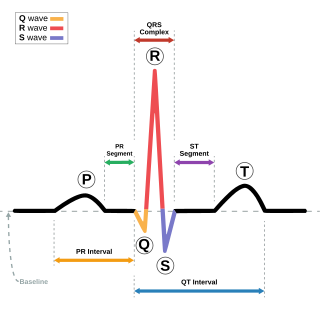
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram, a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances, inadequate coronary artery blood flow, and electrolyte disturbances.

The bow and arrow is a ranged weapon system consisting of an elastic launching device (bow) and long-shafted projectiles (arrows). Humans used bows and arrows for hunting and aggression long before recorded history, and the practice was common to many prehistoric cultures. They were important weapons of war from ancient history until the early modern period, where they were rendered increasingly obsolete by the development of the more powerful and accurate firearms. Today, bows and arrows are mostly used for hunting and sports.
Teratology is the study of abnormalities of physiological development in organisms during their life span. It is a sub-discipline in medical genetics which focuses on the classification of congenital abnormalities in dysmorphology caused by teratogens. Teratogens are substances that may cause non-heritable birth defects via a toxic effect on an embryo or fetus. Defects include malformations, disruptions, deformations, and dysplasia that may cause stunted growth, delayed mental development, or other congenital disorders that lack structural malformations. The related term developmental toxicity includes all manifestations of abnormal development that are caused by environmental insult. The extent to which teratogens will impact an embryo is dependent on several factors, such as how long the embryo has been exposed, the stage of development the embryo was in when exposed, the genetic makeup of the embryo, and the transfer rate of the teratogen.

Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is an abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. PAD can happen in any blood vessel, but it is more common in the legs than the arms.

In the kidney, the loop of Henle is the portion of a nephron that leads from the proximal convoluted tubule to the distal convoluted tubule. Named after its discoverer, the German anatomist Friedrich Gustav Jakob Henle, the loop of Henle's main function is to create a concentration gradient in the medulla of the kidney.
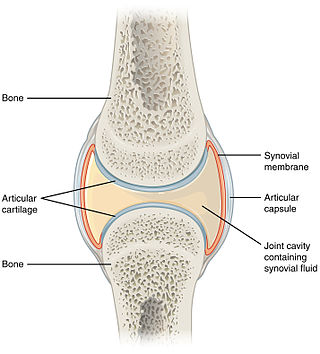
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. The synovial cavity/joint is filled with synovial fluid. The joint capsule is made up of an outer layer of fibrous membrane, which keeps the bones together structurally, and an inner layer, the synovial membrane, which seals in the synovial fluid.
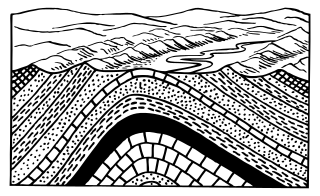
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used.

Juniperus osteosperma is a shrub or small tree native to the southwestern United States.

The mona monkey is an Old World monkey that lives in western Africa between Ghana and Cameroon. The mona monkey can also be found on the island of Grenada as it was transported to the island aboard slave ships headed to the New World during the 18th century. This guenon lives in groups of up to thirty-five in forests. It mainly feeds on fruit, but sometimes eats insects and leaves. The mona monkey has brown agouti fur with a white rump. Its tail and legs are black and the face is blue-grey with a dark stripe across the face. The mona monkey carries food in cheek pouches.

Ohmdenosaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic epoch in what is now Germany. The only specimen – a tibia (shinbone) and ankle – was discovered in rocks of the Posidonia Shale near the village of Ohmden. The specimen, which was originally identified as a plesiosaur, is exhibited in a local museum, the Urweltmuseum Hauff. In the 1970s, it caught the attention of German palaeontologist Rupert Wild, who recognised it as the remains of a sauropod. Wild named Ohmdenosaurus in a 1978 publication; the only known species is Ohmdenosaurus liasicus.
The lumbar enlargement is a widened area of the spinal cord that gives attachment to the nerves which supply the lower limbs.
The cervical enlargement corresponds with the attachments of the large nerves which supply the upper limbs.

The southern needle-clawed bushbaby is a species of strepsirrhine primate in the family Galagidae. Found in Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, and possibly Democratic Republic of the Congo, its natural habitat is tropical moist forests. While the species is not threatened or endangered, some local populations may be threatened by habitat destruction.
Hildegarde's shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found in Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Kenya, Rwanda, and Tanzania. Considered by some authorities to be a subspecies of Crocidura gracilipes, it is now recognised as a separate species, with a diploid chromosome number of 2n = 52. This is one of three species of small mammal named by the British zoologist Oldfield Thomas in honour of anthropologist Hildegarde Beatrice Hinde.

The paralimbic cortex is an area of three-layered cortex that includes the following regions: the piriform cortex, entorhinal cortex, the parahippocampal cortex on the medial surface of the temporal lobe, and the cingulate cortex just above the corpus callosum.
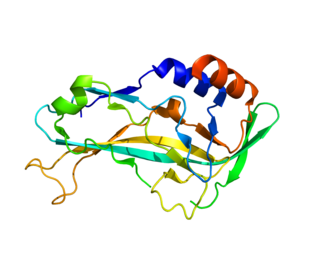
T-box transcription factor TBX5, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBX5 gene. Abnormalities in the TBX5 gene can result in altered limb development, Holt-Oram syndrome, Tetra-amelia syndrome, and cardiac and skeletal problems.

Fibroblast growth factor 8(FGF-8) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGF8 gene.

Homeobox protein engrailed-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EN1 gene.

The head of the radius has a cylindrical form, and on its upper surface is a shallow cup or fovea for articulation with the capitulum of the humerus. The circumference of the head is smooth; it is broad medially where it articulates with the radial notch of the ulna, narrow in the rest of its extent, which is embraced by the annular ligament.

Xiaotingia is a genus of anchiornithid theropod dinosaur from Middle Jurassic or early Late Jurassic deposits of western Liaoning, China, containing a single species, Xiaotingia zhengi.

















