
Breviceps is a genus of frogs in the family Brevicipitidae. Species in the genus Breviceps are commonly known as rain frogs or short-headed frogs. They occur in arid to semiarid climates of East Africa and Southern Africa.

The Indian burrowing frog is a species of frog found in South Asia.

Sclerophrys garmani, also known as Garman's toad or eastern olive toad, is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is widely distributed in East and Southern Africa. However, populations north and south of Tanzania might represent distinct species. If so, the name Sclerophrys garmani would apply to populations from northeastern Africa. Furthermore, its southern boundary towards the range of Sclerophrys poweri in South Africa is also unclear.

Sclerophrys poweri is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is found in extreme southern Angola, northern Namibia, Botswana, southward to central South Africa, and Zambia. The specific name poweri honours John Hyacinth Power, Irish-born director of the McGregor Museum who collected amphibians as well as reptiles and plants.

Hyperolius poweri is a species of frogs in the family Hyperoliidae. It is found in southeastern coast of South Africa and southern Mozambique. The specific name poweri honours John Hyacinth Power, Irish-born director of the McGregor Museum who collected amphibians as well as reptiles and plants. Accordingly, common names Power's reed frog and Power's long reed frog have been proposed for this species.
Breviceps acutirostris, also known as common rain frog, strawberry rain frog, or Cape short-headed frog, is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae. It is endemic to the southwestern Cape region in South Africa. It is burrowing frog that lives in fynbos heatland and forests at elevations below 1,600 m (5,200 ft) above sea level. Development is direct . It is threatened by habitat loss, although much of its habitat is also protected.

Breviceps adspersus, also known as common rain frog, bushveld rain frog, and many other vernacular names, is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae. It is found in Southern Africa, in Angola, Namibia, Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe, South Africa, Eswatini, and Mozambique.

Bilbo's rain frog is an amphibian species in the family Brevicipitidae, endemic to South Africa. The frog was named after Bilbo Baggins, the main character from The Hobbit by J.R.R Tolkien. The frog was named as such, because the scientist who discovered it used to read the novel to his children. It's natural habitats are temperate grasslands and edges of wood plantations, wherein it spends most of it's time in it's burrow. The species is threatened by construction, maintenance of roads, silviculture, general habitat degradation/habitat loss, and by road traffic. As a result, it is listed as Near Threatened in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
Breviceps fichus is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae. It is endemic to the central highlands of Tanzania. Common name highland rain frog has been proposed for it. It occurs in high-altitude grasslands at elevations above 1,500 m (4,900 ft). Males call during the day from shallow burrows at the base of dense grass. Development is, presumably, direct. Threats to this species are not known.
Breviceps fuscus, also known as black rain frog, plain rain frog, brown short-headed frog, and Tsitsikama rainfrog, and is a species of frogs in the family Brevicipitidae. It is endemic to South Africa. The specific name fuscus refers to the dark coloration of this species.

The cape rain frog or giant rain frog is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae. Adults grow up to 45 mm in length. It was the first African frog species to be scientifically described by Carl Linnaeus in 1758, under the name Rana gibbosa. It is the most common and largest of rain frogs.

The desert rain frog, web-footed rain frog, or Boulenger's short-headed frog is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae. It is found in Namibia and South Africa. Its natural habitat is the narrow strip of sandy shores between the sea and the sand dunes. It is threatened by habitat loss by such factors as mining and tourism.

The mountain rain frog is a species of frogs in the family Brevicipitidae.

The Mozambique rain frog, also known as the flat-faced frog, is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae. It is found in Botswana, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Malawi, Mozambique, South Africa, Swaziland, Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and possibly Lesotho. Its natural habitats are dry savanna, moist savanna, temperate shrubland, subtropical or tropical dry shrubland, temperate grassland, subtropical or tropical dry lowland grassland, subtropical or tropical high-altitude grassland, arable land, pasture land and rural gardens.

The Namaqua rain frog or Namaqua short-headed frog is a species of frogs in the family Brevicipitidae. It is found in Namaqualand in western South Africa and extreme southern Namibia.
Rose's rain frog or Rose's rainfrog is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae. It is endemic to the sandveld of south-western coastal South Africa. It is less-frequently known as Rose's short-headed frog, Rose's Blaasop, or the sand rain frog. Some treat Breviceps fasciatus as synonym of this species, although other authorities have expressed doubt.
The forest rain frog is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae. It is endemic to Limpopo, South Africa. Two allopatric subspecies are recognized: the nominate one, Breviceps sylvestris sylvestris, and Breviceps sylvestris taeniatusPoynton, 1963 from near Soutpansberg. Its natural habitats are temperate forests, temperate grassland, and rural gardens. It is threatened by habitat loss.
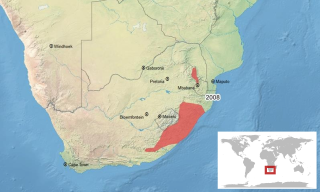
The plaintive rain frog or rough rain frog is a species of frog in the family Brevicipitidae. It is found in Lesotho, South Africa, and Swaziland. Its natural habitats are temperate forests, dry savanna, temperate shrubland, temperate grassland, and rural gardens. It is threatened by habitat loss.

The knocking sand frog, also known as sandveld pyxie or Kruger burrowing frog, is a species of frog in the family Pyxicephalidae. It is found in southern Angola, Namibia, Botswana, southern Zimbabwe, southern Mozambique, northern South Africa, and Swaziland. This species was discovered during the evening of 23 October 1973 in South Africa's Kruger National Park. Two weeks after heavy rain fell in the area, large numbers were found around the Machayi and Mathlakuza Pans in the northeastern part of the Park near the Mozambican frontier.















