In calculus, the chain rule is a formula that expresses the derivative of the composition of two differentiable functions f and g in terms of the derivatives of f and g. More precisely, if is the function such that for every x, then the chain rule is, in Lagrange's notation, or, equivalently,

In mathematics, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions that produces a third function. The term convolution refers to both the resulting function and to the process of computing it. It is defined as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result. Graphically, it expresses how the 'shape' of one function is modified by the other.

The tiger is a large cat and a member of the genus Panthera native to Asia. It has a powerful, muscular body with a large head and paws, a long tail and orange fur with black, mostly vertical stripes. It is traditionally classified into nine recent subspecies, though some recognise only two subspecies, mainland Asian tigers and the island tigers of the Sunda Islands.

In mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is an integral transform that takes a function as input and outputs another function that describes the extent to which various frequencies are present in the original function. The output of the transform is a complex-valued function of frequency. The term Fourier transform refers to both this complex-valued function and the mathematical operation. When a distinction needs to be made, the output of the operation is sometimes called the frequency domain representation of the original function. The Fourier transform is analogous to decomposing the sound of a musical chord into the intensities of its constituent pitches.

In thermodynamics, the Gibbs free energy is a thermodynamic potential that can be used to calculate the maximum amount of work, other than pressure–volume work, that may be performed by a thermodynamically closed system at constant temperature and pressure. It also provides a necessary condition for processes such as chemical reactions that may occur under these conditions. The Gibbs free energy is expressed as where:
Gölhisar is a town in Burdur Province in the Mediterranean region of Turkey. It is the seat of Gölhisar District. Its population is 16,118 (2021).

Balbura is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae.

Oenoanda was a Lycian city, in the upper valley of the River Xanthus. It is noted for the philosophical inscription by the Epicurean, Diogenes of Oenoanda.
Placidus Gervasius Nkalanga, OSB was a Tanzanian Prelate of the Roman Catholic Church. He was a monk of the St Maurus & St Placidus Hanga Abbey in Hanga, Ruvuma Region, Tanzania, a Benedictine monastery of the Congregation of Missionary Benedictines of Saint Ottilien. He lived there for 42 years, from his resignation from the episcopate in 1973 until his death in 2015.
Milyas was a mountainous country in ancient south-west Anatolia. However, it is generally described as being mostly in the northern part of the successor kingdom of Lycia, as well as southern Pisidia, and part of eastern Phrygia. According to Herodotus, the boundaries of Milyas were never fixed.

Cibyra or Kibyra, also referred to as Cibyra Magna, was an Ancient Greek city near the modern town of Gölhisar, in Burdur Province. It lay outside the north-western limits of the ancient province of Lycia and was the chief city of an independent state known as Cibyratis. Since 2016 it has been included in the Tentative list of World Heritage Sites in Turkey.
Balbura fasciata is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It is found in Central America, including Belize, Costa Rica, Guatemala, Mexico and Honduras.
Balbura fresini is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae. It is found in Paraguay.

Balbura dorsisigna is a moth of the subfamily Arctiinae first described by Francis Walker in 1854. It is found in Panama, Honduras, Venezuela and Ecuador.
Several genera of the Lithosiini tribe of lichen moths are placed as incertae sedis due to the uncertainty of their phylogenetic relationships within the tribe.
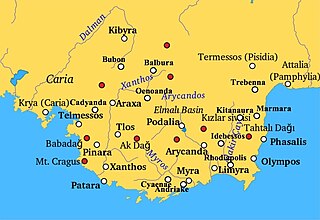
Balbura or Balboura was a town of ancient Lycia, the site of which is at Çölkayiği. The acropolis hill is about 90 metres above the plain of Katara.

Bubon or Boubon was a city of ancient Lycia noted by Stephanus of Byzantium; the ethnic name, he adds, ought to be Βουβώνιος, but it is Βουβωνεύς, for the Lycians rejoice in this form. The truth of this observation of Stephanus is proved by the inscription found on the spot: Βουβωνέων ἡ Βουλὴ καὶ ὁ Δῆμος.
Lucius Julius Marinus Caecilius Simplex was a Roman senator who held several posts in the emperor's service. Simplex was then appointed suffect consul in late 101, with Lucius Arruntius Stella as his colleague. His career is primarily known through inscriptions.
Trimilinda was a town of ancient Lycia, which per the Stadiasmus Patarensis was on a road from Balbura to Kibyra.
Gaius Pompeius Planta was a Roman eques who was a close associate of the emperor Trajan. He is best known for being praefectus or governor of Roman Egypt, which he held from 98 to 100 AD.









