 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
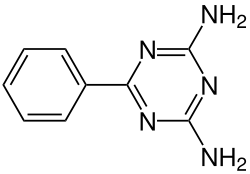
| Preferred IUPAC name 6-Phenyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine | |
| Other names Diamino-6-phenyl-1,3,5-triazine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.905 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H9N5 | |
| Molar mass | 187.206 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.42 g cm−3 |
| Melting point | 227–228 °C (441–442 °F; 500–501 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H331, H332, H412 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P301+P312, P304+P312, P304+P340, P311, P312, P321, P330, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Benzoguanamine is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CNH2)2(CC6H5)N3. It is related to melamine but with one amino group replaced by phenyl. Benzoguanamine is used in the manufacturing of melamine resins. Unlike melamine ((CNH2)3N3), benzoguanamine is not a crosslinker. The "benzo" prefix is historical, as the compound contains phenyl, not a benzo group. A related compound is acetoguanamine. [1]
The compound is prepared by the condensation reaction of cyanoguanidine with benzonitrile: [2]
