Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.

In contemporary education, mathematics education is the practice of teaching and learning mathematics, along with the associated scholarly research.
Multivariable calculus is the extension of calculus in one variable to calculus with functions of several variables: the differentiation and integration of functions involving several variables, rather than just one.

A Course of Pure Mathematics is a classic textbook in introductory mathematical analysis, written by G. H. Hardy. It is recommended for people studying calculus. First published in 1908, it went through ten editions and several reprints. It is now out of copyright in UK and is downloadable from various internet web sites. It remains one of the most popular books on pure mathematics.
Advanced Placement Calculus is a set of two distinct Advanced Placement calculus courses and exams offered by the American nonprofit organization College Board. AP Calculus AB covers basic introductions to limits, derivatives, and integrals. AP Calculus BC covers all AP Calculus AB topics plus additional topics.
Mathematics education in Australia varies significantly between states, especially at the upper secondary level.
Calculus is a branch of mathematics focused on limits, functions, derivatives, integrals, and infinite series. This subject constitutes a major part of contemporary mathematics education. Calculus has widespread applications in science, economics, and engineering and can solve many problems for which algebra alone is insufficient.
The Tennessee Governor's Academy for Mathematics and Science, commonly Tennessee Governor's Academy or TGA, was a residential high school located in Knoxville, Tennessee on the campus of The Tennessee School for the Deaf (TSD). It was founded in 2007 by Governor Phil Bredesen as part of an effort to provide challenges for students across the academic spectrum. Its inaugural class consisted of 24 high school juniors from throughout the state. The Academy was closed on May 31, 2011, due to lack of state funding.
Harley M. Flanders was an American mathematician, known for several textbooks and contributions to his fields: algebra and algebraic number theory, linear algebra, electrical networks, scientific computing.
Math 55 is a two-semester long first-year undergraduate mathematics course at Harvard University, founded by Lynn Loomis and Shlomo Sternberg. The official titles of the course are Honors Abstract Algebra and Honors Real and Complex Analysis. Previously, the official title was Honors Advanced Calculus and Linear Algebra.

Roland "Ron" Edwin Larson is a professor of mathematics at Penn State Erie, The Behrend College, Pennsylvania. He is best known for being the author of a series of widely used mathematics textbooks ranging from middle school through the second year of college.

Andrew Yan-Tak Ng is a British-born American computer scientist and technology entrepreneur focusing on machine learning and AI. Ng was a co-founder and head of Google Brain and was the former Chief Scientist at Baidu, building the company's Artificial Intelligence Group into a team of several thousand people.
Chegg, Inc., is an American education technology company based in Santa Clara, California. It provides digital and physical textbook rentals, textbook solutions, online tutoring, and other student services.
The Tepper School of Business is the business school of Carnegie Mellon University. It is located in the university's 140-acre (0.57 km2) campus in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, US.
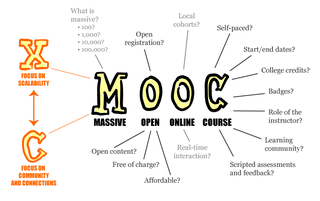
A massive open online course is an online course aimed at unlimited participation and open access via the Web. In addition to traditional course materials, such as filmed lectures, readings, and problem sets, many MOOCs provide interactive courses with user forums or social media discussions to support community interactions among students, professors, and teaching assistants (TAs), as well as immediate feedback to quick quizzes and assignments. MOOCs are a widely researched development in distance education, first introduced in 2008, that emerged as a popular mode of learning in 2012.
MyMathLab is an online interactive and educational system designed by Pearson Education to accompany its published math textbooks. It covers courses from basic math through calculus and statistics, as well as math for business, engineering and future educators. Pearson designed MyMathLab to respond to the needs of instructors and students who wanted more opportunity for practice, immediate feedback, and automated grading.

Coursera Inc. is an American massive open online course provider founded in 2012 by Stanford University computer science professors Andrew Ng and Daphne Koller. Coursera works with universities and other organizations to offer online courses, certifications, and degrees in a variety of subjects. In 2021 it was estimated that about 150 universities offered more than 4,000 courses through Coursera.
A mathematical exercise is a routine application of algebra or other mathematics to a stated challenge. Mathematics teachers assign mathematical exercises to develop the skills of their students. Early exercises deal with addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of integers. Extensive courses of exercises in school extend such arithmetic to rational numbers. Various approaches to geometry have based exercises on relations of angles, segments, and triangles. The topic of trigonometry gains many of its exercises from the trigonometric identities. In college mathematics exercises often depend on functions of a real variable or application of theorems. The standard exercises of calculus involve finding derivatives and integrals of specified functions.

Iversity is a Berlin-based online education platform. Since October 2013, iversity has specialised in providing online courses and lectures in higher education, specifically MOOCs. Courses are free and open for anyone to enroll and participate. Many of them are conducted in English or German, but also other languages. iversity cooperates with individual professors as well as different European universities. Some of the courses were winners of the MOOC Production Fellowship held in early 2013. iversity.org officially launched the MOOC platform online in October 2013 and as of February 2015 has a user base of 600,000 online learners, enrolled in 63 courses offered by 41 partner universities. iversity is the only MOOC platform offering courses with ECTS-integration. iversity has branch offices in Bernau bei Berlin, Germany and Berlin.

Introduction to Electrodynamics is a textbook by the physicist David J. Griffiths. Generally regarded as a standard undergraduate text on the subject, it began as lecture notes that have been perfected over time. Its most recent edition, the fourth, was published in 2013 by Pearson and in 2017 by Cambridge University Press. This book uses SI units exclusively. A table for converting between SI and Gaussian units is given in Appendix C.








