
The genus Cochleanthes is made up of 4 species of orchids native to Mexico, Central America, the West Indies and South America. The name Cochleanthes refers to the shape of the flower.

Bletia is a genus of about 30 species of orchids, almost all of which are terrestrial; some are occasionally lithophytic or epiphytic. It is named after Spanish botanist and pharmacist Don Luis Blet. The genus is widespread across Florida, Mexico, Central America, the West Indies, and South America as far south as Argentina.
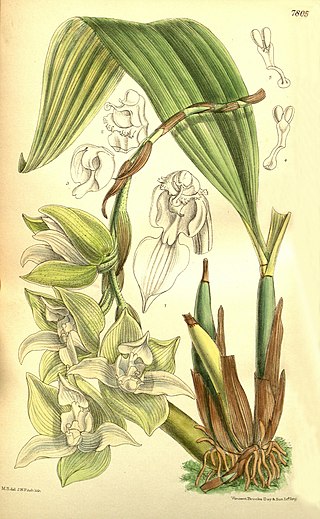
Trevoria is a genus of orchids native to southeastern Central America and northwestern South America. It grows in intermediate temperature and is found from Nicaragua and Costa Rica to Bolivia.

Agonandra is a genus of plants in the family Opiliaceae described as a genus in 1862.

Restrepiella ophiocephala, commonly called the Snake's head restrepiella is an epiphytic orchid native to Mexico, Central America, Colombia, and Florida. The epithet ophiocephala is derived from the Greek words ὄφις, ophis (snake) and κεφαλή, kephalē (head).

Hypolytrum is a genus of plant in the family Cyperaceae. It contains approximately 60–70 species, native to tropical Africa, Asia, Australia, Latin America and various oceanic islands.

Teuscheria is a genus of orchids native to southern Mexico, Central America and northern South America. The genus is named for Henry Teuscher, an award-winning landscape artist and horticulturalist.

Sievekingia is a genus of orchid, comprising 20 species found in Central and South America, from Nicaragua east to the Guianas and south to Bolivia.

Brassia maculata, the spotted brassia, is a species of orchid. It is native to southern Mexico, Central America, Cuba, and Jamaica.

Eulophia alta is a species of orchid, known as the wild coco. It is widespread across tropical and subtropical parts of Africa, South America, Central America, Mexico and the West Indies, as well as the southeastern United States.

Laelia rubescens is a species of orchid native to Mexico and Central America.

Psilochilus is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to South America, Central America, Mexico and the West Indies.
- Psilochilus carinatusGaray - Colombia
- Psilochilus dusenianusKraenzl. ex Garay & Dunst. - Venezuela, Brazil
- Psilochilus macrophyllus(Lindl.) Ames - widespread from central Mexico and the West indies south to Peru
- Psilochilus maderoi(Schltr.) Schltr. - Colombia
- Psilochilus modestusBarb.Rodr. - Venezuela, Brazil
- Psilochilus mollisGaray - Ecuador
- Psilochilus physurifolius(Rchb.f.) Løjtnant - Venezuela, Guyana
- Psilochilus vallecaucanusKolan. & Szlach. - Colombia

Schiedeella is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to the Western Hemisphere: Mexico, the West Indies and Central America, with one species (S. arizonica) in the southwestern United States.

Tinantia is a genus of plants in the Commelinaceae, first described in 1839. They are commonly called widow's tears or false dayflowers due to their resemblance of the closely related true dayflowers of the genus Commelina. Tinantia is native to North and South America from Texas + Hispaniola to Argentina, with a center of diversity from Mexico to Nicaragua. Tinantia pringlei, an alpine native of Mexico, is grown as an ornamental in temperate areas and is also a common greenhouse weed.

Celtis ehrenbergiana, called the desert hackberry or spiny hackberry, is a plant species that has long been called C. pallida by many authors, including in the "Flora of North America" database. It is native to Arizona, Florida, New Mexico and Texas, and to Latin America as far south as central Argentina. It grows in dry locations such as deserts, brushlands, canyons, mesas and grasslands.

Bletia purpurea, common name pine-pink or sharp-petaled bletia, is a species of orchid widespread across much of Latin America and the West Indies, and also found in Florida. They are terrestrial in swamps or sometimes found growing on logs or stumps above the high tide mark.
Calycolpus warscewiczianus is a plant species native to Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panamá and Venezuela.

Ischnosiphon is a genus of plants native to Central America, South America, Trinidad and the Lesser Antilles. It was first described as a genus in 1859.

Asterohyptis is a genus of plants in the Lamiaceae, or mint family, first described in 1932. It is native to Mexico and Central America.
- Asterohyptis mocinoana(Benth.) Epling - widespread from Veracruz to Costa Rica
- Asterohyptis nayaranaB.L.Turner - Durango, Nayarit
- Asterohyptis seemannii(A.Gray) Epling - Chihuahua, Sonora, Sinaloa
- Asterohyptis stellulata(Benth.) Epling - from Sinaloa and Durango south to Honduras

Marsypianthes is a genus of flowering plants in the family Lamiaceae, first described in 1833. It is native to South America, Central America, the West Indies, and southern Mexico.
- Marsypianthes burchelliiEpling - Brazil
- Marsypianthes chamaedrys(Vahl) Kuntze. - from southern Mexico and the West Indies south to Argentina
- Marsypianthes foliolosaBenth. - Brazil
- Marsypianthes hassleriBriq. - Paraguay, southern Brazil, Misiones Province of Argentina
- Marsypianthes montanaBenth. - Brazil



















