Mobile Bay is a shallow inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, lying within the state of Alabama in the United States. Its mouth is formed by the Fort Morgan Peninsula on the eastern side and Dauphin Island, a barrier island on the western side. The Mobile River and Tensaw River empty into the northern end of the bay, making it an estuary. Several smaller rivers also empty into the bay: Dog River, Deer River, and Fowl River on the western side of the bay, and Fish River on the eastern side. Mobile Bay is the fourth-largest estuary in the United States with a discharge of 62,000 cubic feet (1,800 m3) of water per second. Annually, and often several times during the summer months, the fish and crustaceans will swarm the shallow coastline and shore of the bay. This event, appropriately named a jubilee, draws a large crowd because of the abundance of fresh, easily caught seafood.

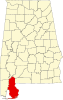
Baldwin County is a county located in the southwestern part of the U.S. state of Alabama, on the Gulf coast. It is one of only two counties in Alabama that border the Gulf of Mexico, along with Mobile County. As of the 2020 census, the population was 231,767, making it the fourth-most populous county in Alabama. The county seat is Bay Minette. The county is named after the founder of the University of Georgia, Senator Abraham Baldwin.

Escambia County is a county located in the south central portion of the U.S. state of Alabama. As of the 2020 census, the population was 36,757. Its county seat is Brewton.

Bay Minette is a city in and the county seat of Baldwin County, Alabama, United States. As of the 2010 census, the population of the city was 8,044.

Daphne is a city in Baldwin County, Alabama, United States, on the eastern shoreline of Mobile Bay. The city is located along I-10, 11 miles east of Mobile and 170 miles southwest of the state capital of Montgomery. The 2020 United States Census lists the population of the city as 27,462, making Daphne the most populous city in Baldwin County. It is a principal city of the Daphne-Fairhope-Foley metropolitan area, which includes all of Baldwin County.

U.S. Route 90 or U.S. Highway 90 (US 90) is an east–west major United States highway in the Southern United States. Despite the "0" in its route number, US 90 never was a full coast-to-coast route. It generally travels near Interstate 10 (I-10) and passes through the southern states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida. US 90 also includes part of the DeSoto Trail between Tallahassee and Lake City, Florida.

U.S. Route 98 is an east–west United States Highway in the Southeastern United States that runs from western Mississippi to southern Florida. It was established in 1933 as a route between Pensacola and Apalachicola, Florida, and has since been extended westward into Mississippi and eastward across the Florida Peninsula. It runs along much of the Gulf Coast between Mobile, Alabama, and Crystal River, Florida, including extensive sections closely following the coast between Mobile and St. Marks, Florida. The highway's western terminus is with US 84 in Bude, Mississippi. Its eastern terminus is Palm Beach, Florida, at State Road A1A (SR A1A) near the Mar-a-Lago resort.

The Alabama & Gulf Coast Railway is a Class II railroad owned by Genesee & Wyoming. It operates 292 miles (470 km) of track from the Pensacola, Florida export terminals, west of downtown, north to Columbus, Mississippi, with trackage rights along BNSF Railway to Amory, Mississippi. A branch uses trackage rights along Norfolk Southern from Kimbrough, Alabama west and south to Mobile, Alabama, with separate trackage at the end of the line in Mobile.

The Fort Mims massacre took place on August 30, 1813, at a fortified homestead site 35-40 miles north of Mobile, Alabama, during the Creek War. A large force of Creek Indians belonging to the Red Sticks faction, under the command of Peter McQueen and William Weatherford, stormed the fort and defeated the militia garrison.

The Alabama red-bellied cooter or Alabama red-bellied turtle, is native to Alabama. It belongs to the turtle family Emydidae, the pond turtles. It is the official reptile of the state of Alabama.
Alabama's 1st congressional district is a United States congressional district in Alabama, which elects a representative to the United States House of Representatives. It includes the entirety of Washington, Mobile, Baldwin and Monroe counties, as well as most of Escambia County. The largest city in the district is Mobile.

The Mobile Metropolitan Area comprises Mobile in the southwest corner of Alabama in the United States. As of the 2020 census the metropolitan area had a population of 430,197. The Mobile metropolitan area is the third-largest metropolitan area in the state of Alabama, after Birmingham and Huntsville. Washington County was part of the Mobile metropolitan area but was removed when the OMB released its statistical definitions effective July 2023.

