
Agylla, also formerly known as Churinga, is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1854.
Anycles is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1854.

Balbura is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae.
Cincia is a monotypic moth genus in the subfamily Arctiinae. Its only species, Cincia conspersa, is found on Jamaica. Both the genus and species were first described by Francis Walker in 1854.

Cosmosoma is a genus of tiger moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Jacob Hübner in 1823.

Ctenucha is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae.

Eurata is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer in 1853.

Eutane is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1854.

Halone is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae from southern Asia and Australia. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1854.
Herea is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1854.

Leucotmemis is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Arthur Gardiner Butler in 1876.
Melisa is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1854.

Palaeosia is a monotypic moth genus in the family Erebidae erected by George Hampson in 1900. Its only species, Palaeosia bicosta, the two-ribbed arctiid or two-ribbed footman, was first described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found in south-eastern Australia.

Sarosa is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1854.

Cyana hamata is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found in Japan, China, Taiwan, Korea and Thailand.
Antona immutata is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found in Brazil.
Antona subluna is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
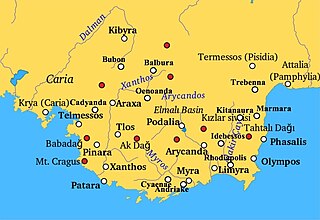
Balbura or Balboura was a town of ancient Lycia, the site of which is at Çölkayiği. The acropolis hill is about 90 metres above the plain of Katara.

Bubon or Boubon was a city of ancient Lycia noted by Stephanus of Byzantium; the ethnic name, he adds, ought to be Βουβώνιος, but it is Βουβωνεύς, for the Lycians rejoice in this form. The truth of this observation of Stephanus is proved by the inscription found on the spot: Βουβωνέων ἡ Βουλὴ καὶ ὁ Δῆμος.
Ann Walker was an Englishwoman, married in Britain's first known lesbian wedding, to diarist and fellow Yorkshire landowner Anne Lister. Their union was solemnised by taking the sacrament together on Easter Sunday in 1834 at Holy Trinity Church, Goodramgate, York, which bears a commemorative plaque acknowledging the event. Walker inherited half of her family's estate, Crow Nest, located in Lightcliffe, West Yorkshire, near Shibden Hall, Lister's family estate, in Calderdale. Both women inherited their respective estates during the early 19th century, when primogeniture, the custom of granting lands and property to the oldest surviving son, dominated European law and society. They were travelling abroad together when Lister fell ill and died. Research into their diaries and letters suggest Walker may have experienced bouts of anxiety and depression throughout portions of her life.











