
Canada Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the northern dock system in Kirkdale. Canada Dock consists of a main basin nearest the river wall with three branch docks and a graving dock to the east. It is connected to Brocklebank Dock to the north and Huskisson Dock to the south.

Salisbury Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the northern dock system in Vauxhall and is connected to Nelson Dock to the north, Trafalgar Dock to the south and inland to Collingwood Dock.

Collingwood Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, in England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the northern dock system in Vauxhall, and is connected to Stanley Dock to the east and Salisbury Dock to the west.

Stanley Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the Vauxhall area of Liverpool and is part of the northern dock system. The dock is connected to the Leeds and Liverpool Canal to the east and Collingwood Dock to the west.

Trafalgar Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, in England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the northern dock system in Vauxhall and connected to Salisbury Dock to the north. The sites of two former docks are located in the vicinity; Victoria Dock was located to the south and Clarence Dock to the east.

Waterloo Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the northern dock system in Vauxhall and connected to Princes Half Tide Dock to the south. The site of Victoria Dock is located to the north.

Prince's Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is the most southerly of the docks situated in the northern part of the Liverpool dock system, connected to Prince's Half-Tide Dock to the north. The dock is now in the buffer zone to one of Liverpool's World Heritage Sites.

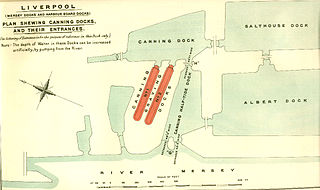
Salthouse Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the southern dock system, connected to Canning Dock to the north, Wapping Dock via Wapping Basin to the south and Albert Dock to the west.

Wapping Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the southern dock system, connected to Salthouse Dock to the north, Queen's Dock to the south. King's Dock was originally located to the west, but has since been filled in.

Queen's Dock is a dock on the River Mersey and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the southern dock system, connected to Wapping Dock to the north and Coburg Dock to the south.

Coburg Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, in England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the southern dock system, connected to Queens Dock to the north, Brunswick Dock to the south.

Brunswick Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, in England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the southern dock system, connected to Coburg Dock to the north, Toxteth Dock to the south.

Harrington Dock was a dock on the River Mersey and part of the Port of Liverpool. Situated in the southern dock system, it was connected to Toxteth Dock to the north and Herculaneum Dock to the south.

Duke's Dock is a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. It is in the southern dock system, connected to Salthouse Dock and Wapping Dock to the east. The Albert Dock is located immediately north, although not directly accessible by water.

Manchester Dock was a dock on the River Mersey in England and a part of the Port of Liverpool. The dock was not part of the interconnected dock system, but was connected directly to the river.

Canning Half Tide Dock on the River Mersey, in Liverpool, England, is a half tide dock and is part of the Port of Liverpool. It is situated in the southern dock system, connected to Canning Dock to the east and Albert Dock to the south.

George's Dock was a dock, on the River Mersey, England, within the Port of Liverpool. It was connected to Canning Dock to the south and George's Basin to the north.
The George's Basin was a dock on the River Mersey, England, within the Port of Liverpool. The basin surface covered 3 acres (1.2 ha) and was surrounded by George's Dock to the south, Prince's Dock to the north and the Mersey to the west.

Sandon Dock was a dock on the River Mersey, England, and part of the Port of Liverpool. Situated in the northern dock system, it was east of Sandon Half Tide Dock, to which it was once connected.
Chester Basin was a tidal basin on the River Mersey, in Liverpool, England. The basin was situated between the Pier Head and Manchester Dock.





















