
Spilomyia sayi, the Four-lined Hornet Fly, is a fairly common species of syrphid fly. This species is found from western Canada to northeastern North America. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. The larvae are known as the short-tailed larvae, suited for moist areas such as rot holes of trees. It is a wasp mimic.

Eristalis flavipes, the orange-legged drone fly, is a species of hoverfly native to North America. It flies from early April to mid-October, and occurs in a wide variety of habitats, particularly wetlands. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. The larvae are aquatic filter-feeders of the rat-tailed type.

Brachyopa flavescens, The Yellow Sapeater, is a fairly common species of syrphid fly. It has been observed in northeastern North America. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. Larvae for this genus are of the rat-tailed type. B.flavescens larvae have not been described.

Chrysogaster antitheus , the Short-haired Wrinkle Fly, is a fairly common species of syrphid fly found in North America. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. The larvae in this genus are aquatic rat-tailed larvae.

Helophilus fasciatus, the narrow-headed marsh fly, is an abundant species of syrphid fly observed throughout the United States and Canada. Hoverflies can remain nearly motionless in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. The larvae of this genus are associated with wet decaying organic material, particularly accumulations of decaying vegetation in ponds and mud and farmyard manure or silage. The adults of this species lays eggs on vegetation overhanging the water. The larvae hatch and drop into the water.

Eristalis anthophorina, the orange-spotted drone fly, is a species of syrphid fly with a Holarctic distribution. It is a common fly in wetlands, including bogs, fens, and woodland pools. In North America, it occurs throughout much of Canada and primarily in the northern parts of the United States. It may be introduced in North America.

Eristalis transversa, the transverse banded drone fly, is a common species of syrphid fly first officially described by Wiedemann in 1830. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. The larvae are rat-tailed type but larvae of this specific species has not been reported.

Orthonevra pictipennis (Loew,1863), the Dusky-veined Mucksucker, is an uncommon species of syrphid fly. It has been observed in North America. O. pictipennis shares much of the same range as O. pulchella, O. nitida and O. feei. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies, for they are commonly found around and on flowers from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. Larvae for this genus are of the rat-tailed type. O. pictipennis larvae have not been described.

Brachyopa vacua , the Yellow-spotted Sapeater, is a rare, species of syrphid fly. It has been observed in Canada, Alaska and northern United States. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. Larvae for this genus are of the rat-tailed type. B.vacua larvae were collected from the juice of decaying fungi under dead bark.

Sericomyia bifasciata, the Long-nosed Pond Fly, is an uncommon species of syrphid fly. They have been observed from the northeastern part of North America. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. The larvae in the genus Sericomyia are known as the rat-tailed with a long breathing tube taylored for aquatic environments. The larvae for this species are unknown.

Brachyopa daeckei, the black-tailed sapeater, is a rare species of syrphid fly that has been observed in northeastern North America. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. Larvae for this genus are of the rat-tailed type. B.daeckei larvae have not been described.

Helophilus obscurus , the Obscure Marsh Fly, is a common species of syrphid fly observed throughout Canada and the northern United States and Rocky Mountains. Hoverflies can remain nearly motionless in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. The larvae of this genus are associated with wet decaying organic material, particularly accumulations of decaying vegetation in ponds and mud and farmyard manure or silage the larvae of this species are not known.
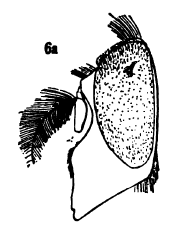
Volucella evecta, the eastern swiftwing, is an uncommon species of hoverfly that has been considered a subspecies of Volucella bombylans, but has been shown to be a distinct species. This species is a bumblebee mimic. It resembles a number of species, including Bombus pensylvanicus, Bombus affinis, Bombus bimaculatus, and Habropoda laboriosa. The range of this species is from Eastern North America and Canada from Georgia to New Brunswick. The adults have been observed feeding on Geum, Viburnum, Rubus, and other flowering plants. Larvae of this species are not known, but larvae in this genus feed on the debris and larvae in bee and wasp nests.
Brachyopa punctipennis, commonly known as the spot-winged sapeater, is a fly species in the syrphid family. First appearing in Oregon, this rarely collected species had been considered a form of Brachyopa notata until Curran named it a separate species in 1925.

Brachyopa caesariata, the Plain-winged Sapeater, is an uncommon species of syrphid fly. It has been observed in Canada, Alaska and northern United States. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. Larvae for this genus are of the rat-tailed type. B.caesariata larvae have not been described.

Brachyopa cinereovittata, the Grey-striped Sapeater, is a rare species of syrphid fly. It has been observed in northwestern North America. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. Larvae for this genus are of the rat-tailed type. B.cinereovittata larvae have not been described.

Brachyopa diversa , the Pale-striped Sapeater, is a rare species of syrphid fly. It has been observed in the northeastern part of North America. Hoverflies get their names from the ability to remain nearly motionless while in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found around and on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. Larvae for this genus are of the rat-tailed type. B.diversa larvae have not been described.
Sericomyia carolinensis, is a rare species in the family Syrphidae, found in the Southeastern part of the United States. It is distinguished by its all yellow face, single pair of small narrow yellow spots, and yellow pilose scutellum. Adults noted feeding on pear blossoms. The larval stage is unknown but is likely a "rat tailed" type larvae inhabiting nutrient rich waters, typical for the genus Sericomyia.
Microdon cothurnatus , the orange-legged ant fly, is a species of syrphid fly observed across the Northern United States and Canada. Hoverflies can remain nearly motionless in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found on flowers except Microdon species are seldom observed around flowers. Larvae have been found in several species of ant.
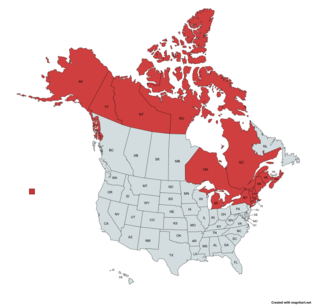
Dasysyrphus laticaudus, the boreal conifer fly, is a common species of syrphid fly observed in Eastern and Northern North America. Hoverflies can remain nearly motionless in flight. The adults are also known as flower flies for they are commonly found on flowers, from which they get both energy-giving nectar and protein-rich pollen. The larvae of this genus are aphid predators. .
















