
Flaviviridae is a family of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which mainly infect mammals and birds. They are primarily spread through arthropod vectors. The family gets its name from the yellow fever virus; flavus is Latin for "yellow", and yellow fever in turn was named because of its propensity to cause jaundice in victims. There are 89 species in the family divided among four genera. Diseases associated with the group include: hepatitis (hepaciviruses), hemorrhagic syndromes, fatal mucosal disease (pestiviruses), hemorrhagic fever, encephalitis, and the birth defect microcephaly (flaviviruses).

Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold, while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19. In cows and pigs they cause diarrhea, while in mice they cause hepatitis and encephalomyelitis.
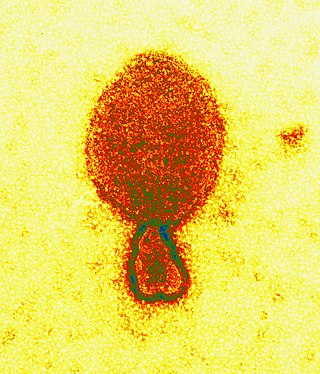
Henipavirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses in the family Paramyxoviridae, order Mononegavirales containing six established species, and numerous others still under study. Henipaviruses are naturally harboured by several species of small mammals, notably pteropid fruit bats, microbats of several species, and shrews. Henipaviruses are characterised by long genomes and a wide host range. Their recent emergence as zoonotic pathogens capable of causing illness and death in domestic animals and humans is a cause of concern.

Defective interfering particles (DIPs), also known as defective interfering viruses, are spontaneously generated virus mutants in which a critical portion of the particle's genome has been lost due to defective replication or non-homologous recombination. The mechanism of their formation is presumed to be as a result of template-switching during replication of the viral genome, although non-replicative mechanisms involving direct ligation of genomic RNA fragments have also been proposed. DIPs are derived from and associated with their parent virus, and particles are classed as DIPs if they are rendered non-infectious due to at least one essential gene of the virus being lost or severely damaged as a result of the defection. A DIP can usually still penetrate host cells, but requires another fully functional virus particle to co-infect a cell with it, in order to provide the lost factors.

Bunyavirales is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses with mainly tripartite genomes. Member viruses infect arthropods, plants, protozoans, and vertebrates. It is the only order in the class Ellioviricetes. The name Bunyavirales derives from Bunyamwera, where the original type species Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus was first discovered. Ellioviricetes is named in honor of late virologist Richard M. Elliott for his early work on bunyaviruses.

Coronaviridae is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect amphibians, birds, and mammals. Commonly referred to as coronaviruses in the English language, the family coronaviridae includes the subfamilies Letovirinae and Orthocoronavirinae; the latter also known as coronavirinae.
Avian coronavirus is a species of virus from the genus Gammacoronavirus that infects birds; since 2018, all gammacoronaviruses which infect birds have been classified as this single species. The strain of avian coronavirus previously known as infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) is the only coronavirus that infects chickens. It causes avian infectious bronchitis, a highly infectious disease that affects the respiratory tract, gut, kidney and reproductive system. IBV affects the performance of both meat-producing and egg-producing chickens and is responsible for substantial economic loss within the poultry industry. The strain of avian coronavirus previously classified as Turkey coronavirus causes gastrointestinal disease in turkeys.

Murine coronavirus (M-CoV) is a virus in the genus Betacoronavirus that infects mice. Belonging to the subgenus Embecovirus, murine coronavirus strains are enterotropic or polytropic. Enterotropic strains include mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) strains D, Y, RI, and DVIM, whereas polytropic strains, such as JHM and A59, primarily cause hepatitis, enteritis, and encephalitis. Murine coronavirus is an important pathogen in the laboratory mouse and the laboratory rat. It is the most studied coronavirus in animals other than humans, and has been used as an animal disease model for many virological and clinical studies.

The Coronavirus packaging signal is a conserved cis-regulatory element found in Betacoronavirus. It has an important role in regulating the packaging of the viral genome into the capsid. As part of the viral life cycle, within the infected cell, the viral genome becomes associated with viral proteins and assembles into new infective progeny viruses. This process is called packaging and is vital for viral replication.
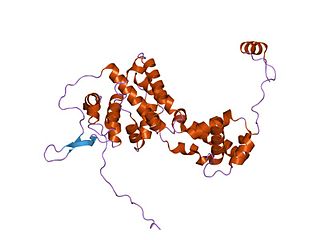
The Borna disease viruses 1 and 2 are members of the species Mammalian 1 orthobornavirus and cause Borna disease in mammals.

DNA dC->dU-editing enzyme APOBEC-3H, also known as Apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzyme catalytic polypeptide-like 3H or APOBEC-related protein 10, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APOBEC3H gene.

Betacoronavirus hongkonense is a species of coronavirus in humans and animals. It causes an upper respiratory disease with symptoms of the common cold, but can advance to pneumonia and bronchiolitis. It was first discovered in January 2004 from one man in Hong Kong. Subsequent research revealed it has global distribution and earlier genesis.

Alphacoronaviruses (Alpha-CoV) are members of the first of the four genera of coronaviruses. They are positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses that infect mammals, including humans. They have spherical virions with club-shaped surface projections formed by trimers of the spike protein, and a viral envelope.

Deltacoronavirus (Delta-CoV) is one of the four genera of coronaviruses. It is in the subfamily Orthocoronavirinae of the family Coronaviridae. They are enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses. Deltacoronaviruses infect mostly birds and some mammals.
Rhinolophus bat coronavirus HKU2 is a novel enveloped, single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus species in the Alphacoronavirus, or Group 1, genus with a corona-like morphology.
Scotophilus bat coronavirus 512 is an enveloped, single-stranded positive-sense RNA virus species in the Alphacoronavirus, or Group 1, genus with a corona-like morphology. It was isolated from a lesser Asiatic yellow house bat discovered in southern China.

Coronavirus HKU15, sometimes called Porcine coronavirus HKU15 is a virus first discovered in a surveillance study in Hong Kong, China, and first reported to be associated with porcine diarrhea in February 2014. In February 2014, PorCoV HKU15 was identified in pigs with clinical diarrhea disease in the U.S. state of Ohio. The complete genome of one US strain has been published. Since then, it has been identified in pig farms in Canada. The virus has been referred to as Porcine coronavirus HKU15, Swine deltacoronavirus and Porcine deltacoronavirus.

Coronavirus diseases are caused by viruses in the coronavirus subfamily, a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, the group of viruses cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the common cold, while more lethal varieties can cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19. As of 2021, 45 species are registered as coronaviruses, whilst 11 diseases have been identified, as listed below.
Helicobacter cetorum is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral (helical) bacterium that is usually found in the stomachs of whales and dolphins. Based on 16S rRNA sequencing, its genome is very similar to that of Helicobacter pylori in that it can cause gastric disease in these animals. Originally isolated among Atlantic white-sided dolphins and Beluga whales in 2000, H. cetorum has been associated with hemorrhages throughout its entire gastrointestinal tract, but its role has not yet been discovered. Prior to the discovery of H. cetorum, there have not been any other Helicobacter species reported in dolphins.

The cetacean microbiome is the group of communities of microorganisms that reside within whales.














