
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine class. It is mainly used recreationally, as a eugeroic (wakefulness promoter) or as a mild cognitive enhancer to increase alertness and attentional performance. Caffeine acts by blocking binding of adenosine to the adenosine A1 receptor, which enhances release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Caffeine has a three-dimensional structure similar to that of adenosine, which allows it to bind and block its receptors. Caffeine also increases cyclic AMP levels through nonselective inhibition of phosphodiesterase.
In toxicology, the median lethal dose, LD50 (abbreviation for "lethal dose, 50%"), LC50 (lethal concentration, 50%) or LCt50 is a toxic unit that measures the lethal dose of a given substance. The value of LD50 for a substance is the dose required to kill half the members of a tested population after a specified test duration. LD50 figures are frequently used as a general indicator of a substance's acute toxicity. A lower LD50 is indicative of increased toxicity.
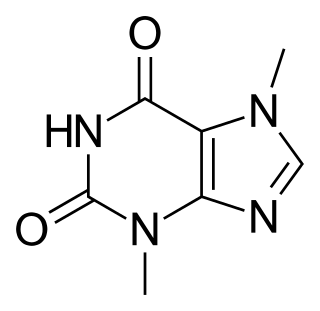
Theobromine, also known as xantheose, is the principal alkaloid of Theobroma cacao. Theobromine is slightly water-soluble (330 mg/L) with a bitter taste. In industry, theobromine is used as an additive and precursor to some cosmetics. It is found in chocolate, as well as in a number of other foods, including the leaves of the tea plant, and the kola nut. It is a white or colourless solid, but commercial samples can appear yellowish.

Stimulants is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase the activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription as performance-enhancing or recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or comedown at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and prescription stimulants" the value was 0.7%, and for MDMA 0.4%.

Guaraná is a climbing plant in the family Sapindaceae, native to the Amazon basin and especially common in Brazil. Guaraná has large leaves and clusters of flowers, and is best known for the seeds from its fruits, which are about the size of a coffee bean.
Substance intoxication is a transient condition of altered consciousness and behavior associated with recent use of a substance. It is often maladaptive and impairing, but reversible. If the symptoms are severe, the term "substance intoxication delirium" may be used.
Caffeinism is a state of intoxication caused by excessive consumption of caffeine. This intoxication covers a variety of unpleasant physical and mental symptoms associated with the consumption of excessive amounts of caffeine.

Zolpidem, sold under the brand name Ambien among others, is a medication primarily used for the short-term treatment of sleeping problems. Guidelines recommend that it be used only after cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia and behavioral changes, such as sleep hygiene, have been tried. It decreases the time to sleep onset by about fifteen minutes and at larger doses helps people stay asleep longer. It is taken by mouth and is available in conventional tablets, sublingual tablets, or oral spray.
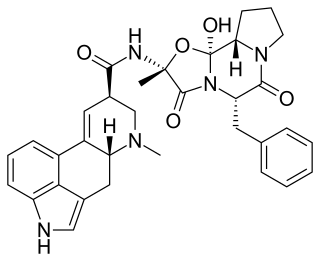
Ergotamine, sold under the brand names Cafergot and Ergomar among others, is an ergopeptine and part of the ergot family of alkaloids; it is structurally and biochemically closely related to ergoline. It possesses structural similarity to several neurotransmitters, and has biological activity as a vasoconstrictor.
The gateway drug effect is a comprehensive catchphrase for the often observed effect that the use of a psychoactive substance is coupled to an increased probability of the use of further substances. Possible causes are biological alterations in the brain due to the earlier substance exposure and similar attitudes of people who use different substances across different substances. In 2020, the National Institute on Drug Abuse released a study backing allegations that marijuana is a "gateway" to more dangerous substance use, though not for the majority of people who use substances. A literature review by the United States Department of Justice found no conclusive evidence that the link is causal.

HU-210 is a synthetic cannabinoid that was first synthesized in 1988 from (1R,5S)-myrtenol by a group led by Raphael Mechoulam at the Hebrew University. HU-210 is 100 to 800 times more potent than natural THC from cannabis and has an extended duration of action. HU-210 has a binding affinity of 0.061nM at CB1 and 0.52nM at CB2 in cloned human cannabinoid receptors compared to Delta-9-THC of 40.7nM at CB1. HU-210 is the (–)-1,1-dimethylheptyl analog of 11-hydroxy- Δ8- tetrahydrocannabinol; in some references it is called 1,1-dimethylheptyl- 11-hydroxytetrahydrocannabinol. The abbreviation "HU" stands for Hebrew University.

Caffeine dependence is the condition of having a substance dependence on caffeine, a commonplace central nervous system stimulant drug which occurs naturally in coffee, tea, yerba mate, cocoa, and other plants. Caffeine is one of the most common additives in many consumer products, including pills and beverages such as caffeinated alcoholic beverages, energy drinks, and colas. Studies have found that 89 percent of adults in the U.S. consume on average 200 mg of caffeine daily. Cultural influence is a large factor in deciding how and what way caffeine is used. For example, in African, Asian and Pacific countries, tea is the most popular form of caffeine, while in Europe and North America, coffee is the mainstream choice.

Polysubstance use or poly drug use refers to the use of combined psychoactive substances. Polysubstance use may be used for entheogenic, recreational, or off-label indications, with both legal and illegal substances. In many cases one drug is used as a base or primary drug, with additional drugs to leaven or compensate for the side effects, or tolerance, of the primary drug and make the experience more enjoyable with drug synergy effects, or to supplement for primary drug when supply is low.
Performance-enhancing substances, also known as performance-enhancing drugs (PEDs), are substances that are used to improve any form of activity performance in humans. A well-known example of cheating in sports involves doping in sport, where banned physical performance-enhancing drugs are used by athletes and bodybuilders. Athletic performance-enhancing substances are sometimes referred as ergogenic aids. Cognitive performance-enhancing drugs, commonly called nootropics, are sometimes used by students to improve academic performance. Performance-enhancing substances are also used by military personnel to enhance combat performance.
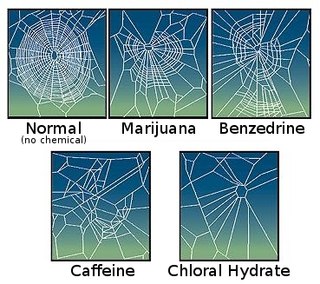
Psychoactive drugs, such as caffeine, amphetamine, mescaline, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), cannabis, chloral hydrate, theophylline, IBMX and others, can have strong effects on certain animals. It is believed that plants developed caffeine as a chemical defense against insects.

Naphyrone, also known as O-2482 and naphthylpyrovalerone, is a substituted cathinone drug derived from pyrovalerone that acts as a triple reuptake inhibitor, producing stimulant effects and has been reported as a novel designer drug. No safety or toxicity data is available on the drug.

A caffeinated alcoholic drink is a drink that contains both alcohol and a significant amount of caffeine. Caffeine, a stimulant, masks some of the depressant effects of alcohol. However, in 2010 and 2011, this type of drink faced criticism for posing health risks to its drinkers. In some places there is a ban on caffeinated alcoholic drinks.

A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent, or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance that changes the function of the nervous system and results in alterations of perception, mood, cognition, and behavior. These substances may be used medically, recreationally, for spiritual reasons, or for research. Some categories of psychoactive drugs may be prescribed by physicians and other healthcare practitioners because of their therapeutic value.

A diuretic is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin, is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine.
Caffeine-induced anxiety disorder is a subclass of the DSM-5 diagnosis of substance/medication-induced anxiety disorder.
















