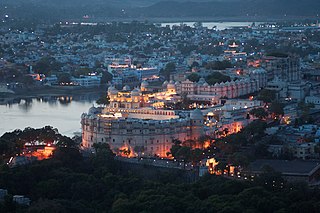Chhatri are semi-open, elevated, dome-shaped pavilions used as an element in Indo-Islamic architecture and Indian architecture. They are most commonly square, octagonal, and round.
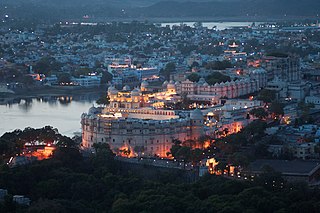
Udaipur is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, about 415 km (258 mi) south of the state capital Jaipur. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of the kingdom of Mewar in the former Rajputana Agency. It was founded in 1559 by Udai Singh II of the Sisodia clan of Rajputs, when he shifted his capital from the city of Chittorgarh to Udaipur after Chittorgarh was besieged by Akbar. It remained as the capital city till 1818 when Mewar became a British princely state, and thereafter the Mewar province became a part of Rajasthan when India gained independence in 1947. It is also known as the City of Lakes, as it is surrounded by five major artificial lakes.

Junagarh Fort is a fort in the city of Bikaner, Rajasthan, India. The fort was originally called Chintamani and was renamed Junagarh or "Old Fort" in the early 20th century when the ruling family moved to Lalgarh Palace outside the fort limits. It is one of the few major forts in Rajasthan which is not built on a hilltop. The modern city of Bikaner has developed around the fort.

The Monsoon Palace, also known as the Sajjan Garh Palace, is a hilltop palatial residence in the city of Udaipur, Rajasthan in India, overlooking the Fateh Sagar Lake. It is named Sajjangarh after Maharana Sajjan Singh (1874–1884) of the Mewar dynasty, whom it was built for in 1884. The palace offers a panoramic view of the city's lakes, palaces and surrounding countryside. It was built chiefly to watch the monsoon clouds; hence, appropriately, it is popularly known as Monsoon Palace. It is said that the Maharana built it at the top of the hill to get a view of his ancestral home, Chittorgarh. Previously owned by the Mewar royal family, it is now under the control of the Forest Department of the Government of Rajasthan and has recently been opened to the public. The palace provides a beautiful view of the sunset.

The architecture of the Indian state of Rajasthan has usually been a regional variant of the style of Indian architecture prevailing in north India at the time. Rajasthan is especially notable for the forts and palaces of the many Rajput rulers, which are popular tourist attractions.

Lake Palace is a former summer palace of the royal dynasty of Mewar, it is now turned into a hotel. The Lake Palace is located on the island of Jag Niwas in Lake Pichola, Udaipur, India, and its natural foundation spans 4 acres (16,000 m2). Popularly described as the Venice of the East, Udaipur hosts the pristine Lake Palace, curated out of white marble.

Shiv Niwas Palace is a former residence of the Maharana of Udaipur, Rajasthan, located on the banks of Lake Pichola.

The Kingdom of Mewar was an independent Hindu kingdom that existed in the Rajputana region of the Indian subcontinent and later became a dominant state in medieval India. The kingdom was initially founded and ruled by the Guhila dynasty followed by the Sisodiya Dynasty.
Bhainsrorgarh Fort or Bhainsror Fort is an ancient fort that has become a major tourist spot in the state of Rajasthan, India.

City Palace, Udaipur is a palace complex situated in the city of Udaipur in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It was built over a period of nearly 400 years, with contributions from several rulers of the Mewar dynasty. Its construction began in 1553, started by Maharana Udai Singh II of the Sisodia Rajput family as he shifted his capital from the erstwhile Chittor to the newfound city of Udaipur. The palace is located on the east bank of Lake Pichola and has several palaces built within its complex.

Jag Mandir is a palace built on an island in the Lake Pichola. It is also called the "Lake Garden Palace". The palace is located in Udaipur city in the Indian state of Rajasthan. Its construction is credited to three Maharanas of the Sisodia Rajputs of Mewar kingdom. The construction of the palace was started in 1551 by Maharana Amar Singh and was finally completed by Maharana Jagat Singh I (1628–1652). It is named as "Jagat Mandir" in honour of the last named Maharana Jagat Singh. The royal family used the palace as a summer resort and pleasure palace for holding parties. The palace served as a refuge to asylum seekers for one occasion.

Lake Pichola, situated in Udaipur city in the Indian state of Rajasthan, is an artificial fresh water lake, created in the year 1362, named after the nearby Picholi village. It is one of the several contiguous lakes, and developed over the last few centuries in and around the famous Udaipur city. The lakes around Udaipur were primarily created by building dams to meet the drinking water and irrigation needs of the city and its neighbourhood. Two islands, Jag Niwas and Jag Mandir are located within Pichola Lake, and have been developed with several palaces to provide views of the lake.

Saheliyon-ki-Bari is a major garden and a popular tourist space in Udaipur in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It lies in the northern part of the city and has fountains and kiosks, a lotus pool and marble elephants. It was built by Rana Sangram Singh. There is also a small museum here which has a lot of information about Indian history.

HH 108 Shri Maharajadhiraj Raj Rajeshwar Ravi Kula Bushana-Mahi Mahendra Yavadarya Kula Kamaldhivakara Chattis Rajkul Shringar Maharana Shri Sir FATEH SINGHJI Bahadur Hindua Suraj Hindupati, was the Sisodia Rajput ruler of the Princely State of Udaipur once known as Kingdom of Mewar for nearly 46 years from the year 1884 to 1930, with Udaipur as his capital, and resided in the grandiose City Palace, Udaipur.
Devi Garh Palace is a heritage hotel and resort, housed in the 18th-century Devi Garh palace in the village of Delwara. It was the royal residence of the rulers of Delwara principality, from the mid-18th century till the mid-20th century. Situated in the Aravalli hills, 28 km northeast of Udaipur, Rajasthan, Devigarh forms one of the three main passes into the valley of Udaipur.

The Shrinathji Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to Shrinathji located in Nathdwara. It is considered an important pilgrimage centre by Vaishnavas.

Maharana Amar Singh I, the Maharana (ruler) of Mewar Kingdom, was the eldest son and successor of Maharana Pratap I. He was the 14th Rana of Mewar, ruling from 19 January 1597 until his death on 26 January 1620.

Ravla Khempur is a haveli and heritage hotel in Khempur in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It was built in the 1620s and became known as The Best Exotic Marigold Hotel after being used as the filming location for the 2011 film's hotel and its 2015 sequel, The Second Best Exotic Marigold Hotel. The hotel is surrounded by a Marwari horse breeding stable and paddocks and caters to horse lovers.

Rajput architecture is an architectural style associated with the forts and palaces of the many Rajput rulers. Many of the Rajput forts are UNESCO World Heritage Sites and popular tourist attractions.