Related Research Articles
This is a list of the extreme points of Asia, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location on the continent.
The extreme points of South America are the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location on the continent. The continent's southernmost point is often said to be Cape Horn, but Águila Islet of the Diego Ramírez Islands lies further south.
This is a list of the extreme points of The Americas, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location on the continent. The continent's southernmost point is often said to be Cape Horn, which is the southernmost point of the Chilean islands. The Americas cross 134° of longitude east to west and 124° of latitude north to south.
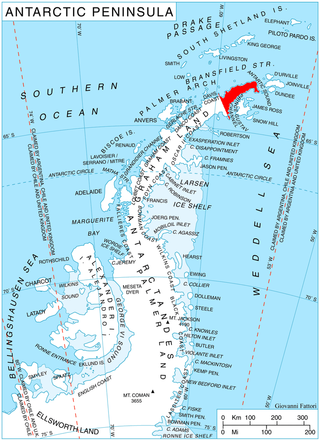
Trinity Peninsula is the northernmost part of the Antarctic Peninsula. It extends northeastward for about 130 km (80 mi) to Cape Dubouzet from an imaginary line connecting Cape Kater on the north-west coast and Cape Longing on the south-east coast. Prime Head is the northernmost point of this peninsula. Some 20 kilometers southeast of Prime Head is Hope Bay with the year-round Argentinian Esperanza Base.
The Welcome Islands are a small rocky archipelago to the north of the main island of South Georgia. They are to the east of Bird Island.
Cape Harcourt is a headland on the eastern extremity of Harcourt Island on the north coast of South Georgia, forming the north side of the entrance to Royal Bay. The name dates back to at least 1920 and is now well established. Sacramento Bight lies on the coast between Cape Harcourt and Calf Head.

Cape Buller is a rugged headland forming the west side of the entrance to the Bay of Isles on the north coast of South Georgia. It was discovered and named in 1775 by a British expedition under James Cook.
You may be looking for Undine South Harbour near Ducloz Head, South Georgia

The Bay of Isles is a bay 9 miles (14 km) wide and receding 3 miles (5 km), lying between Cape Buller and Cape Wilson along the north coast of South Georgia. It was discovered in 1775 by a British expedition under James Cook and so named by him because numerous islands lie in the bay. Of South Georgia's 31 breeding bird species, 17 are found here.

Murchison Promontory, a cape (promontory) in the northern Canadian Arctic, is the northernmost mainland point of the Americas and of Canada. Located 1,087 nautical miles from the North Pole, it is 64 km (40 mi) farther north than Point Barrow, Alaska, the northernmost point of all U.S. territory.
Prevot Island is a small rocky island 0.5 nautical miles (0.9 km) northeast of Miller Island, forming the northernmost of the Wauwermans Islands, in the Wilhelm Archipelago. The name was approved by the Argentine geographic coordinating committee in 1956, replacing the provisional toponym "Fernando." Named in memory of First Lieutenant Prevot, commander of the mobile detachment in the operations of the Argentine Air Force unit for Antarctica. He died on active duty.

The borders of the oceans are the limits of Earth's oceanic waters. The definition and number of oceans can vary depending on the adopted criteria. The principal divisions of the five oceans are the Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean, Indian Ocean, Southern (Antarctic) Ocean, and Arctic Ocean. Smaller regions of the oceans are called seas, gulfs, bays, straits, and other terms. Geologically, an ocean is an area of oceanic crust covered by water.
Cape Dalton is a point marking the southeast end of a snow-covered island, located 1 nautical mile (2 km) north of Abrupt Point on the western side of Edward VIII Bay. It was first mapped by Norwegian cartographers from air photos taken by the Lars Christensen Expedition (1936–37) and, though not specifically named on the map, the point appears to have been included as part of two larger features called "Skutenes" and "Skutenesmulen." Skutenes was subsequently mapped by Australian National Antarctic Research Expeditions (ANARE) as two snow-covered islands, making this descriptive name and Skutenesmulen, a derivative, inappropriate. ANARE named the point Cape Dalton for R.F.M. Dalton, officer in charge of ANARE work at Macquarie Island, 1953.
Harcourt Island is a small island at the north side of the entrance to Royal Bay, South Georgia. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1971 after Cape Harcourt, the easternmost point of this island.

Hole Rock is the largest of several rocks lying close north of North Foreland, the northeast cape of King George Island, in the South Shetland Islands. It was charted in 1937 by Discovery Investigations personnel on the Discovery II and so named because a conspicuous hole extends through it.
References
 This article incorporates public domain material from "North, Cape". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "North, Cape". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.