Talaromyces marneffei, formerly called Penicillium marneffei, was identified in 1956. The organism is endemic to southeast Asia, where it is an important cause of opportunistic infections in those with HIV/AIDS-related immunodeficiency. Incidence of T. marneffei infections has increased due to a rise in HIV infection rates in the region.

Blastomycosis, also known as Gilchrist's disease, is a fungal infection, typically of the lungs, which can spread to brain, stomach, intestine and skin, where it appears as crusting purplish warty plaques with a roundish bumpy edge and central depression. Around half of people with the disease have symptoms, which can include fever, cough, night sweats, muscle pains, weight loss, chest pain, and fatigue. Symptoms usually develop between three weeks and three months after breathing in the spores. In 25% to 40% of cases, the infection also spreads to other parts of the body, such as the skin, bones or central nervous system. Although blastomycosis is especially dangerous for those with weak immune systems, most people diagnosed with blastomycosis have healthy immune systems.
In mycology, the terms teleomorph, anamorph, and holomorph apply to portions of the life cycles of fungi in the phyla Ascomycota and Basidiomycota:

Eurotiomycetes is a large class of ascomycetes with cleistothecial ascocarps within the subphylum Pezizomycotina, currently containing around 3810 species according to the Catalogue of Life. It is the third largest lichenized class, with more than 1200 lichen species that are mostly bitunicate in the formation of asci. It contains most of the fungi previously known morphologically as "Plectomycetes".

Fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is a disease caused by fungi. Different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected; superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. Superficial fungal infections include common tinea of the skin, such as tinea of the body, groin, hands, feet and beard, and yeast infections such as pityriasis versicolor. Subcutaneous types include eumycetoma and chromoblastomycosis, which generally affect tissues in and beneath the skin. Systemic fungal infections are more serious and include cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, pneumocystis pneumonia, aspergillosis and mucormycosis. Signs and symptoms range widely. There is usually a rash with superficial infection. Fungal infection within the skin or under the skin may present with a lump and skin changes. Pneumonia-like symptoms or meningitis may occur with a deeper or systemic infection.

Paracoccidioides is a genus of fungi in the order Onygenales. Species are known human pathogens producing yeast-like states under pathogenic conditions. They include the causative agents of paracoccidioidomycosis and lobomycosis.
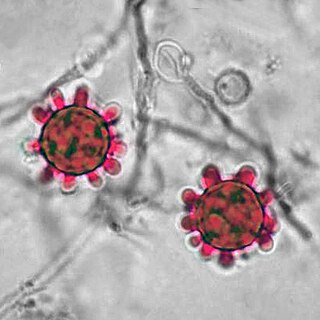
Histoplasma is a genus of fungi in the order Onygenales. Species are known human pathogens producing yeast-like states under pathogenic conditions. They are the causative agents of histoplasmosis in humans and epizootic lymphangitis in horses.
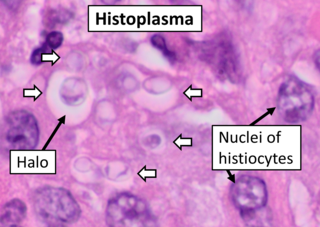
Histoplasma capsulatum is a species of dimorphic fungus. Its sexual form is called Ajellomyces capsulatus. It can cause pulmonary and disseminated histoplasmosis.

Blastomyces dermatitidis is a dimorphic fungus that causes blastomycosis, an invasive and often serious fungal infection found occasionally in humans and other animals. It lives in soil and wet, decaying wood, often in an area close to a waterway such as a lake, river or stream. Indoor growth may also occur, for example, in accumulated debris in damp sheds or shacks. The fungus is endemic to parts of eastern North America, particularly boreal northern Ontario, southeastern Manitoba, Quebec south of the St. Lawrence River, parts of the U.S. Appalachian mountains and interconnected eastern mountain chains, the west bank of Lake Michigan, the state of Wisconsin, and the entire Mississippi Valley including the valleys of some major tributaries such as the Ohio River. In addition, it occurs rarely in Africa both north and south of the Sahara Desert, as well as in the Arabian Peninsula and the Indian subcontinent. Though it has never been directly observed growing in nature, it is thought to grow there as a cottony white mold, similar to the growth seen in artificial culture at 25 °C (77 °F). In an infected human or animal, however, it converts in growth form and becomes a large-celled budding yeast. Blastomycosis is generally readily treatable with systemic antifungal drugs once it is correctly diagnosed; however, delayed diagnosis is very common except in highly endemic areas.
Geomyces is a genus of filamentous fungi in the family Myxotrichaceae. Members of the genus are widespread in distribution, especially in northern temperate regions. Known to be psychrotolerant and associated with Arctic permafrost soils, they are equally prevalent in the air of domestic dwellings, and children's sandpits. Species of Geomyces have previously been placed in the genus Chrysosporium.

