
Microcotyle is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea. Species of Microcotyle are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated.

Cichlidogyrus is a genus of monopisthocotylean monogeneans in the family Ancyrocephalidae. The type-species of the genus is Cichlidogyrus arthracanthusPaperna, 1960, by original designation. All the species of the genus are parasites on the gills of fish, namely African Cichlidae, Nandidae and Cyprinodontidae.

Clamps are the main attachment structure of the Polyopisthocotylean monogeneans.
These ectoparasitic worms have a variable number of clamps on their haptor ; each clamp is attached to the host fish, generally to its gill. Clamps include sclerotised elements, called the sclerites, and muscles. The structure of clamps varies according to the groups within the Polyopisthocotylean monogeneans; microcotylids have relatively simple clamps, whereas gastrocotylids have more complex clamps.

Gastrocotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans. All the species in this family are parasitic on fish.
Plectanocotylidae is a family of polyopisthocotylean monogeneans. All the species in this family are parasitic on the gills of marine fish.

Bychowskicotylidae is a family of monogeneans in the order Mazocraeidea. The name of the family, and of its type-genus Bychowskicotyle, was created to honour Boris Evseevitch Bychowsky, a Soviet scientist and parasitologist, specialist of monogeneans.

Microcotyle archosargi is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae. It was first described by MacCallum in 1913 based on ten specimens. Hargis (1956) pointed out that the description and figures given by MacCallum were poor in details.

Microcotyle donavini is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle victoriae is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.

Microcotyle pomatomi is a species of monogenean that is parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
Microcotyle danielcarrioni is a species of monogenean, parasitic on the gills of a marine fish. It belongs to the family Microcotylidae.
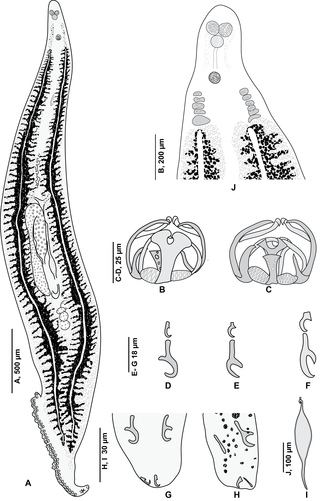
Pseudaxine is a genus which belongs to the phylum Platyhelminthes and class Monogenea; all its species are parasites of fish.
Atriasterinae is a subfamily within family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. This subfamily was created by Maillard & Noisy in 1979.
Metamicrocotyla is a genus which belongs to the family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. It was created by Yamaguti in 1953 to include Metamicrocotyla bora and Metamicrocotyla filiformis from the gills off the flathead grey mullet Mugil cephalus (Mugilidae). As all Monogenea, species of Metamicrocotyla are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated. Members of Metamicrocotyla are characterized by a symmetrical haptor, a variable number of postovarian testes and with no cirrus nor vagina. their genital atrium is provided with paired groups of spines or hooks.

Microcotylinae is a subfamily within family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. This subfamily was created by Taschenberg in 1879.
Atriostella is a genus which belongs to the family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. As all Monogenea, species of Atriostella are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated.
Bivagina is a genus of monogeneans. As all Monogenea, species in the genus are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated.
Diplasiocotyle is a genus which belongs to the family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. As all Monogenea, species of Microcotylidae are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated.
Jaliscia is a genus which belongs to the family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea. As all Monogenea, species of Jaliscia are ectoparasites that affect their host by attaching themselves as larvae on the gills of the fish and grow into adult stage. This larval stage is called oncomiracidium, and is characterized as free swimming and ciliated.
Solostamenides is a genus which belongs to the family Microcotylidae and class Monogenea.







