
Karaganda or Qaraghandy is the capital of Karaganda Region in the Republic of Kazakhstan. It is the fourth most populous city in Kazakhstan, behind Almaty (Alma-Ata), Nur-Sultan and Shymkent. Population: 497,777 ; 459,778 ; 436,864 . Karaganda is approximately 230 km south-east of Kazakhstan's capital Nur-Sultan.

Caragana is a genus of about 80–100 species of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae, native to Asia and eastern Europe.

Caragana arborescens, the Siberian peashrub, Siberian pea-tree, or caragana, is a species of legume native to Siberia and parts of China and neighboring Mongolia and Kazakhstan. It was taken to the United States by Eurasian immigrants, who used it as a food source while travelling west. In some areas of the United States it is considered an invasive species.

Achnatherum is a genus of plants which includes several species of needlegrass. Several needlegrass species have been switched between Achnatherum and genus Stipa; taxonomy between the two closely related genera is still uncertain.

Halimodendron is a monotypic genus of legume containing the single species Halimodendron halodendron, which is known by several common names, including common salt tree and Russian salt tree. It is closely related to the genus Caragana. It is native to Russia and southern Asia, but it can be found on other continents where it is an introduced species, and one that is often a noxious weed. This is a deciduous spiny shrub sprawling to a few meters in maximum width and up to three meters tall. Stems branch from the base and bear clusters of about four leaflets on sharp spurs. The ends of branches narrow to spines. Flowers also appear at the ends of spurs in clusters of two to four pink pealike blossoms each one to two centimeters wide. The fruit is a black woody inflated pod about 2 centimeters long containing legume seeds. The plant has a deep and wide root system, with the lateral roots sending up new shoots. In this manner the plant forms extensive thickets. When introduced to an area of suitable climate, such as California where it is a known weed, it can invade cultivated land and spread relatively quickly. It is tolerant of saline soils.
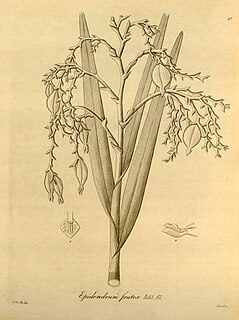
Epidendrum frutex is a high-altitude species of reed-stemmed Epidendrum orchid native to Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela.

α-Viniferin is a stilbene trimer. It can be isolated from Caragana chamlagu and from Caragana sinica and from the stem bark of Dryobalanops aromatica. It is also present in relation to resistance to Botrytis cinerea and Plasmopara viticola in Vitis vinifera and Vitis riparia.
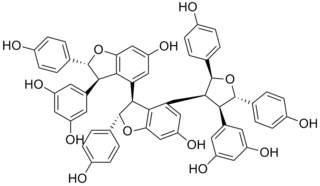
Kobophenol A is a stilbenoid. It is a tetramer of resveratrol. It can be isolated from Caragana chamlagu, from Caragana sinica and from Carex folliculata seeds.

The Northwestern Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of the elevations of the northwestern Himalaya of China, India, and Pakistan.

Neolycaena rhymnus is a butterfly of the family Lycaenidae. It is found from Ukraine and southern and central Russia to the southern Ural mountains, Zauralye, the western and southern Altai Region, the Sayan mountains and Kazakhstan. Seitz gives this description - T. rhymnus Ev.. Tailless, the wings brown above and beneath. The underside irrorated with numerous white short dashes, which are partly placed in rows and partly irregularly dispersed. — In South Russia, South Siberia to the Altai, in May and June, on steppes.

Caragana pygmaea is a flowering plant species in the genus Caragana.
The Montana Arboretum and Gardens are located on the Montana State University campus in Bozeman, Montana. The Arboretum proper is located at the northwestern corner of campus by the intersection of West College Avenue and South 11th Avenue, but plantings occur throughout campus.
Athrips aquila is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It is found in Russia and south-eastern Kazakhstan. The habitat consists of steppes with dominant shrubs such as Spiraea crenata, Spiraea hypericifolia, Caragana frutex and Cotoneaster melanocarpus.
Athrips stepposa is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It is found in Ukraine, Russia, north-western Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan.
Anacolosa frutescens, also known as galo or galonut, is a plant in the family Olacaceae. The specific epithet frutescens is from the Latin frutex meaning "shrub". It produces edible fruits and nuts eaten in the Philippines.
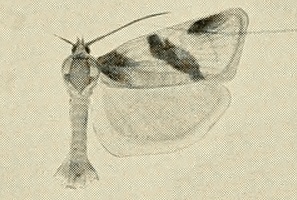
Clepsis praeclarana is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in Russia, Kazakhstan, Georgia, Kyrgyzstan and Mongolia.
Quercus frutex is a species of plant in the family Fagaceae. It is endemic to central Mexico, found in México State, D.F., Tlaxcala, Hidalgo, Jalisco, Puebla, and Oaxaca.

Micrurapteryx caraganella is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is found in Siberia, and possibly Tajikistan and the Russian Far East.

The East European forest steppe ecoregion is a patchwork of broadleaf forest stands and grasslands (steppe) that stretches 2,100 km across eastern Europe from the Ural Mountains in Ural, through Povolzhye, Central Russia to the middle of Ukraine.There are also isolated areas of similar character off the western end in eastern Romania, Moldova, and Bulgaria. The region forms a transition zone between the temperate forests to the north, and the steppe to the south. The forest-steppe is an area of Russia in which precipitation and evaporation are approximately equal. The ecoregion is in the Palearctic realm, with a Humid Continental climate. It covers 727,269 km2 (280,800 sq mi).