Lomentospora prolificans is an emerging opportunistic fungal pathogen that causes a wide variety of infections in immunologically normal and immunosuppressed people and animals. It is resistant to most antifungal drugs and infections are often fatal. Drugs targeting the Class II dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) proteins of L. prolificans, Scedosporium, Aspergillus and other deadly moulds are the basis for at least one new therapy, Olorofim, which is currently in phase 2b clinical trials and has received breakthrough status by FDA. For information on all DHODH proteins, please see Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase.

Trichophyton mentagrophytes is a species in the fungal genus Trichophyton. It is one of three common fungi which cause ringworm in companion animals. It is also the second-most commonly isolated fungus causing tinea infections in humans, and the most common or one of the most common fungi that cause zoonotic skin disease. Trichophyton mentagrophytes is being frequently isolated from dogs, cats, rabbits, guinea pigs and other rodents, though at least some genetic variants possess the potential of human-to-human transmission, e.g. Type VII and Type VIII. Particular genetic variants of the fungus have distinct geographic ranges.
Polytolypa is a monotypic genus of fungus containing the single species Polytolypa hystricis. First classified in the Onygenaceae family, as of 2008 it is considered to be in the Ajellomycetaceae, although there is still uncertainty as to its phylogenetic relationships with other similar genera. This species is only known from a single specimen derived in the laboratory from a specimen of dung of the North American porcupine, Erethizon dorsatum, collected in Ontario, Canada. Polytolypa hystricis contains bioactive compounds that have antifungal activity.

Richard C. Summerbell is a Canadian mycologist, author and award-winning songwriter. He was editor in chief of an international scientific journal in mycology from 2000 to 2004. In the 1970s and 80s, he was a gay activist and an early commentator on (then) controversial topics such as AIDS and promiscuity and attitudes to homosexuality in organized religion.

Exophiala dermatitidis is a thermophilic black yeast, and a member of the Herpotrichiellaceae. While the species is only found at low abundance in nature, metabolically active strains are commonly isolated in saunas, steam baths, and dish washers. Exophiala dermatitidis only rarely causes infection in humans, however cases have been reported around the world. In East Asia, the species has caused lethal brain infections in young and otherwise healthy individuals. The fungus has been known to cause cutaneous and subcutaneous phaeohyphomycosis, and as a lung colonist in people with cystic fibrosis in Europe. In 2002, an outbreak of systemic E. dermatitidis infection occurred in women who had received contaminated steroid injections at North Carolina hospitals.
Emmonsia parva is a filamentous, saprotrophic fungus and one of three species within the genus Emmonsia. The fungus is most known for its causal association with the lung disease, adiaspiromycosis which occurs most commonly in small mammals but is also seen in humans. The disease was first described from rodents in Arizona, and the first human case was reported in France in 1964. Since then, the disease has been reported from Honduras, Brazil, the Czech Republic, Russia, the United States of America and Guatemala. Infections in general are quite rare, especially in humans.
Apinisia keratinophila, formerly Myriodontium keratinophilum, is a fungus widespread in nature, most abundantly found in keratin-rich environments such as feathers, nails and hair. Despite its ability to colonize keratinous surfaces of human body, the species has been known to be non-pathogenic in man and is phylogentically distant to other human pathogenic species, such as anthropophilic dermatophytes. However, its occasional isolation from clinical specimens along with its keratinolytic properties suggest the possibility it may contribute to disease.
Emmonsiosis, also known as emergomycosis, is a systemic fungal infection that can affect the lungs, generally always affects the skin and can become widespread. The lesions in the skin look like small red bumps and patches with a dip, ulcer and dead tissue in the centre.
Emergomyces is a genus of fungi in the order Onygenales. Species are known human pathogens and show thermal dimorphism, converting from hyphal states under saprobic conditions to yeast-like states under pathogenic conditions. They are the causative agents of emergomycosis, a systemic mycosis in immunocompromised patients. The name Emergomyces refers to these newly emerging mycoses, only encountered in the last few decades.

Libero Ajello was an American mycologist. He cofounded and was first president of the International Society of Human and Animal Mycology (ISHAM). He was the head of the Division of Mycotic Diseases at the Communicable Disease Center (CDC), and editor of the ISHAM Journal Medical Mycology for several years. He was one of the first researchers to investigate histoplasmosis and coccidioidomycosis in the United States and made valuable contributions to the comprehensive field of veterinary and human fungal disease diagnosis.













