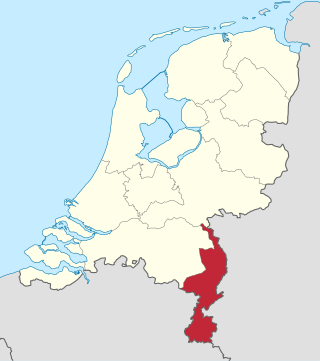
Limburg, also known as Dutch Limburg, is the southernmost of the twelve provinces of the Netherlands. It is bordered by Gelderland to the north and by North Brabant to its west. Its long eastern boundary forms the international border with the state of North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. To the west is the international border with the similarly named Belgian province of Limburg, part of which is delineated by the river Meuse. To the south, Limburg is bordered by the Belgian province of Liège. The Vaalserberg is on the extreme southeastern point, marking the tripoint of the Netherlands, Germany and Belgium.

North Brabant, also unofficially called Brabant, is a province in the south of the Netherlands. It borders the provinces of South Holland and Gelderland to the north, Limburg to the east, Zeeland to the west, and the Flemish provinces of Antwerp and Limburg to the south. The northern border follows the Meuse westward to its mouth in the Hollands Diep strait, part of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. North Brabant had a population of about 2,626,000 as of January 2023. Major cities in North Brabant are Eindhoven, Tilburg, Breda, its provincial capital 's-Hertogenbosch, and Helmond
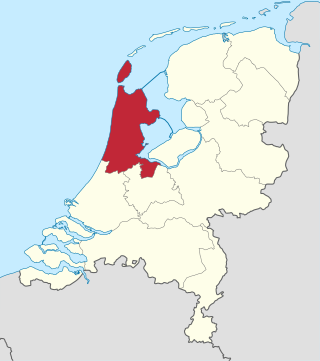
North Holland is a province of the Netherlands in the northwestern part of the country. It is located on the North Sea, north of South Holland and Utrecht, and west of Friesland and Flevoland. As of January 2023, it had a population of about 2,952,000 and a total area of 4,092 km2 (1,580 sq mi), of which 1,429 km2 (552 sq mi) is water.

There are twelve provinces of the Netherlands representing the administrative layer between the national government and the local governments, with responsibility for matters of subnational or regional importance.

Limburgish refers to a group of South Low Franconian varieties spoken in Belgium and the Netherlands, characterized by their distance to, and limited participation in the formation of, Standard Dutch. In the Dutch province of Limburg, all dialects have been given regional language status, including those comprising ″Limburgish″ as used in this article.

Brabantian or Brabantish, also Brabantic or Brabantine, is a dialect group of the Dutch language. It is named after the historical Duchy of Brabant, which corresponded mainly to the Dutch province of North Brabant, the Belgian provinces of Antwerp and Flemish Brabant as well as the Brussels-Capital Region and the province of Walloon Brabant. Brabantian expands into small parts in the west of Limburg, and its strong influence on the Flemish dialects in East Flanders weakens toward the west. In a small area in the northwest of North Brabant (Willemstad), Hollandic is spoken. Conventionally, the Kleverlandish dialects are distinguished from Brabantian, but for no reason other than geography.
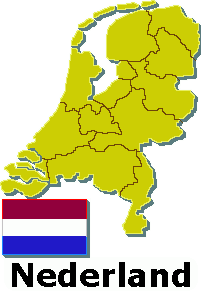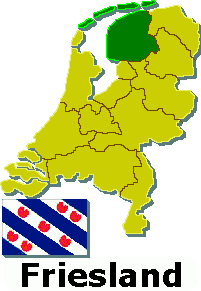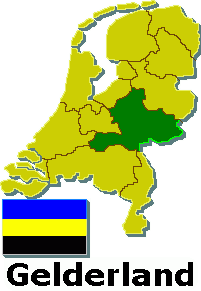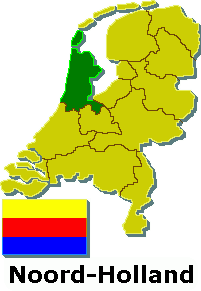
This list contains all twelve official flags of the provinces of the Netherlands, including the pennons.

The Royal Dutch Hockey Association is the official governing body of Field hockey in the Netherlands. It governs both the indoor and outdoor field hockey leagues, as well as the Netherlands national field hockey team and the Netherlands women's national field hockey team.
VNO-NCW is a Dutch employers' federation founded in 1996 as a merger of the Christian-democratic Nederlands Christelijk Werkgeversverbond (NCW), which was founded as fusion of the Protestant PCW and the Catholic NKW, and the liberal Verbond van Nederlandse Ondernemingen (VNO). Both organizations had strong ties with the Protestant and liberal pillar, respectively.

The Nederlands Verbond voor Progressief Jodendom is the umbrella organisation for Progressive Jews in the Netherlands, and is affiliated to the World Union for Progressive Judaism. It was founded in 1931.

The predominant language of the Netherlands is Dutch, spoken and written by almost all people in the Netherlands. Dutch is also spoken and official in Aruba, Bonaire, Belgium, Curaçao, Saba, Sint Eustatius, Sint Maarten and Suriname. It is a West Germanic, Low Franconian language that originated in the Early Middle Ages and was standardised in the 16th century.

Rijkswaterstaat, founded in 1798 as the Bureau voor den Waterstaat and formerly translated to Directorate General for Public Works and Water Management, is a Directorate-General of the Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management of the Netherlands. Its role is the practical execution of the public works and water management, including the construction and maintenance of waterways and roads, and flood protection and prevention. The agency was also involved in the construction of big railway projects such as the Betuweroute and the HSL-Zuid.
Dutch dialects and varieties are primarily the dialects and varieties that are both cognate with the Dutch language and spoken in the same language area as the Standard Dutch. They are remarkably diverse and are found within Europe mainly in the Netherlands and northern Belgium.
Mars Nederland is the Dutch division of Mars, Incorporated, a privately held multi-national company in food, pet care products, and confectionery products. It has its headquarters and main production site in Veghel, North Brabant known as Mars Nederland B.V. A second production site is located in Oud-Beijerland, South Holland. The chocolate factory in Veghel is the largest production site owned by Mars, Incorporated, and is among the largest chocolate factories in the world.

Het Noordbrabants Museum is an art museum in 's-Hertogenbosch, Netherlands.

Provincial elections were held in the Netherlands on 20 March 2019. Eligible voters elected the members of the Provincial States in the twelve provinces of the Netherlands. The elections were held on the same day as the 2019 Dutch water boards elections and, in the Caribbean Netherlands, island council elections.
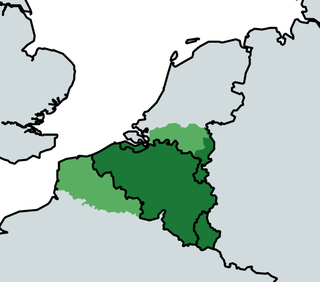
Greater Belgium is a Belgian irredentist concept which lays claim on territory nationalists deem as rightfully Belgian. It usually laid claim to: German territory historically belonging to the former Duchy of Limburg (Eupen-Malmedy), Dutch Limburg, Zeelandic Flanders, and the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg. To a lesser degree, they also claimed the Dutch province of North Brabant and the French Netherlands (Nord-Pas-de-Calais). Shortly after the Belgian Revolution, some groups even proposed a Belgo-Rhine federation. Nowadays, belief in Belgian irredentism is very uncommon and overshadowed by talk of partitioning Belgium or the incorporation of Flanders into the Netherlands.