
A Birney or Birney Safety Car is a type of streetcar that was manufactured in the United States in the 1910s and 1920s. The design was small and light and was intended to be an economical means of providing frequent service at a lower infrastructure and labor cost than conventional streetcars. Production of Birney cars lasted from 1915 until 1930, and more than 6,000 of the original, single-truck version were built. Several different manufacturers built Birney cars. The design was "the first mass-produced standard streetcar " in North America.

St Kilda is a seaside suburb in Adelaide, South Australia. St Kilda has a small number of houses and a 2006 population of 246. There is a single connecting road to the rest of Adelaide which, where the road enters the suburb's residential area, is surrounded by salt crystallisation lagoons used in the manufacture of soda ash. The inhabited section of the suburb occupies less than 100 hectares along the seafront, with the remainder used for salt lagoons and also settlement ponds of nearby Bolivar sewage treatment works.

Until 1958, trams formed a network spanning most of Adelaide, with a history dating back to 1878. Adelaide ran horse trams from 1878 to 1914 and electric trams from 1909, but has primarily relied on buses for public transport since 1958. Electric trams and trolleybuses were Adelaide's main public transport throughout the life of the electric tram network. All tram services except the Glenelg tram were closed in 1958. The Glenelg tram remains in operation and has been progressively upgraded and extended since 2005.

The earliest trams in Australia operated in the latter decades of the 19th century, hauled by horses or "steam tram motors". At the turn of the 20th century, propulsion almost universally turned to electrification, although cable trams lingered in Melbourne. In cities and towns that had trams, they were a major part of public transport assets.

The H type Adelaide tram was a class of 30 trams built by A Pengelly & Co, Adelaide in 1929 for use on the Glenelg tram line. They operated the service until replaced by Flexity Classics in 2006.

Trams in Ballarat were first used for public transport in 1887. They ceased to operate as a means of public transport in 1971, but a section continues to be operated today as a tourist attraction.

The Adelaide trolleybus system formed part of the public transport network in Adelaide, South Australia from 1932 until 1963.

Angas Street is a main street in the CBD of the centre of Adelaide, South Australia. The rear of St Aloysius College faces the street, and various law courts are on the street, including the Dame Roma Mitchell Building. The South Australia Police headquarters and South Australian Metropolitan Fire Service Adelaide station are further down the street.
The O-class Melbourne tram were a group of four trams built in 1912 by Duncan & Fraser (Adelaide) for the Prahran & Malvern Tramways Trust (P&MTT) upon the recommendation of W. G. T. Goodman, Chief Engineer and General manager of the Adelaide tramways. They were allocated P&MTT fleet numbers 21 to 24. At the time of their introduction, they were by far the largest street-vehicles in Melbourne, and earned the nicknames Zeppelins and Dreadnoughts. Proving to be less than satisfactory in service, they were later sold to the Hawthorn Tramways Trust (HTT) in August 1916 as "surplus to requirements", however P&MTT soon ordered replacement tramcars. Co-incidentally they retained their fleet numbers whilst at Hawthorn.

The P-class was a class of eight trams built by Duncan & Fraser, Adelaide for the Hawthorn Tramway Trust (HTT) as 25-32. All passed to the Melbourne & Metropolitan Tramways Board on 2 February 1920 when it took over the HTT becoming the P-class and being renumbered 131-138.

The Tramway Museum, St Kilda is Australia's principal museum of the 19th and 20th century trams of Adelaide, South Australia. It is situated at St Kilda, 24 km (15 mi) north of the centre of Adelaide. Most of the trams operate when rostered along a 1.6 km (1.0 mi) purpose-built track that runs between the museum and a large adventure playground.
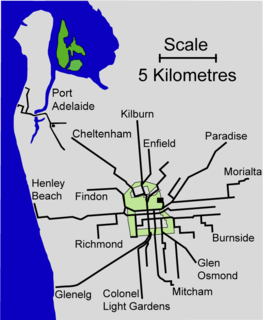
The tram network in Adelaide was converted from horse-drawn trams to electric trams between 1909 and 1914. Most of the tram network was closed in the 1950s, and began expanding again in the 21st century.

The A type Adelaide tram was a class of 70 drop-end, Californian combination trams built by Duncan & Fraser, Adelaide in 1908/09 for the Municipal Tramways Trust (MTT). They were used on tram lines to Kensington, Marryatville, Maylands, Payneham, Wakerville, North Adelaide, Parkside, Unley and Hyde Park. In later years they were cascaded to quieter services to Croydon and the isolated Port Adelaide network.

The B type Adelaide tram was a class of 30 straight sill, open cross-bench trams built by Duncan & Fraser, Adelaide in 1909 for the Municipal Tramways Trust (MTT). Although popular in summer, they were less so in winter when exposed to inclement weather. Thus in 1917 with the MTT requiring more trams, 41-60 were converted to Californian combination trams, closely resembling the A type trams. When the MTT introduced an alpha classification system in 1923, they were designated the B type. Numbers 41-43 became the A2 type and 44-60 the A1 type. The A2s were used exclusively on the isolated Port Adelaide network.
The Adelaide D type tram was a class of trams operated by the Municipal Tramways Trust on the Adelaide tram network from 1910 until 1958.

The E type Adelaide tram was a class of 20 bogie, half open, half closed combination trams with one drop and one straight sill end built by A Pengelly & Co, Adelaide in 1910 for the Municipal Tramways Trust (MTT). In 1918/19, all were remotored with 65hp General Electric 201s with the original 50hp General Electric 202s reused in the C type trams. When the MTT introduced an alpha classification system in 1923, they were designated the E type. In 1936, all were converted to E1s with crossbenches removed and the saloon extended along the full length.

The F type Adelaide tram was a class of 84 bogie, drop centre, combination trams built between 1921 and 1929 for the Municipal Tramways Trust (MTT). All bar three were built by A Pengelly & Co, Adelaide with 262, 283 and 284 being built by the MTT's Hackney workshops. The first 50 were built as the F type, while the last 34 were classified as the F1 type, the latter having an all steel as opposed to partly wooden underframe. Some remained in service until the network closed in November 1958.

The G type Adelaide tram was a class of four single truck Birney trams manufactured by JG Brill Company. They arrived in completely knocked down being assembled by the Municipal Tramways Trust.

Horse trams in Adelaide























