
Latrodectus is a broadly distributed genus of spiders with several species that are commonly known as the true widows. This group is composed of those often loosely called black widow spiders, brown widow spiders, and similar spiders. However, the diversity of species is much greater. A member of the family Theridiidae, this genus contains 34 species, which include several North American "black widows". Besides these, North America also has the red widow Latrodectus bishopi and the brown widow Latrodectus geometricus, which, in addition to North America, has a much wider geographic distribution. Elsewhere, others include the European black widow, the Australian redback spider and the closely related New Zealand katipō, several different species in Southern Africa that can be called button spiders, and the South American black-widow spiders. Species vary widely in size. In most cases, the females are dark-coloured and can be readily identified by reddish markings on the central underside (ventral) abdomen, which are often hourglass-shaped.

Atypidae, also known as atypical tarantulas or purseweb spiders, is a spider family containing only three genera. They are accomplished ambush predators that spend most of their time in a sock-like, silken retreat on the ground from where they kill their prey.

Crevice weaver spiders (Filistatidae) comprise cribellate spiders with features that have been regarded as "primitive" for araneomorph spiders. They are weavers of funnel or tube webs. The family contains 18 genera and more than 120 described species worldwide.

Chlorophytum comosum, usually called spider plant or common spider plant due to its spider-like look, also known as spider ivy, airplane plant, ribbon plant, and hen and chickens, is a species of evergreen perennial flowering plant of the family Asparagaceae. It is native to tropical and Southern Africa but has become naturalized in other parts of the world, including Western Australia and Bangladesh. Chlorophytum comosum is easy to grow as a houseplant because of its resilience, but it can be sensitive to the fluoride in tap water, which commonly gives it "burnt tips". Variegated forms are the most popular.

The Tooth Cave spider, formerly Neoleptoneta myopica, now Tayshaneta myopica, is a 1.6 mm long spider in the family Leptonetidae. It is endemic to limestone caves near Austin, Texas in the United States and is considered an endangered species.
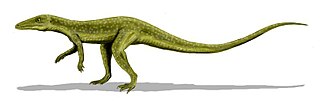
Saltoposuchus is an extinct genus of small, long-tailed crocodylomorph reptile (Sphenosuchia), from the Norian of Europe. The name translated means "leaping foot crocodile". It has been proposed that Terrestrisuchus gracilis and Saltoposuchus connectens represent different ontogenetic stages of the same genus. Saltoposuchus was commonly referred to in popular literature as the ancestor to dinosaurs; however, recent scientific research shows that this is not the case.

Latrodectus tredecimguttatus, also known as the Mediterranean black widow or the European black widow, is a species in the genus Latrodectus of the widow spiders. It is commonly found throughout the Mediterranean region, ranging from southern Iberia to southwest and central Asia, hence the name. Specimens from central Asia are also known by the binomial name Latrodectus lugubris; that name, however, is now considered improper, though it is still commonly found in the literature. Latrodectus tredecimguttatus was previously considered a subspecies of Latrodectus mactans.

Actinopodidae is a family of mygalomorph spiders found in mainland Australia and South America usually in open forest. Species are most common in Queensland, Australia. It includes mouse spiders, whose bites, though rare, are considered medically significant and potentially dangerous.

Argiope aurantia is a species of spider, commonly known as the yellow garden spider, black and yellow garden spider, golden garden spider, writing spider, zigzag spider, zipper spider, black and yellow argiope, corn spider, Steeler spider, or McKinley spider. The species was first described by Hippolyte Lucas in 1833. It is common to the contiguous United States, Hawaii, southern Canada, Mexico, and Central America. It has distinctive yellow and black markings on the abdomen and a mostly white cephalothorax. Its scientific Latin name translates to "gilded silver-face". The body length of males range from 5–9 mm (0.20–0.35 in); females range from 19–28 mm (0.75–1.10 in). These spiders may bite if disturbed or harassed, but the venom is harmless to non-allergic humans, roughly equivalent to a bumblebee sting in intensity.
Megapaloelodus is an extinct genus of stem flamingo of the family Palaelodidae. Megapaloelodus is primarily known from Miocene America, from South Dakota and Oregon in the north to Argentina in the south, but the species Megapaloelodus goliath was found in Europe. Additionally, one unnamed species was discovered in Miocene sediments from Namibia. Due to a lack of skull material, little can be said about the ecology of Megapaloelodus. Species of this genus are typically larger than those of Palaelodus and appear to have inhabited similar brackish lake environments. Additionally, they may have been capable of "locking" their legs in a standing position.

