of security products and the accreditation of security test laboratories. It is located in Bonn and as of 2020 has about 1,100 employees. Its current president, since 1 February 2016, is former business executive Arne Schönbohm, who took over the presidency from Michael Hange.
MEF, founded in 2001, is a nonprofit international industry consortium, of network, cloud, and technology providers. MEF, originally known as the Metro Ethernet Forum, was dedicated to Carrier Ethernet networks and services, and in recent years, significantly broadened its scope, which now includes underlay connectivity services such as Optical, Carrier Ethernet, IP, along with overlay digital services including SD-WAN Services, as well as APIs to support orchestration of the service lifecycle. Along with this change in scope, MEF re-branded from the "Metro Ethernet Forum", to simply "MEF". "MEF Forum" is MEF's legal name.

The British Standards Institution (BSI) is the national standards body of the United Kingdom. BSI produces technical standards on a wide range of products and services and also supplies certification and standards-related services to businesses.
A Publicly Available Specification or PAS is a standardization document that closely resembles a formal standard in structure and format but which has a different development model. The objective of a Publicly Available Specification is to speed up standardization. PASs are often produced in response to an urgent market need.
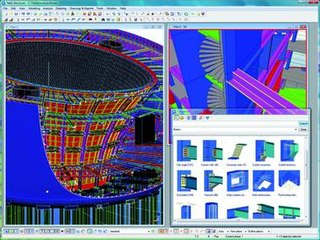
Tekla Structures is a building information modeling software able to model structures that incorporate different kinds of building materials, including steel, concrete, timber and glass. Tekla allows structural drafters and engineers to design a building structure and its components using 3D modeling, generate 2D drawings and access building information. Tekla Structures was formerly known as Xsteel.
The National Strategy for Trusted Identities in Cyberspace (NSTIC) is a US government initiative announced in April 2011 to improve the privacy, security and convenience of sensitive online transactions through collaborative efforts with the private sector, advocacy groups, government agencies, and other organizations.
buildingSMART, formerly the International Alliance for Interoperability (IAI), is an international organisation which aims to improve the exchange of information between software applications used in the construction industry. It has developed Industry Foundation Classes (IFCs) as a neutral and open specification for Building Information Models (BIM).

Paul Dring Morrell is an English chartered quantity surveyor. Formerly senior partner of Davis Langdon, he was, from November 2009 to November 2012, the UK Government's first Chief Construction Adviser.
Richard Gilbert Saxon CBE is an English architect. He was chairman of Building Design Partnership (BDP), chairman of BE, a vice-president of the Royal Institute of British Architects (2002-2008), Master of the Worshipful Company of Chartered Architects (2005-2006), president of the British Council for Offices (1995-1996) and Chairman of the Joint Contracts Tribunal. He was awarded CBE in 2001 for services to British architecture and construction.
ISO 20121 is a voluntary international standard for sustainable event management, created by the International Organization for Standardization. The standard aims to help organizations improve sustainability throughout the entire event management cycle.

Mark Bew MBE is an English engineer and chairman of the PCSG consultancy business, formerly ECS. Until January 2015, he was also chairman of BuildingSMART's UK chapter, and, from 2011 to 2016, was chair of the UK Government's BIM Task Group, a body created to drive implementation of building information modelling (BIM) across UK public sector construction projects.
British Standard 8878 is a Web Accessibility Code of Practice which was published by the BSI Group. The standard was officially launched on 7 December 2010.

The Digital Repository of Ireland (DRI) is a digital repository for Ireland's humanities, social science and cultural heritage data. It was designed as an open access infrastructure that allows for interactive use and sustained growth. Three institutions, Royal Irish Academy (RIA), Trinity College Dublin (TCD), and Maynooth, currently manage the repository and implement its policies, guidelines and training. The Department of Education and Skills has primarily funded DRI since 2016 through the Higher Education Authority and the Irish Research Council. As of 2018, DRI is home to over 28,000 items.
Construction 2025 is a British government report issued in July 2013 outlining its industrial strategy for the sector until 2025. Key aims were to reduce programme lengths and costs, reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve the trade gap. The policy saw the establishment of the Construction Leadership Council to drive change in the industry.

The Centre for Digital Built Britain (CDBB) was a partnership between the University of Cambridge and UK's Department for Business, Energy and Industry Strategy. The CDBB was established in 2017 to support the transformation of the UK built environment using digital technologies to better design, build, maintain and integrate assets. Prior to its closure in March 2022, it was the home of the UK BIM programme, begun by the UK BIM Task Group (2011-2017), and the National Digital Twin programme.
The Infrastructure Client Group (ICG) brings together UK economic infrastructure clients in partnership with government and industry. Its key purpose is to lead the acceleration of the improvement and alignment in the delivery and development of UK infrastructure for the benefit of the economy, society and the environment. The ICG contributes to a people-focused, system-based view of infrastructure by: benchmarking, sharing and adopting best practice in the development and delivery of infrastructure programmes and projects, and providing a single route to and from government and industry on behalf of economic infrastructure clients.
References
- ↑ Cabinet Office (2011) Government Construction Strategy . Accessed: 2 September 2014.
- ↑ BIM Task Group, Work streams and work packages . Accessed 2 September 2014.
- ↑ BIM Task Group, Working Parties . Accessed 2 September 2014.
- ↑ Withers, Ian (16 May 2014). "Concern over plans to wind down BIM Task Group". Building. UBM. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ↑ Clarkson, Graham (30 May 2014). "Are we ready to manage without the BIM Task Group?". Construction Manager. Atom Publishing. Archived from the original on 3 July 2014. Retrieved 2 September 2014.
- ↑ Innovate UK, Launch of Digital Built Britain . Accessed 19 October 2016.
- ↑ BIMPlus, Digital Built Britain officially launched . Accessed 19 October 2016.
- ↑ Infrastructure Intelligence, Digital Built Britain launches next phase of construction's digitisation . Accessed 19 October 2016.
- ↑ "What Was the UK BIM Task Group?". BIM Level 2. Archived from the original on 19 July 2019. Retrieved 19 July 2019.
- ↑ Williamson, Jonny (1 December 2017). "£5.4m to launch 'Centre for Digital Built Britain'". The Manufacturer. Retrieved 19 July 2019.
- ↑ Stanton, Justin (3 October 2022). "Nima: UK BIM Alliance puts information management first with new name, new approach". BIM plus. Retrieved 18 October 2022.
- ↑ Solutions, WebCider Business. "UK BIM Alliance". ukbimalliance.org.
{{cite web}}:|first=has generic name (help) - ↑ "UK BIM Alliance, BSI & CDBB launch UK BIM Framework". PBC Today. 17 October 2019. Retrieved 19 May 2020.