
Mouthwash, mouth rinse, oral rinse, or mouth bath is a liquid which is held in the mouth passively or swilled around the mouth by contraction of the perioral muscles and/or movement of the head, and may be gargled, where the head is tilted back and the liquid bubbled at the back of the mouth.

Listerine is an American brand of antiseptic mouthwash that is promoted with the slogan "Kills germs that cause bad breath", Named after Joseph Lister, who pioneered antiseptic surgery at the Glasgow Royal Infirmary in Scotland, Listerine was developed in 1879 by Joseph Lawrence, a chemist in St. Louis, Missouri.

A first aid kit or medical kit is a collection of supplies and equipment used to give immediate medical treatment, primarily to treat injuries and other mild or moderate medical conditions. There is a wide variation in the contents of first aid kits based on the knowledge and experience of those putting it together, the differing first aid requirements of the area where it may be used, and variations in legislation or regulation in a given area.

A mouth ulcer (aphtha) is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases and by many different mechanisms, but usually there is no serious underlying cause. Rarely, a mouth ulcer that does not heal may be a sign of oral cancer. These ulcers may form individually or multiple ulcers may appear at once. Once formed, an ulcer may be maintained by inflammation and/or secondary infection.

Benzalkonium chloride, also known as alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride (ADBAC) and by the trade name Zephiran, is a type of cationic surfactant. It is an organic salt classified as a quaternary ammonium compound. ADBACs have three main categories of use: as a biocide, a cationic surfactant, and a phase transfer agent. ADBACs are a mixture of alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chlorides, in which the alkyl group has various even-numbered alkyl chain lengths.
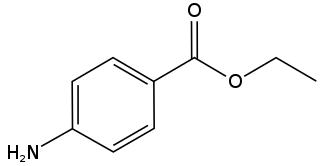
Benzocaine, sold under the brand name Orajel amongst others, is an ester local anesthetic commonly used as a topical pain reliever or in cough drops. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter anesthetic ointments such as products for oral ulcers. It is also combined with antipyrine to form A/B otic drops to relieve ear pain and remove earwax. In the US, products containing benzocaine for oral application are contraindicated in children younger than two years old. In the European Union, the contraindication applies to children under 12 years of age.

Methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil) is an organic compound with the formula C8H8O3. It is the methyl ester of salicylic acid. It is a colorless, viscous liquid with a sweet, fruity odor reminiscent of root beer, but often associatively called "minty", as it is an ingredient in mint candies. It is produced by many species of plants, particularly wintergreens. It is also produced synthetically, used as a fragrance and as a flavoring agent.

Teething is the process by which an infant's first teeth appear by emerging through the gums, typically arriving in pairs. The mandibular central incisors are the first primary teeth to erupt, usually between 6 and 10 months of age and usually causes discomfort and pain to the infant. It can take several years for all 20 teeth to complete the tooth eruption. Though the process of teething is sometimes referred to as "cutting teeth", when teeth emerge through the gums they do not cut through the flesh. Instead, hormones are released within the body that cause some cells in the gums to die and separate, allowing the teeth to come through.
Kaopectate is an orally taken medication from Arcadia Consumer Healthcare for the treatment of mild diarrhea. It is also sometimes used to treat indigestion, nausea, and stomach ulcers. The active ingredients have varied over time, and are different between the United States and Canada. The original active ingredients were kaolinite and pectin. In the US, the active ingredient is now bismuth subsalicylate. In Switzerland, attapulgite is used.

Povidone-iodine (PVP-I), also known as iodopovidone, is an antiseptic used for skin disinfection before and after surgery. It may be used both to disinfect the hands of healthcare providers and the skin of the person they are caring for. It may also be used for minor wounds. It may be applied to the skin as a liquid or a powder.
Germolene is the brand name used on a range of antiseptic products produced by the Bayer company, who purchased the brand from GlaxoSmithKline, then known as Smithkline Beecham, in 1999. It is manufactured for Bayer UK by the Devon based Wrafton Laboratories division of US over-the counter and supermarket own-label preparation producer Perrigo.

Hand sanitizer is a liquid, gel or foam generally used to kill many viruses/bacteria/microorganisms on the hands. In most settings, hand washing with soap and water is generally preferred. Hand sanitizer is less effective at killing certain kinds of germs, such as norovirus and Clostridium difficile, and unlike hand washing, it cannot physically remove harmful chemicals. People may incorrectly wipe off hand sanitizer before it has dried, and some are less effective because their alcohol concentrations are too low.

Oxybutynin, sold as under the brand names Ditropan among others, is a medication used to treat overactive bladder. It works similar to tolterodine, Darifenacin, and Solifenacin. While used for bed wetting in children, evidence to support this use is poor. It is taken by mouth or applied to the skin.
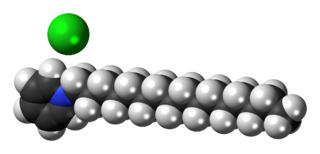
Cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC) is a cationic quaternary ammonium compound used in some types of mouthwashes, toothpastes, lozenges, throat sprays, breath sprays, and nasal sprays. It is an antiseptic that kills bacteria and other microorganisms. It has been shown to be effective in preventing dental plaque and reducing gingivitis. It has also been used as an ingredient in certain pesticides. Though one study seems to indicate cetylpyridinium chloride does not cause brown tooth stains, at least one mouthwash containing CPC as an active ingredient bears the warning label "In some cases, antimicrobial rinses may cause surface staining to teeth," following a failed class-action lawsuit brought by customers whose teeth were stained.

Synthol is a liquid medical product brand available in France since 1920, though the nature of the product has changed through the brand's history.

Lysol is a brand of American cleaning and disinfecting products distributed by Reckitt, which markets the similar Dettol or Sagrotan in other markets. The line includes liquid solutions for hard and soft surfaces, air treatment, and hand washing. The active ingredient in many Lysol products is benzalkonium chloride, but the active ingredient in the Lysol "Power and Free" line is hydrogen peroxide. Lysol has been used since its invention in the late 19th century as a household and industrial cleaning agent, and previously as a medical disinfectant.

Euthymol is a brand of antiseptic, fluoride-free toothpaste distributed by LG H&H UK that is characterised by its bright pink colour and medicinal taste. It is also notable for its packaging, which is old fashioned, having merely a pattern and the product name.

Sulfonated phenolics/sulfuric acid liquid topical agent that is used in the treatment of ulcerating oral mucosal lesions and minor oral abrasions.
Gelclair is an oral gel containing poly-vinyl-pyrrolidone (PVP) and hyaluronic acid that coats the surface of the mouth forming a thin protective film over painful oral lesions, such as those caused by radiotherapy or chemotherapy treatment for cancer.
Nurofen is a brand name range of pain-relief medication containing ibuprofen made by Reckitt. Introduced in 1983, the Nurofen brand was acquired following Reckitt Benckiser's acquisition of Boots in 2005. The brand is primarily marketed and sold in the United Kingdom, other parts of Europe, South Africa, Australia and New Zealand. In 2016 it was the biggest selling branded over-the-counter medication sold in Great Britain, with sales of £116.8 million.
















