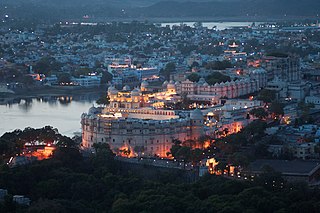Hello

The Ahar River is a tributary of the Berach River.
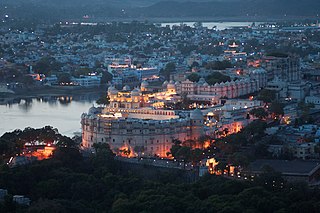
Udaipur is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. it is also known as the ''City of Lakes''. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capital of the kingdom of Mewar in the former Rajputana Agency. It was founded in 1559 by Udai Singh II of the Sisodia clan of Rajputs, when he shifted his capital from the city of Chittorgarh to Udaipur after Chittorgarh was besieged by Akbar. It remained as the capital city till 1818 when it became a British princely state, and thereafter the Mewar province became a part of Rajasthan when India gained independence in 1947.
Panna Dai was a 16th-century nursemaid to Udai Singh II, the fourth son of Rana Sanga. She was a Rajput of Kheechi clan.
Amet is a town and a municipality located in Rajsamand district in the Indian state of Rajasthan.

The Monsoon Palace, also known as the Sajjan Garh Palace, is a hilltop palatial residence in the city of Udaipur, Rajasthan in India, overlooking the Fateh Sagar Lake. It is named Sajjangarh after Maharana Sajjan Singh (1874–1884) of the Mewar dynasty, whom it was built for in 1884. The palace offers a panoramic view of the city's lakes, palaces and surrounding countryside. It was built chiefly to watch the monsoon clouds; hence, appropriately, it is popularly known as Monsoon Palace. It is said that the Maharana built it at the top of the hill to get a view of his ancestral home, Chittorgarh. Previously owned by the Mewar royal family, it is now under the control of the Forest Department of the Government of Rajasthan and has recently been opened to the public. The palace provides a beautiful view of the sunset.

Udai Singh II was the Maharana of Mewar and the founder of the city of Udaipur in the present-day Rajasthan state of India. He was the 12th ruler of the Kingdom of Mewar. He was the fourth son of Rana Sanga and Rani Karnavati, a princess of Bundi.

Chetak or Cetak is the name given in traditional literature to the horse ridden by Maharana Pratap at the Battle of Haldighati, fought on 18 June 1576 at Haldighati, in the Aravalli Mountains of Rajasthan, in western India.

City Palace, Udaipur is a palace complex situated in the city of Udaipur in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It was built over a period of nearly 400 years, with contributions from several rulers of the Mewar dynasty. Its construction began in 1553, started by Maharana Udai Singh II of the Sisodia Rajput family as he shifted his capital from the erstwhile Chittor to the newfound city of Udaipur. The palace is located on the east bank of Lake Pichola and has several palaces built within its complex.

Lake Pichola, situated in Udaipur city in the Indian state of Rajasthan, is an artificial fresh water lake, created in the year 1362, named after the nearby Picholi village. It is one of the several contiguous lakes, and developed over the last few centuries in and around the famous Udaipur city. The lakes around Udaipur were primarily created by building dams to meet the drinking water and irrigation needs of the city and its neighbourhood. Two islands, Jag Niwas and Jag Mandir are located within Pichola Lake, and have been developed with several palaces to provide views of the lake.

Fateh Sagar Lake is situated in the city of Udaipur in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It is an artificial lake named after Maharana Fateh Singh of Udaipur and Mewar, constructed north-west of Udaipur, to the north of Lake Pichola in the 1680s.

Saheliyon-ki-Bari is a major garden and a popular tourist space in Udaipur in the Indian state of Rajasthan. It lies in the northern part of the city and has fountains and kiosks, a lotus pool and marble elephants. It was built by Rana Sangram Singh. There is also a small museum here which has a lot of information about Indian history.

Maharana Sir Fateh Singh, ruled Mewar for 46 years from 1884 to 1930, with Udaipur as capital, and resided in the City Palace, Udaipur.
Devi Garh Palace is a heritage hotel and resort, housed in the 18th-century Devi Garh palace in the village of Delwara. It was the royal residence of the rulers of Delwara principality, from mid-18th century till mid-20th century. Situated amidst in the Aravalli hills, 28 km northeast of Udaipur, Rajasthan, Devigarh forms one of the three main passes into the valley of Udaipur.
Ambamata Temple, a large Hindu temple in the middle of Udaipur in Rajasthan, is considered one of the major places of worship in Udaipur. This temple was constructed by Maharana Raj Singh of Udaipur. It is assumed that he built this temple on the instructions of the goddess Amba Mata in Gujarat.

Udaipur, India was founded in 1553, by Maharana Udai Singh II in the fertile circular Girwa Valley to the southwest of Nagda, on the Banas River. The city was established as the new capital of the Mewar kingdom.

Pratap Gaurav Kendra Rashtriya Tirtha is a tourist spot at Tiger Hill in Udaipur city, Rajasthan state, India. The project, which was started by the Veer Shiromani Maharana Pratap Samiti, aims at providing information about Maharana Pratap and the historical heritage of the area with the help of modern technology.
Swaroop Sagar Lake is situated in the city of Udaipur in the Rajasthan state of India. It is an artificially created lake, named after Maharana Swarup Singh of Udaipur. It is also known as Kumharia Talab, which is a combined water body comprising other nearby lakes Fateh Sagar Lake and Lake Pichola.

Mewar Vibhuti, Pradhan Rai Pannalal Mehta (1843–1919) served four Maharanas, as Prime Minister of Mewar state in former state of Rajputana in India.