Periegops is a genus of spiders with six eyes instead of the usual eight. It is the only genus in its family (Periegopidae) and has three described species. It was long considered to be a member of Sicariidae or Segestriidae until Raymond Forster elevated it to the family level in 1995.

Deinacrida connectens, often referred to as the alpine scree wētā, is one of New Zealand's largest alpine invertebrates and is a member of the Anostostomatidae family. Deinacrida connectens is a flightless nocturnal insect that lives under rocks at high elevation. Mountain populations vary in colour. This species is the most widespread of the eleven species of giant wētā (Deinacrida).

Macropodia rostrata, common names, the common spider crab, long-legged spider crab, long-legged crab, is a species of marine crab in the family Inachidae. The Macropodia Rostrata visually mimics many other types of small crabs with the exception of its long legs. By attaching algae to their thin legs, they can be confused with the stem of seaweed. This is both a defense mechanism and a predatory advantage, as unsuspecting fish will hide in seaweed beds from nearby predators. This behavior can be absent among larger crabs, and those that live at great depths like giant Japanese spider crabs.
Pinkfloydia is a genus of small Australian long-jawed orb-weavers, reaching a maximum lengths of about 4.5 millimetres (0.18 in). It was first described by D. Dimitrov & G. Hormiga in 2011, and contains two species, found in New South Wales and Western Australia: P. harveyi and P. rixi. They have a unique rounded, cone-shaped head structure with one pair of large eyes and three pairs of smaller eyes. The genus is named after British rock band Pink Floyd.
Agyneta serratichelis is a species of sheet weaver spider found in Sudan. It was described by Jacques Denis in 1964.

Menemerus soldani is a species of jumping spider in the genus Menemerus that lives in Algeria, Egypt and Tunisia. It was first described in 1826 by Jean Victor Audouin. He identified both the male and female but not in much detail and it was not until 1999 that a thorough description was completed. This led to confusion, with many museums holding examples of different species labelled Menemerus soldani. When the female was described by Hippolyte Lucas and Wanda Wesołowska, they were designated as different species, both of these being declared junior synonyms by subsequent arachnologists. The spider is small, with a total length between 3.11 and 5.65 mm, and has a brown carapace, yellow abdomen and orange legs. The spiders have characteristic copulatory organs. The female has a characteristic semi-circular notch at the rear of its epigyne while the male has a large bulbous patellar apophysis that other species in the genus lack. The male has a flat projection or apophysis on its pedipalp tibia. The spider lives in palm groves and Quercus suber forests.
Brachycerasphora is a genus of dwarf spiders that was first described by J. Denis in 1962.

Acanthinozodium is a genus of spiders in the family Zodariidae. It was described in 1966 by Jacques Denis.

Aelurillus hirtipes, synonym Aelurillus sinaicus, is a species of jumping spider in the genus Aelurillus that lives in North Africa. First identified by Jacques Denis in Chad in 1960 as part of the Missions Berliet-Ténéré, it has also been found in Algeria, Egypt and Morocco. The spider is small, with a brown carapace that is between 3.5 and 3.6 mm long and a yellow abdomen that measures between 3 and 4 mm in length. The male has a small hooked embolus protruding from its palpal bulb and the female has S-shaped flaps on the epigyne and short copulatory ducts. The spider has a covering of light hairs, whiter on the female and more yellow on the male. These hairs help distinguish it from the related Aelurillus v-insignitus and Aelurillus plumipes
Zodarion wesolowskae is a species of ant spider in the genus Zodarion that lives in Morocco. The species was first described in 2020 by Souâd Benhalima and Robert Bosmans. Only the male has been described, although Benhalima and Bosmans suggest that the female could be one of the spiders described as Zodarion trianguliferum. The spider is small, typically 3.4 mm (0.13 in) long, with a plain brown to dark brown carapace and a black abdomen which has faint white stripes. The spider is a member of the mostafai group within the genus, which lack a tooth at the end of the embolus. It can be further distinguished from other members of the genus by its very long and thin tibial apophysis. The genus Zodarion is known to use ant mimicry for both defence against predators and to deceive ants to prey on them. This attribute could be used as a form of biological pest control.














