
The Miocene is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about 23.03 to 5.333 million years ago (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words μείων and καινός and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene.

Deep-sea fish are fish that live in the darkness below the sunlit surface waters, that is below the epipelagic or photic zone of the sea. The lanternfish is, by far, the most common deep-sea fish. Other deep-sea fishes include the flashlight fish, cookiecutter shark, bristlemouths, anglerfish, viperfish, and some species of eelpout.

Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the International Ornithologists' Union (IOU) adopted a consensus taxonomy of seven genera. The great cormorant and the common shag are the only two species of the family commonly encountered in Britain and Ireland and "cormorant" and "shag" appellations have been later assigned to different species in the family somewhat haphazardly.

Scapanorhynchus is an extinct genus of goblin shark that lived during the Cretaceous period, from the Aptian to the end of the Maastrichtian. Later records, such as those from the Miocene assigned to the species S. subulatus, are highly dubious and may be misidentified sand sharks.

The Paratethys sea, Paratethys ocean, Paratethys realm or just Paratethys, was a large shallow inland sea that covered much of mainland Europe and parts of western Asia during the middle to late Cenozoic, from the late Paleogene to the late Neogene. At its greatest extent, it stretched from the region north of the Alps over Central Europe to the Aral Sea in Central Asia.

Diplocynodon is an extinct genus of alligatoroid crocodilian that lived during the Paleocene to Middle Miocene in Europe. Some species may have reached lengths of 3 metres (9.8 ft), while others probably did not exceed 1 metre (3.3 ft). They are almost exclusively found in freshwater environments. The various species are thought to have been opportunistic aquatic predators.

Interatherium is an extinct genus of interatheriid notoungulate from the Early to Middle Miocene (Colhuehuapian-Mayoan). Fossils have been found in the Santa Cruz, Collón Curá and Sarmiento Formations in Argentina.

Metaxytherium is an extinct genus of dugong that lived from the Oligocene until the end of the Pliocene. Fossil remains have been found in Africa, Europe, North America and South America. Generally marine seagrass specialists, they inhabited the warm and shallow waters of the Paratethys, Mediterranean, Caribbean Sea and Pacific coastline. American species of Metaxytherium are considered to be ancestral to the North Pacific family Hydrodamalinae, which includes the giant Steller's sea cow.
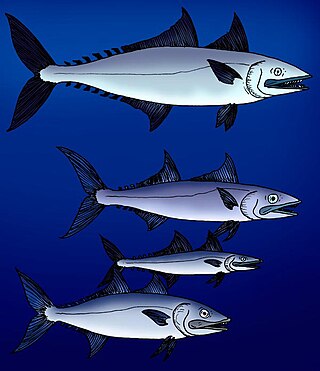
Euzaphlegidae is a family of extinct escolar-like ray-finned fish closely related to the snake mackerels. Fossils of euzaphlegids are found from Paleocene to Late Miocene-aged marine strata of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains, India, Iran, Turkmenistan, Italy, and Southern California.

Laytonia is an extinct genus of prehistoric halosaur that lived in deep water off the North American Pacific Coast from the Zemorrian Epoch until during the Upper Miocene subepoch, when tectonic uplift effectively destroyed the genus' habitat by making the deep water too shallow.

Hippocampus sarmaticus is an extinct species of seahorse, found in 2005 in the coprolitic horizon of the Tunjice hills Lagerstätte in Slovenia, along with the related Hippocampus slovenicus.

Hippocampus slovenicus is an extinct species of seahorse found in 2005 in the coprolitic horizon of the Tunjice hills Lagerstätte in Slovenia along with remains of the related species Hippocampus sarmaticus. The horizon dates 13 million years back to the lower Sarmatian during the middle Miocene period, making the two species the earlier known seahorse fossils in the world. The remains consist mostly of juvenile specimens and of head and backbones of adults. H. slovenicus had a narrow head with a long snout about 50% HL with 11 trunk rings and a short tail 50% more of body with 25-26 tail rings and an extremely long dorsal fin base. Hippocampusslovenicus had numerous small black spots of pigment all over the body.

Tomistominae is a subfamily of crocodylians that includes one living species, the false gharial. Many more extinct species are known, extending the range of the subfamily back to the Eocene epoch. In contrast to the false gharial, which is a freshwater species that lives only in southeast Asia, extinct tomistomines had a global distribution and lived in estuaries and along coastlines.
Paleontology in California refers to paleontologist research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of California. California contains rocks of almost every age from the Precambrian to the Recent.

Bathynectes is a genus of crabs in the family Polybiidae.
Navidad Formation is a marine Neogene sedimentary formation located in Central Chile. The formation is known for its diverse and abundant fossil record and is considered the reference unit for the marine Neogene in Chile. Originally described by Charles Darwin in 1846 the formation has attracted the attention of numerous prominent geologists and paleontologists since then. As a key formation Navidad has been subject to a series of differing interpretations and scientific disputes over time.

Atocetus is an extinct genus of pontoporiid dolphin found in Miocene-age marine deposits in Peru and California.

Ciuciulea is a genus of cetotheriid mysticete found in middle Miocene marine deposits in Moldova.
Asterostemma is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived during the Middle Miocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.
Micrurus gallicus is an extinct species of coral snake that lived in France and Germany from 20 to 11.1 million years ago. The remains of this snake consist of some vertebrae. The locality in which it was found was an MN 7 + 8 fissure fill in France called La Grive M, dating from the late Middle Miocene.
