Fowl River is a 14.4-mile-long (23.2 km) brackish river in Mobile County, Alabama. It originates near the Mobile suburb of Theodore and then splits into the East Fowl River and the West Fowl River. The East Fowl River discharges into Mobile Bay south of Belle Fontaine. The West Fowl River discharges into the Mississippi Sound east of Coden. It was named by the original French colonists as the Riviere aux Poules, which can be translated into English as Fowl River.

Interstate 10 (I-10) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that runs from Santa Monica, California, to Jacksonville, Florida. In Alabama, the Interstate Highway runs 66.269 miles (106.650 km) from the Mississippi state line near Grand Bay east to the Florida state line at the Perdido River. I-10 is the primary east–west highway of the Gulf Coast region of Alabama. The highway connects Mobile, the largest city in South Alabama, with Pascagoula, Mississippi, to the west and Pensacola, Florida, to the east. Within the state, the highway connects Mobile and Mobile County with the Baldwin County communities of Daphne and Fairhope. I-10 connects Mobile and Baldwin County by crossing the northern end of Mobile Bay and the southern end of the Mobile-Tensaw River Delta via the George Wallace Tunnel in Mobile and the Jubilee Parkway viaduct system between Mobile and Daphne.

Historic Blakeley State Park is located on the site of the former town of Blakeley in Baldwin County, Alabama on the Tensaw River delta. The park encompasses an area once occupied by settlers in what was a thriving community on the river. Later, Confederate soldiers were garrisoned here and fought against Union forces in the last major battle of the U.S. Civil War.

The Mobile–Tensaw River Delta is the largest river delta and wetland in Alabama. It encompasses approximately 260,000 acres (110,000 ha) in a 40-by-10-mile area and is the second largest delta in the contiguous United States. This large river delta is approximately 45 miles long and averages 8 miles wide, being 16 miles wide at its widest point. It covers approximately 300 square miles. Of its 260,000 acres, 20,000 acres consist of open water, 10,000 acres of marsh, 70,000 acres of swamp; and more than 85,000 acres of bottomland forest. It drains an area of about 44,000 sq miles, which includes 64% of Alabama and small portions of Georgia and Mississippi.
Carpenter's Station is a community located in Baldwin County, Alabama. It appears as "Carpenter" on the Bay Minette South U.S. Geological Survey Map.
The Pensacola were a Native American people who lived in the western part of what is now the Florida Panhandle and southwestern Alabama for centuries before first contact with Europeans until early in the 18th century. They spoke a Muskogean language. They are the source of the name of Pensacola Bay and the city of Pensacola. They lived in the area until the mid-18th century, but were thereafter assimilated into other groups.

The Pensacola culture was a regional variation of the Mississippian culture along the Gulf Coast of the United States that lasted from 1100 to 1700 CE. The archaeological culture covers an area stretching from a transitional Pensacola/Fort Walton culture zone at Choctawhatchee Bay in Florida to the eastern side of the Mississippi River Delta near Biloxi, Mississippi, with the majority of its sites located along Mobile Bay in the Mobile-Tensaw River Delta. Sites for the culture stretched inland, north into the southern Tombigee and Alabama River valleys, as far as the vicinity of Selma, Alabama.
Hybart is an unincorporated community in Monroe County, in the U.S. state of Alabama. Hybart is located at 31°49′36″N87°22′56″W. It is located at the intersection of Alabama State Route 41 and Monroe County Road 56, in the northwestern part of Monroe County, just a short distance from its border with Wilcox County, Alabama. Hybart is the host of a locally famous Alabama turkey hunting competition called the Butterball which has appeared in Mobile Bay Magazine. The area is also known for being a good hunting spot for whitetail deer, turkey, quail, dove, and duck. Hybart is on the northwestern edge of the Red Hills region of southwestern Alabama, a hilly, wooded, and still largely undeveloped part of the state, geologically distinct from the Gulf Coastal Plain to its south, and the Black Belt region to its north. Within the Red Hills region, the Forever Wild Land Trust of Alabama owns two large tracts of land a few miles to the southeast of Hybart. Recreational opportunities in these tracts include hunting, woods road hiking/exploration, wildflower viewing, photography, and bird and wildlife watching. The Red Hills tracts are open to visitors year-round.