
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae, a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Earth except glaciers. The world's richest diversity of orchid genera and species is found in the tropics.

Bulbophyllum is a genus of mostly epiphytic and lithophytic orchids in the family Orchidaceae. It is the largest genus in the orchid family and one of the largest genera of flowering plants with more than 2,000 species, exceeded in number only by Astragalus. These orchids are found in diverse habitats throughout most of the warmer parts of the world including Africa, southern Asia, Latin America, the West Indies, and various islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Orchids in this genus have thread-like or fibrous roots that creep over the surface of trees or rocks or hang from branches. The stem is divided into a rhizome and a pseudobulb, a feature that distinguished this genus from Dendrobium. There is usually only a single leaf at the top of the pseudobulb and from one to many flowers are arranged along an unbranched flowering stem that arises from the base of the pseudobulb. Several attempts have been made to separate Bulbophyllum into smaller genera, but most have not been accepted by the World Checklist of Selected Plant Families.

Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) of formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue (400–500 nm peak) fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation.

Phenanthrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) with formula C14H10, consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a colorless, crystal-like solid, but can also appear yellow. Phenanthrene is used to make dyes, plastics and pesticides, explosives and drugs. It has also been used to make bile acids, cholesterol and steroids.

Dioscorea communis or Tamus communis is a species of flowering plant in the yam family Dioscoreaceae and is commonly known as black bryony, lady's-seal or black bindweed.

Phenanthrenoids are chemical compounds formed with a phenanthrene backbone. These compounds occur naturally in plants, although they can also be synthesized.

Dendrobium nobile, commonly known as the noble dendrobium, is a member of the family Orchidaceae. It has become a popular cultivated decorative house plant, because it produces colourful blooms in winter and spring, at a time when little else is in flower. It is also one of the 50 fundamental herbs used in traditional Chinese medicine, known as shí hú or shí hú lán. Dendrobium nobile is one of the most widespread ornamental members of the orchid family. Its blooms are variegated in colour, shading from white through pink and purple, and the many different cultivated varieties produce different sized and coloured blooms.
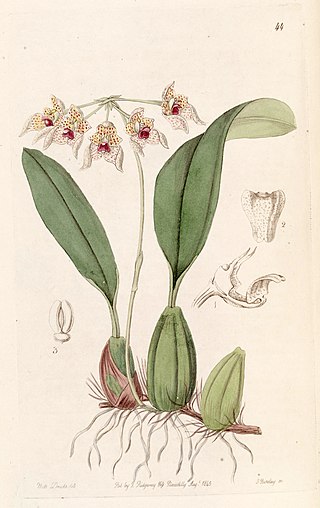
Bulbophyllum umbellatum is a species of orchid. It is native to tropical parts of South Asia, from the west central Himalayas to Taiwan and Indo-China.

Coelogyne cristata is an epiphytic orchid that comes from cool, moist areas of the eastern Himalayas and Vietnam. It blooms every spring, before the snow begins to melt. Its genus name Coelogyne originates from two Greek words, koilos ("hollow") and gyne ("woman"), because of the orchid's pistil. Cristata takes its species name from crista, the Latin word for "comb", because of the look of the flower's lip.

Maxillaria densa, the crowded maxillaria, is a species of orchid ranging from Mexico south to Nicaragua.
Bulbophyllum reptans is a species of orchid in the genus Bulbophyllum.

In organic chemistry, the Mallory reaction is a photochemical-cyclization–elimination reaction of diaryl-ethylene structures to form phenanthrenes and other polycyclic form polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heteroaromatics. This name reaction is named for Frank Mallory, who discovered it while a graduate student.
Bulbophyllum crabro, commonly called "Kam Pu Ma" in Thai, is a small orchid that grows as an epiphyte or is sometimes found as lithophyte. It grows in rainforests 1,600-2,000 m above sea level. It was formerly known as Monomeria barbata and was the type species of the genus Monomeria, now synonymous with Bulbophyllum. It is used in traditional Chinese medicine for treating coughs, pulmonary tuberculosis and trauma.

Dihydrostilbenoids (bibenzyls) are natural phenols formed from the dihydrostilbene (bibenzyl) backbone.

Dendrobieae is a tribe in the subfamily Epidendroideae, in the family Orchidaceae. The Dendrobieae are mostly tropical, epiphytic orchids which contain pseudobulbs.
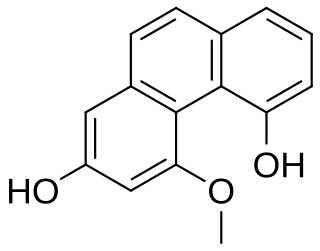
Plicatol B is one of the three phenanthrenes that can be isolated from the stems of the orchid Flickingeria fimbriata. It can also be isolated from Dendrobium densiflorum, D. loddigesii, D. moschatum, D. rotundatum and Bulbophyllum kwangtungense

Coelogin is a phenanthrenoid found in the high altitude Himalayan orchid Coelogyne cristata. This molecule has a phenanthro[4,5-bcd]pyran structure.
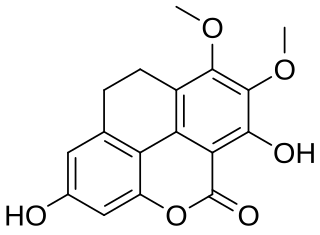
Coeloginin is a phenanthrenoid found in the high altitude Himalayan orchid Coelogyne cristata. This molecule has a phenanthro[4,5-bcd]pyrone structure.
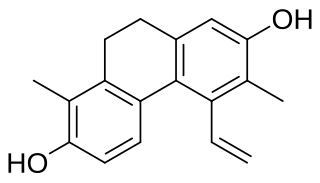
Juncusol is a 9,10-dihydrophrenathrene found in Juncus species such as J. acutus, J. effusus or J. roemerianus.
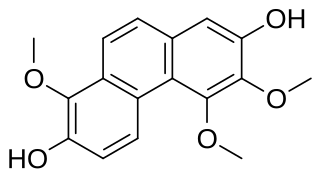
Confusarin is a phenanthrenoid found in the orchids Eria confusa and Bulbophyllum reptans. It can also be synthesized.


















