
Rungholt was a low-lying settlement in North Frisia, in what was then the Danish Duchy of Schleswig. The area today lies in Germany. Rungholt was flooded, with massive erosion, when a storm tide hit the coast on 15 or 16 January 1362.

Nordfriesland, also known as North Frisia, is the northernmost district of Germany, part of the state of Schleswig-Holstein. It includes almost all of traditional North Frisia, as well as adjacent parts of the Schleswig Geest to the east and Stapelholm to the south, and is bounded by the districts of Schleswig-Flensburg and Dithmarschen, the North Sea and the Danish county of South Jutland. The district is called Kreis Nordfriesland in German, Kreis Noordfreesland in Low German, Kris Nordfraschlönj in Mooring North Frisian, Kreis Nuurdfresklun in Fering North Frisian and Nordfrislands amt in Danish.
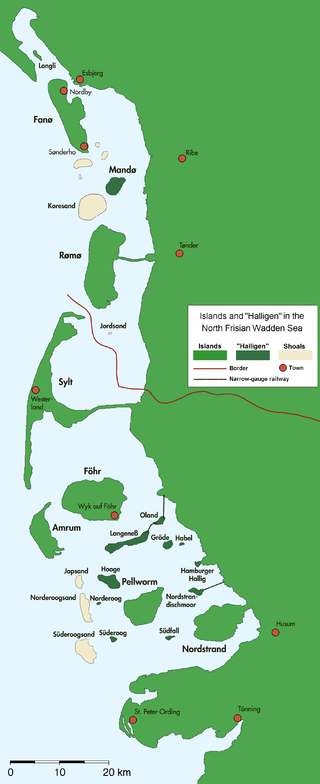
The North Frisian Islands are the Frisian Islands off the coast of North Frisia.

is a municipality in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany.

is a peninsula and former island in North Frisia on the North Sea coast of Germany. It is part of the Nordfriesland district in the federal state of Schleswig-Holstein. Its area is 50 km² and its population is 2,300. Nordstrand has two municipalities, Nordstrand and smaller Elisabeth-Sophien-Koog, which are part of the Amt Nordsee-Treene.

North Frisian is a minority language of Germany, spoken by about 10,000 people in North Frisia. The language is part of the larger group of the West Germanic Frisian languages. The language comprises 10 dialects which are themselves divided into an insular and a mainland group.

Dagebüll is a municipality located at the west coast of Schleswig-Holstein in the Nordfriesland district, Germany. Today's Dagebüll was created in 1978 as a merger of the municipalities of Fahretoft, Juliane-Marien-Koog and Waygaard. Dagebüll used to be a Hallig, the oldest houses were built on artificial dwelling hills which in parts can still be seen today. In 1704 the area was secured by sea dikes.

Tönning is a town in the district of Nordfriesland in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein.
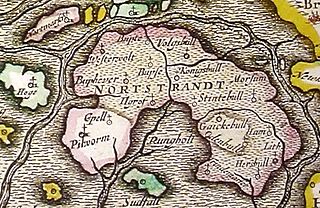
Strand was an island on the west coast of Nordfriesland in Schleswig, which was a fiefdom of the Danish crown. The area now belongs to Schleswig-Holstein in northern Germany.

The North Sea flood of 1962 was a natural disaster affecting mainly the coastal regions of West Germany and in particular the city of Hamburg in the night from 16 February to 17 February 1962. In total, the homes of about 60,000 people were destroyed, and the death toll amounted to 315 in Hamburg. The extratropical cyclone responsible for the flooding had previously crossed the United Kingdom as the Great Sheffield Gale, devastating the city of Sheffield and killing nine people.

North Frisia is the northernmost portion of Frisia, located in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, between the rivers Eider and Wiedau. It also includes the North Frisian Islands and Heligoland. The region is traditionally inhabited by the North Frisians.

Reußenköge is a sparsely populated municipality in the district of Nordfriesland, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated directly adjacent the shoreline of the North Sea coast, in a driving distance of in between 15 up to 29 km northwest of the county-capital city of Husum.

Süderoog is one of the Halligen, a group of islands in the North Frisian Wadden Sea, off the west coast of Schleswig-Holstein in north Germany. It belongs administratively to the parish of Pellworm and is a bird reserve.

Uthlande, Utlande is a term for the islands, halligen and marshes off the mainland of North Frisia in the Southwest Jutland, modern Nordfriesland district, Germany.

Südfall is a small island in the Wadden Sea off the west coast of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, one of the ten German Hallig islands. It has a permanent population of two people. It covers an area of 0.56 square kilometres (0.22 sq mi) and is administratively part of Pellworm Municipality.
Strand Frisian was a dialect of the North Frisian language which was originally spoken on Strand island, Duchy of Schleswig. Strand was destroyed in the Burchardi flood of 1634 with its remnants forming the islands Pellworm and Nordstrand which are now part of Germany. Strand Frisian is counted among the mainland group of North Frisian dialects.

Edoms Hundred was a mediaeval hundred located in the southern part of North Frisia in the Danish region of Southern Schleswig, part of the Frisian Uthlande. It encompassed the eastern part of the island of Strand, which sank in 1634 during the Burchardi flood, including some of the land which now comprises the peninsula of Nordstrand. Edoms Hundred bordered the other so-called Five Hundreds or Strand Hundreds on the island: Beltring Hundred to the north, Pellworm Hundred to the west, Southern Goes Hundred to the east, and Lundenberg Hundred to the south.

Beltring Hundred was a mediaeval hundred located in the southern part of North Frisia in the Danish region of Southern Schleswig, part of the Frisian Uthlande. It encompassed the northern part of the island of Strand, which sank in 1634 during the Burchardi flood. Some of the land of Beltring Hundred survived the flood, however, and became the Hallig of Nordstrandischmoor as well as the site of the modern municipality of Ockholm. Beltring Hundred was one of the so-called Five Hundreds or Strand Hundreds on the island, the others being Edoms Hundred, Pellworm Hundred, Southern Goes Hundred, and Lundenberg Hundred.

Lundenberg Hundred was a mediaeval hundred located in the southern part of North Frisia in the Danish region of Southern Schleswig, part of the Frisian Uthlande. Lundenberg Hundred was one of the so-called Five Hundreds or Strand Hundreds on the island, the others being Edoms Hundred, Beltring Hundred, Southern Goes Hundred, and Pellworm Hundred. It encompassed the southeastern part of the former island of Strand, between what are now the peninsulae of Nordstrand and Eiderstedt.

Hamburger Hallig is an area on the westcoast of Nordfriesland district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, that is not protected by sea dikes. It is therefore counted among the Halligen islands.




















