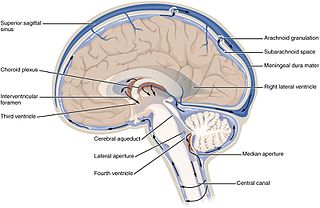
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), previously known as pseudotumor cerebri and benign intracranial hypertension, is a condition characterized by increased intracranial pressure without a detectable cause. The main symptoms are headache, vision problems, ringing in the ears, and shoulder pain. Complications may include vision loss.

Syringomyelia is a generic term referring to a disorder in which a cyst or cavity forms within the spinal cord. Often, syringomyelia is used as a generic term before an etiology is determined. This cyst, called a syrinx, can expand and elongate over time, destroying the spinal cord. The damage may result in loss of feeling, paralysis, weakness, and stiffness in the back, shoulders, and extremities. Syringomyelia may also cause a loss of the ability to feel extremes of hot or cold, especially in the hands. It may also lead to a cape-like bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation along the upper chest and arms. The combination of symptoms varies from one patient to another depending on the location of the syrinx within the spinal cord, as well as its extent.

Hydrocephalus is a condition in which an accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs within the brain. This typically causes increased pressure inside the skull. Older people may have headaches, double vision, poor balance, urinary incontinence, personality changes, or mental impairment. In babies, it may be seen as a rapid increase in head size. Other symptoms may include vomiting, sleepiness, seizures, and downward pointing of the eyes.

In medicine, a shunt is a hole or a small passage that moves, or allows movement of, fluid from one part of the body to another. The term may describe either congenital or acquired shunts; acquired shunts may be either biological or mechanical.

Lumbar puncture (LP), also known as a spinal tap, is a medical procedure in which a needle is inserted into the spinal canal, most commonly to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic testing. The main reason for a lumbar puncture is to help diagnose diseases of the central nervous system, including the brain and spine. Examples of these conditions include meningitis and subarachnoid hemorrhage. It may also be used therapeutically in some conditions. Increased intracranial pressure is a contraindication, due to risk of brain matter being compressed and pushed toward the spine. Sometimes, lumbar puncture cannot be performed safely. It is regarded as a safe procedure, but post-dural-puncture headache is a common side effect if a small atraumatic needle is not used.
Normal-pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), also called malresorptive hydrocephalus, is a form of communicating hydrocephalus in which excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs in the ventricles, and with normal or slightly elevated cerebrospinal fluid pressure. As the fluid builds up, it causes the ventricles to enlarge and the pressure inside the head to increase, compressing surrounding brain tissue and leading to neurological complications. The disease presents in a classic triad of symptoms, which are memory impairment, urinary frequency, and balance problems/gait deviations. The disease was first described by Salomón Hakim and Adams in 1965.

A cerebral shunt is a device permanently implanted inside the head and body to drain excess fluid away from the brain. They are commonly used to treat hydrocephalus, the swelling of the brain due to excess buildup of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). If left unchecked, the excess CSF can lead to an increase in intracranial pressure (ICP), which can cause intracranial hematoma, cerebral edema, crushed brain tissue or herniation. The drainage provided by a shunt can alleviate or prevent these problems in patients with hydrocephalus or related diseases.

Intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), also known as intraventricular bleeding, is a bleeding into the brain's ventricular system, where the cerebrospinal fluid is produced and circulates through towards the subarachnoid space. It can result from physical trauma or from hemorrhagic stroke.

Leptomeningeal cancer is a rare complication of cancer in which the disease spreads from the original tumor site to the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord. This leads to an inflammatory response, hence the alternative names neoplastic meningitis (NM), malignant meningitis, or carcinomatous meningitis. The term leptomeningeal describes the thin meninges, the arachnoid and the pia mater, between which the cerebrospinal fluid is located. The disorder was originally reported by Eberth in 1870.

An external ventricular drain (EVD), also known as a ventriculostomy or extraventricular drain, is a device used in neurosurgery to treat hydrocephalus and relieve elevated intracranial pressure when the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the brain is obstructed. An EVD is a flexible plastic catheter placed by a neurosurgeon or neurointensivist and managed by intensive care unit (ICU) physicians and nurses. The purpose of external ventricular drainage is to divert fluid from the ventricles of the brain and allow for monitoring of intracranial pressure. An EVD must be placed in a center with full neurosurgical capabilities, because immediate neurosurgical intervention can be needed if a complication of EVD placement, such as bleeding, is encountered.

A cerebrospinal fluid leak is a medical condition where the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounding the brain or spinal cord leaks out of one or more holes or tears in the dura mater. A cerebrospinal fluid leak can be either cranial or spinal, and these are two different disorders. A spinal CSF leak can be caused by one or more meningeal diverticula or CSF-venous fistulas not associated with an epidural leak.
Bobble-head doll syndrome is a rare neurological movement disorder in which patients, usually children around age 3, begin to bob their head and shoulders forward and back, or sometimes side-to-side, involuntarily, in a manner reminiscent of a bobblehead doll. The syndrome is related to cystic lesions and swelling of the third ventricle in the brain. Symptoms of bobble-head doll syndrome are diverse but can be grouped into two categories: physical and neurological. The most common form of treatment is surgical implanting of a shunt to relieve the swelling of the brain.
A lumbar–peritoneal shunt is a technique to channelise the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the lumbar thecal sac into the peritoneal cavity.
Salomón Hakim Dow was a Colombian neurosurgeon, researcher, and inventor. A descendant of Lebanese immigrants, he is known for his work on neurosurgery and for the precursor of the modern valve treatment for hydrocephalus.

Lymphocytic pleocytosis is an abnormal increase in the amount of lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). It is usually considered to be a sign of infection or inflammation within the nervous system, and is encountered in a number of neurological diseases, such as pseudomigraine, Susac's syndrome, and encephalitis. While lymphocytes make up roughly a quarter of all white blood cells (WBC) in the body, they are generally rare in the CSF. Under normal conditions, there are usually less than 5 white blood cells per µL of CSF. In a pleocytic setting, the number of lymphocytes can jump to more than 1,000 cells per µL. Increases in lymphocyte count are often accompanied by an increase in cerebrospinal protein concentrations in addition to pleocytosis of other types of white blood cells.

Neurohydrodynamics is a division of neurophysics that focuses on the hydrodynamics of the neurological system. It applies physical principles and design concepts to neurophysics seeking to close the gap between fluid mechanics and neurosurgical and neurological medicine. It combines fluid mechanics principles with neuroscience to improve neurological disorder healthcare diagnosis, monitoring and therapy.

ShuntCheck is a non-invasive diagnostic medical device which detects flow in the cerebral shunts of hydrocephalus patients. Neurosurgeons can use ShuntCheck flow results along with other diagnostic tests to assess shunt function and malfunction.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow MRI is used to assess pulsatile CSF flow both qualitatively and quantitatively. Time-resolved 2D phase-contrast MRI with velocity encoding is the most common method for CSF analysis. CSF Fluid Flow MRI detects back and forth flow of Cerebrospinal fluid that corresponds to vascular pulsations from mostly the cardiac cycle of the choroid plexus. Bulk transport of CSF, characterized by CSF circulation through the Central Nervous System, is not used because it is too slow to assess clinically. CSF would have to pass through the brain's lymphatic system and be absorbed by arachnoid granulations.
Petra Klinge is a neurosurgeon and academic. She is professor of neurosurgery at Brown University.














