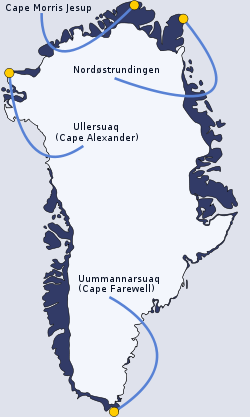
Cape Farewell Nunap Isua, Kap Farvel | |
|---|---|
| Coordinates: 59°46′23″N43°55′21″W / 59.77306°N 43.92250°W | |
| Location | Kujalleq, Greenland |
| Offshore water bodies | North Atlantic Ocean |
| Area | |
| • Total | Arctic |
Cape Farewell (Greenlandic : Nunap Isua; [1] Danish : Kap Farvel) [2] is a headland on the southern shore of Egger Island, Nunap Isua Archipelago, Greenland. As the southernmost point of the country, it is one of the important landmarks of Greenland.