
Rio Grande do Sul is a state in the southern region of Brazil. It is the fifth-most-populous state and the ninth largest by area. Located in the southernmost part of the country, Rio Grande do Sul is bordered clockwise by Santa Catarina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, the Uruguayan departments of Rocha, Treinta y Tres, Cerro Largo, Rivera and Artigas to the south and southwest, and the Argentine provinces of Corrientes and Misiones to the west and northwest. The capital and largest city is Porto Alegre. The state has the highest life expectancy in Brazil, and the crime rate is relatively low compared to the Brazilian national average. Despite the high standard of living, unemployment is still high in the state, as of 2017. The state has 5.4% of the Brazilian population and it is responsible for 6.6% of the Brazilian GDP.

Mariana Pimentel is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It is located approximately 75 km from the state's capital, Porto Alegre.

São Gabriel is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
Gangamopteris is a genus of Carboniferous-Permian plants, very similar to Glossopteris. Previously, it was classified as fern with reproduction by seed. The genus is usually only applied to leaves, making it a form taxon. Gangamopteris dominates some coal deposits, such as those of the Beacon Supergroup.

Konzhukovia is an amphibian genus that belongs to an extinct group of temnospondyls, the largest clade of basal tetrapods including about 198 genera, 292 species, and more than half of which were alive during the early Mesozoic period. The animal was a predator that lived about 260 million years ago, and could get up to about three meters in length. Specifically, Konzukovia lived during the Permian, between 252 and 270 million years ago according to the type of rock the fossil was found in. There are three species within this genus, K. vetusta, K. tarda, and K. sangabrielensis, the first two originating from Russia while the latest originating from Southern Brazil. The discovery of this specimen in Southern Brazil provided more evidence to support the idea that during this animals existence, there was a “biological corridor” because of the supercontinent Pangea, allowing these species to be found so far apart from each other. Konzhukovia belongs to the family Archegosauridae, a family consisted of large temnospondyls that most likely compare to modern day crocodiles. Since the discovery of the latest species, K. sangabrielensis, Pacheco proposes that there must be the creation of a new family, Konzhokoviidae, a monophyletic group in a sister-group relationship with Stereospondlyi in order to accommodate the three species. Konzhukovia skulls usually exhibit typical rhinesuchid features including an overall parabolic shape, small orbits located more posteriorly, and the pterygoids do not reach the vomer. These animals were long-snouted amphibians that had clear adaptations made for fish catching, as well as exemplifying aquatic features.

Aceguá is a municipality in the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
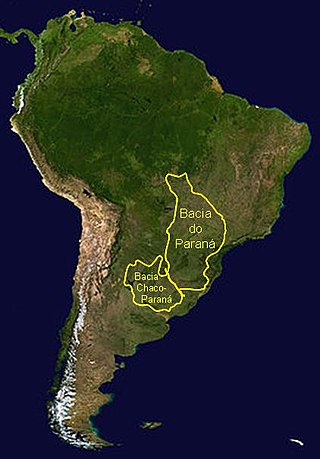
The Paraná Basin is a large cratonic sedimentary basin situated in the central-eastern part of South America. About 75% of its areal distribution occurs in Brazil, from Mato Grosso to Rio Grande do Sul states. The remainder area is distributed in eastern Paraguay, northeastern Argentina and northern Uruguay. The shape of the depression is roughly elliptical and covers an area of about 1,500,000 km2 (580,000 sq mi).

Tiarajudens is an extinct genus of saber-toothed herbivorous anomodonts which lived during the Middle Permian period in what is now Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. It is known from the holotype UFRGS PV393P, a nearly complete skull. The type species T. eccentricus was named in 2011.
Provelosaurus is an extinct Pareiasaur genus of the Late Permian found on the road between Aceguá and Bagé in the Paleorrota, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Found in the Rio do Rasto Formation, aged about 260 million years. The holotype specimen found measures 1.2 metres in length.
Bageherpeton is an extinct genus of archegosaurid temnospondyl amphibian from the Upper Permian period of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil (Paleorrota). It was found in the Rio do Rasto Formation, and was named in honor of the city of Bagé near where it was found. It was described from a lower jaw.

Pampaphoneus is an extinct genus of carnivorous dinocephalian therapsid belonging to the family Anteosauridae. It lived 268 to 265 million years ago during the Wordian age of the Guadalupian period in what is now Brazil. Pampaphoneus is known by an almost complete skull with the lower jaw still articulated, discovered on the lands of the Boqueirão Farm, near the city of São Gabriel, in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. A second specimen from the same locality was reported in 2019 and 2020 but has not yet been described. It is composed of a skull associated with postcranial remains. It is the first South American species of dinocephalian to have been described. The group was previously known in South America only by a few isolated teeth and a jaw fragment reported in 2000 in the same region of Brazil. Phylogenetic analysis conducted by Cisneros and colleagues reveals that Pampaphoneus is closely related to anteosaurs from European Russia, indicating a closer faunal relationship between South America and Eastern Europe than previously thought, thus promoting a Pangea B continental reconstruction.
The Rio Bonito Formation is a geological formation of the Paraná and Pelotas Basins of Permian age. It is represented by a succession of cyclic sedimentary packages of sandstones, siltstones and shales which bear extensive deposits of coal that has been extracted since the 19th century. The Rio Bonito Formation was deposited in a coastal environment, formed by rivers, deltas, bays and estuaries with tidal plains, barrier islands and shallow marine platform, at a time when the Paraná Basin was a large gulf of the ancient supercontinent Gondwana. This gulf was open to the southwest, to the old ocean Panthalassa. The Rio Bonito Formation outcrops occur mainly in the eastern border of the Paraná Basin, in a narrow band in the states of São Paulo, Paraná, Santa Catarina, Rio Grande do Sul and Uruguay. The Rio Bonito Formation belongs to the second-order stratigraphic supersequence called Gondwana I.
The genus Phyllotheca was created in 1828, when Brongniart described the type species Phyllotheca australis coming from Hawkesbury River, Australia.
Samaropsis is a form genus named by Goeppert in 1864. Later Sewart (1917) redefined the taxon to refer only to the seeds.
Cordaicarpus is a form genus named by Geinitz (1862) and redefined by Seward (1917) to avoid confusion with another genus and to establish that the genus refers only seeds. Seward defined the differences between Cordaicarpus and Samaropsis.
Brazilea is an extinct genus of algae. The species Brazilea helby and Brazilea scissa were located in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel, the geopark Paleorrota. The outcrop dates to the Sakmarian of the Permian.
Leiosphaeridia is an extinct genus of algae or acritarchs. The genus of undefined species were found in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel in Brazil, the geopark Paleorrota. The outcrop date Sakmarian in Permian.
Tetraporina is an extinct genus of algae. The genus of undefined species were found in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel in Brazil, the geopark Paleorrota, on Rio Bonito Formation. The outcrop date Sakmarian in Permian.
Quadrisporites is an extinct genus of acritarchs. The species Q. horridus was located in outcrop Morro do Papaléo in the town of Mariana Pimentel in Brazil, the geopark Paleorrota. The outcrop is in the Rio Bonito Formation and date of Sakmarian in the Permian.

The Rio do Rasto Formation is a Late Permian sedimentary geological formation in the South Region of Brazil. The official name is Rio do Rasto, although in some publications it appears as Rio do Rastro.








