Related Research Articles
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period 358.9 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, 298.9 million years ago. The name Carboniferous means "coal-bearing", from the Latin carbō ("coal") and ferō, and refers to the many coal beds formed globally during that time.

Edward Oscar Ulrich was an invertebrate paleontologist specializing in the study of Paleozoic fossils.

The Visean, Viséan or Visian is an age in the ICS geologic timescale or a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is the second stage of the Mississippian, the lower subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Visean lasted from 346.7 to 330.9 Ma. It follows the Tournaisian age/stage and is followed by the Serpukhovian age/stage.
The Serpukhovian is in the ICS geologic timescale the uppermost stage or youngest age of the Mississippian, the lower subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Serpukhovian age lasted from 330.9 Ma to 323.2 Ma. It is preceded by the Visean and is followed by the Bashkirian. The Serpukhovian correlates with the lower part of the Namurian Stage of European stratigraphy and the middle and upper parts of the Chesterian Stage of North American stratigraphy.
The Kasimovian is a geochronologic age or chronostratigraphic stage in the ICS geologic timescale. It is the third stage in the Pennsylvanian, lasting from 307 to 303.7 Ma. The Kasimovian Stage follows the Moscovian and is followed by the Gzhelian. The Kasimovian saw an extinction event which occurred around 305 mya, referred to as the Carboniferous Rainforest Collapse. It roughly corresponds to the Missourian in North American geochronology and the Stephanian in western European geochronology.

Helenodora is an extinct onychophoran genus known from the Carboniferous Carbondale Formation of Illinois. The only known species described is H. inopinata.

Strophomenida is an extinct order of articulate brachiopods which lived from the lower Ordovician period to the mid-Carboniferous period. Strophomenida is part of the extinct class Strophomenata, and was the largest known order of brachiopods, encompassing over 400 genera. Some of the largest and heaviest known brachiopod species belong to this class. Strophomenids were among the most diverse and abundant brachiopods during the Ordovician, but their diversity was strongly impacted at the Late Ordovician mass extinction. Survivors rediversified into new morphologies in the Silurian, only to be impacted once again at the Late Devonian mass extinction. They finally died out in the Carboniferous period.
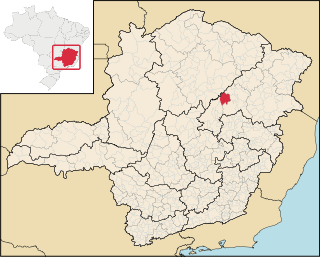
Carbonita is a municipality in the northeast of the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais. As of 2020 the population was 9,414 in a total area of 1,454 km2. The elevation of the town center is 751 meters. It is part of the IBGE statistical meso-region of Jequitinhonha and the micro-region of Capelinha. It became a municipality in 1963.
Letognathus is a genus of rhizodont tetrapodomorph that lived during the Carboniferous period. Its remains come from the Blue Beach Member of the Horton Bluff Formation, near Hantsport, Nova Scotia. Like most rhizodonts, it was of relatively large size, had a large recurved fang at the symphysis of the lower jaw, and a row of three coronoid fangs along the length of the jaw in addition to its marginal dentition. Letognathus is important for rhizodont systematics because it retains a number of primitive features, such as ossified Meckel's cartilage, are not found in the genera Rhizodus and Strepsodus.
Cytherellidae is a family of ostracods, and is the only living family in the order, Platycopida, although the family Punciidae is also sometimes included. Members of the family have existed since the Jurassic. It contains 6 genera:

Cyprididae is "the most diverse group of freshwater ostracods". It contains 1000 species, which represents 50% of the known species of freshwater ostracods. Around 60% of genera in the family are endemic to a single zoogeographic region. The family contains 25 subfamilies, and is most diverse in the Afrotropical realm, with over 300 species in 45 genera. Many Cyprididae occur in temporary water bodies and have drought-resistant eggs, mixed/parthenogenetic reproduction and ability to swim. These biological attributes pre-adapt them to form successful radiations in these habitats. Bennelongia is an interesting genus of the family Cyprididae. It may be the last true descendant genus of the Mesozoic lineage of Cypridea, which was a dominant lineage of ostracod in non-marine waters in the Cretaceous.
Fish egg fossils are the fossilized remains of fish eggs. Fossil fish eggs have an extensive record going at least as far back as the Devonian and spanning into the Cenozoic era. The eggs of many different fish taxa have contributed to this record, including lobe-finned fish, placoderms, and sharks. Occasionally eggs are preserved still within the mother's body, or associated with fossil embryos. Some fossil eggs possibly laid by fish cannot be confidently distinguished from those laid by amphibians; for example, the ichnogenus Mazonova is known from impressions of eggs which resemble eggs of both fish and amphibians. Paleontologist B.K. Hall has observed that the discovery of fossil fish eggs, embryos and larvae link the sciences of paleontology with evo-devo.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2016 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods of every kind that have been described during the year 2016, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to arthropod paleontology that occurred in the year 2016.
Alternognathus is an extinct conodont genus in the family Elictognathidae. An extensive study on its population dynamics and lifespan has recently been published.
Quasillites is a fossil genus of ostracod from the Devonian and Carboniferous Periods.
Candona is a genus of ostracods in the family Candonidae.
Betty Kellett Nadeau (1906-?) was an American paleontologist and micro-paleontologist who studied Palaeozoic ostracod. Numerous marine species were discovered due to the work she had done throughout her fruitful career. This work is evident to the genus Bekena named after her.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2018 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids, and other fossil arthropods of every kind that were described during the year 2018, as well as other significant discoveries, and events related to arthropod paleontology that are scheduled to occur in the year 2018.

Amphissites is an extinct genus of ostracod belonging to the suborder Beyrichicopina and family Amphissitinae. Species belonging to the genus lived from the Devonian to the Permian in Europe, North America, Australia, and east Asia. The genus were likely deposit-feeders, and may have survived briefly into the Triassic.
Polytylites is an extinct genus of ostracod belonging to the order Palaeocopida and family Amphissitidae. Specimens have been found in beds of Carboniferous to Permian age in North America and Asia.
References
- 1 2 Julie B. Retrum & Roger L. Kaesler (2005). "Early Permian Carbonitidae (Ostracoda): ontogeny, affinity, environment and systematics" (PDF). Journal of Micropalaeontology . 24 (2): 179–190. doi: 10.1144/jm.24.2.179 . S2CID 46953008.
- Carboniferous Ostracoda, the Genus Carbonita Strand. FW Anderson, 1970
- Quantitative analysis of dimorphism in Carbonita humilis (Jones and Kirkby). MJM Bless, JE Pollard, American Bulletin of Paleontology, 1975