Montage of Caldwell Catalogue objects. | |
| | |
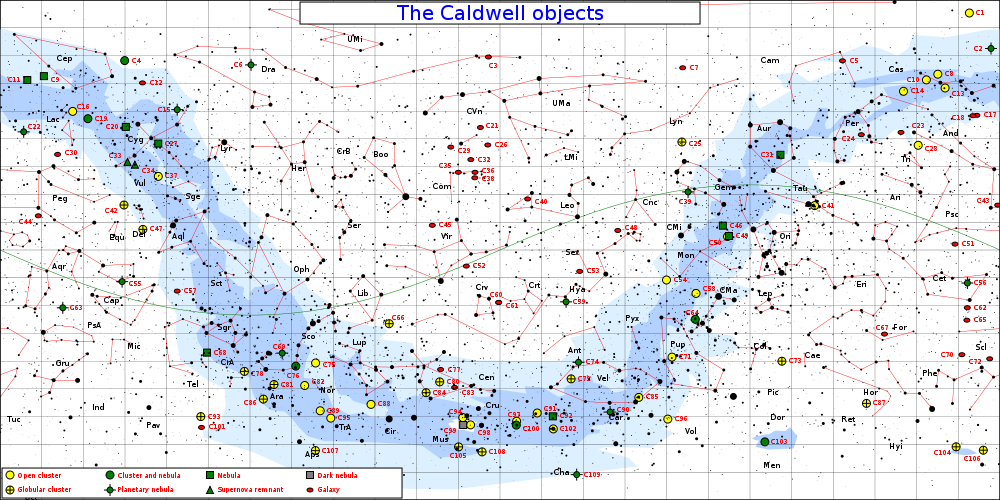
The Caldwell catalogue is an astronomical catalogue of 109 star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies for observation by amateur astronomers. The list was compiled by Patrick Moore as a complement to the Messier catalogue. [1]
Contents
- Reception
- Caldwell star chart
- Number of objects by type in the Caldwell catalogue
- Caldwell objects
- See also
- References
- External links
While the Messier catalogue is used by amateur astronomers as a list of deep-sky objects for observation, Moore noted that Messier's list was not compiled for that purpose and excluded many of the sky's brightest deep-sky objects, [1] such as the Hyades, the Double Cluster (NGC 869 and NGC 884), and the Sculptor Galaxy (NGC 253). The Messier catalogue was actually compiled as a list of known objects that might be confused with comets. Moore also observed that since Messier compiled his list from observations in Paris, it did not include bright deep-sky objects visible in the Southern Hemisphere, such as Omega Centauri, Centaurus A, the Jewel Box, and 47 Tucanae. [1] [2] Moore compiled a list of 109 objects to match the commonly accepted number of Messier objects (he excluded M110 [3] ), and the list was published in Sky & Telescope in December 1995. [3]
Moore used his other surname – Caldwell – to name the list, since the initial of "Moore" is already used for the Messier catalogue. [1] [4] Entries in the catalogue are designated with a "C" and the catalogue number (1 to 109).
Unlike objects in the Messier catalogue, which are listed roughly in the order of discovery by Messier and his colleagues, [5] the Caldwell catalogue is ordered by declination, with C1 being the most northerly and C109 being the most southerly, [1] although two objects (NGC 4244 and the Hyades) are listed out of sequence. [1] Other errors in the original list have since been corrected: it incorrectly identified the S Norma Cluster (NGC 6087) as NGC 6067 and incorrectly labelled the Lambda Centauri Cluster (IC 2944) as the Gamma Centauri Cluster. [1]