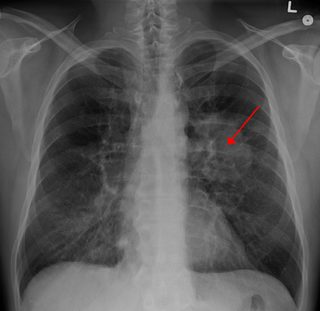
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant tumor that begins in the lung. Lung cancer is caused by genetic damage to the DNA of cells in the airways, often caused by cigarette smoking or inhaling damaging chemicals. Damaged airway cells gain the ability to multiply unchecked, causing the growth of a tumor. Without treatment, tumors spread throughout the lung, damaging lung function. Eventually lung tumors metastasize, spreading to other parts of the body.

A brain tumor occurs when abnormal cells form within the brain. There are two main types of tumors: malignant tumors and benign (non-cancerous) tumors. These can be further classified as primary tumors, which start within the brain, and secondary tumors, which most commonly have spread from tumors located outside the brain, known as brain metastasis tumors. All types of brain tumors may produce symptoms that vary depending on the size of the tumor and the part of the brain that is involved. Where symptoms exist, they may include headaches, seizures, problems with vision, vomiting and mental changes. Other symptoms may include difficulty walking, speaking, with sensations, or unconsciousness.

Prostate cancer is the uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Early prostate cancer causes no symptoms. Most cases are detected after screening tests – typically blood tests for levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) – indicate unusual growth of prostate tissue. Diagnosis requires a biopsy of the prostate. If cancer is present, the pathologist assigns a Gleason score, with a higher score representing a more dangerous tumor. Medical imaging is performed to look for cancer that has spread outside the prostate. Based on the Gleason score, PSA levels, and imaging results, a cancer case is assigned a stage 1 to 4. Higher stage signifies a more advanced, more dangerous disease.

Testicular cancer is cancer that develops in the testicles, a part of the male reproductive system. Symptoms may include a lump in the testicle or swelling or pain in the scrotum. Treatment may result in infertility.

A bone tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in bone, traditionally classified as noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). Cancerous bone tumors usually originate from a cancer in another part of the body such as from lung, breast, thyroid, kidney and prostate. There may be a lump, pain, or neurological signs from pressure. A bone tumor might present with a pathologic fracture. Other symptoms may include fatigue, fever, weight loss, anemia and nausea. Sometimes there are no symptoms and the tumour is found when investigating another problem.

Pleurisy, also known as pleuritis, is inflammation of the membranes that surround the lungs and line the chest cavity (pleurae). This can result in a sharp chest pain while breathing. Occasionally the pain may be a constant dull ache. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, fever, or weight loss, depending on the underlying cause. Pleurisy can be caused by a variety of conditions, including viral or bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, and pulmonary embolism.

Pancreatic cancer arises when cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a mass. These cancerous cells have the ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of pancreatic cancer are known.

Uterine cancer, also known as womb cancer, includes two types of cancer that develop from the tissues of the uterus. Endometrial cancer forms from the lining of the uterus, and uterine sarcoma forms from the muscles or support tissue of the uterus. Endometrial cancer accounts for approximately 90% of all uterine cancers in the United States. Symptoms of endometrial cancer include changes in vaginal bleeding or pain in the pelvis. Symptoms of uterine sarcoma include unusual vaginal bleeding or a mass in the vagina.
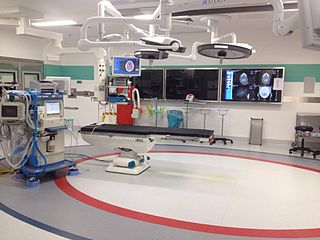
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement, and angioplasty of narrowed structures.

Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism. Ischemia is generally caused by problems with blood vessels, with resultant damage to or dysfunction of tissue i.e. hypoxia and microvascular dysfunction. It also implies local hypoxia in a part of a body resulting from constriction. Ischemia causes not only insufficiency of oxygen, but also reduced availability of nutrients and inadequate removal of metabolic wastes. Ischemia can be partial or total blockage. The inadequate delivery of oxygenated blood to the organs must be resolved either by treating the cause of the inadequate delivery or reducing the oxygen demand of the system that needs it. For example, patients with myocardial ischemia have a decreased blood flow to the heart and are prescribed with medications that reduce chronotrophy and ionotrophy to meet the new level of blood delivery supplied by the stenosed vasculature so that it is adequate.
A VIPoma or vipoma is a rare endocrine tumor that overproduces vasoactive intestinal peptide. The incidence is about 1 per 10,000,000 per year. VIPomas usually originate from the non-β islet cells of the pancreas. They are sometimes associated with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Roughly 50–75% of VIPomas are malignant, but even when they are benign, they are problematic because they tend to cause a specific syndrome: the massive amounts of VIP cause a syndrome of profound and chronic watery diarrhea and resultant dehydration, hypokalemia, achlorhydria, acidosis, flushing and hypotension, hypercalcemia, and hyperglycemia. This syndrome is called Verner–Morrison syndrome (VMS), WDHA syndrome, or pancreatic cholera syndrome (PCS). The eponym reflects the physicians who first described the syndrome.
Pancreatic diseases are diseases that affect the pancreas, an organ in most vertebrates and in humans and other mammals located in the abdomen. The pancreas plays a role in the digestive and endocrine system, producing enzymes which aid the digestion process and the hormone insulin, which regulates blood sugar levels. The most common pancreatic disease is pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas which could come in acute or chronic form. Other pancreatic diseases include diabetes mellitus, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, cystic fibrosis, pseudocysts, cysts, congenital malformations, tumors including pancreatic cancer, and hemosuccus pancreaticus.

Nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), or nasopharynx cancer, is the most common cancer originating in the nasopharynx, most commonly in the postero-lateral nasopharynx or pharyngeal recess, accounting for 50% of cases. NPC occurs in children and adults. NPC differs significantly from other cancers of the head and neck in its occurrence, causes, clinical behavior, and treatment. It is vastly more common in certain regions of East Asia and Africa than elsewhere, with viral, dietary and genetic factors implicated in its causation. It is most common in males. It is a squamous cell carcinoma of an undifferentiated type. Squamous epithelial cells are a flat type of cell found in the skin and the membranes that line some body cavities. Undifferentiated cells are cells that do not have their mature features or functions.
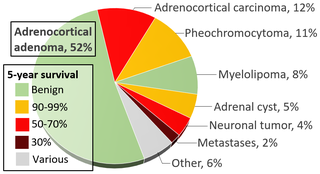
An adrenal tumor or adrenal mass is any benign or malignant neoplasms of the adrenal gland, several of which are notable for their tendency to overproduce endocrine hormones. Adrenal cancer is the presence of malignant adrenal tumors, and includes neuroblastoma, adrenocortical carcinoma and some adrenal pheochromocytomas. Most adrenal pheochromocytomas and all adrenocortical adenomas are benign tumors, which do not metastasize or invade nearby tissues, but may cause significant health problems by unbalancing hormones.

Leptomeningeal cancer is a rare complication of cancer in which the disease spreads from the original tumor site to the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord. This leads to an inflammatory response, hence the alternative names neoplastic meningitis (NM), malignant meningitis, or carcinomatous meningitis. The term leptomeningeal describes the thin meninges, the arachnoid and the pia mater, between which the cerebrospinal fluid is located. The disorder was originally reported by Eberth in 1870. It is also known as leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, leptomeningeal disease (LMD), leptomeningeal metastasis, meningeal metastasis and meningeal carcinomatosis.
Ovarian diseases refer to diseases or disorders of the ovary.
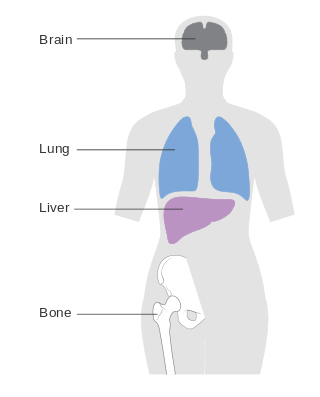
Metastatic breast cancer, also referred to as metastases, advanced breast cancer, secondary tumors, secondaries or stage IV breast cancer, is a stage of breast cancer where the breast cancer cells have spread to distant sites beyond the axillary lymph nodes. There is no cure for metastatic breast cancer; there is no stage after IV.
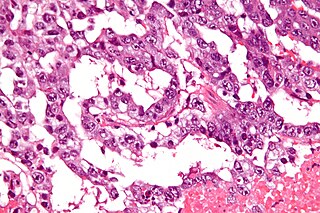
An extracranial germ cell tumor (EGCT) occurs in the abnormal growth of germ cells in the gonads and the areas other than the brain via tissue, lymphatic system, or circulatory system. The tumor can be benign or malignant (cancerous) by its growth rate. According to the National Cancer Institute and St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, the chance of children who are under 15 years old having EGCTs is 3%, in comparison to adolescents, a possibility of 14% with aged 15 to 19 can have EGCTs. There is no obvious cut point in between children and adolescents. However, common cut points in researches are 11 years old and 15 years old.
A central nervous system tumor is an abnormal growth of cells from the tissues of the brain or spinal cord. CNS tumor is a generic term encompassing over 120 distinct tumor types. Common symptoms of CNS tumors include vomiting, headache, changes in vision, nausea, and seizures. A CNS tumor can be detected and classified via neurological examination, medical imaging, such as x-ray imaging, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT), or after analysis of a biopsy.
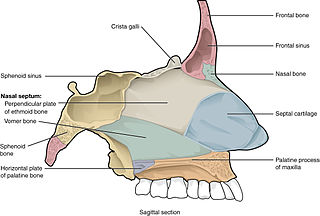
Paranasal sinus and nasal cavity cancer is a type of cancer that is caused by the appearance and spread of malignant cells into the paranasal sinus and nasal cavity. The cancer most commonly occurs in people between 50 and 70 years old, and occurs twice as often in males as in females. During early phases of the cancer, symptoms may include nasal obstruction and hyposmia, as well as other symptoms. More symptoms may develop as malignant cells further grow and spread into other nearby tissue such as the palate or orbital floor. X-rays of the head and MRI can aid in diagnosis of the cancer while tumor resection surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy can be used for treatment of the cancer.
















