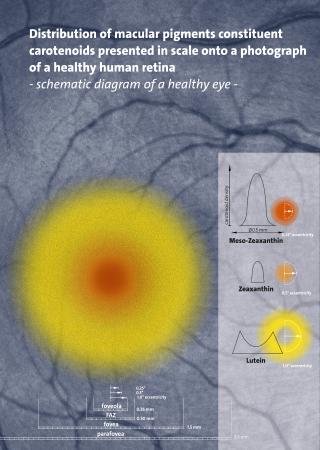
Carotenoids are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Over 1,100 identified carotenoids can be further categorized into two classes – xanthophylls and carotenes.

Carotenoid oxygenases are a family of enzymes involved in the cleavage of carotenoids to produce, for example, retinol, commonly known as vitamin A. This family includes an enzyme known as RPE65 which is abundantly expressed in the retinal pigment epithelium where it catalyzed the formation of 11-cis-retinol from all-trans-retinyl esters.

The acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme is a protein found in plants and micro-organisms. ALS catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of the branched-chain amino acids.

In enzymology, beta-carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase, (EC 1.13.11.63) is an enzyme with systematic name beta-carotene:oxygen 15,15'-dioxygenase (bond-cleaving). In human it is encoded by the BCDO2 gene. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
In enzymology, a leucocyanidin oxygenase (EC 1.14.11.19) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Apo-beta-carotenoid-14',13'-dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.67 is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Beta-apo-4'-carotenal oxygenase (EC 1.2.1.82, beta-apo-4'-carotenal dehydrogenase, YLO-1, carD (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 4'-apo-beta,psi-carotenal:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:

15-cis-phytoene desaturases, are enzymes involved in the carotenoid biosynthesis in plants and cyanobacteria. Phytoene desaturases are membrane-bound enzymes localized in plastids and introduce two double bonds into their colorless substrate phytoene by dehydrogenation and isomerize two additional double bonds. This reaction starts a biochemical pathway involving three further enzymes called the poly-cis pathway and leads to the red colored lycopene. The homologous phytoene desaturase found in bacteria and fungi (CrtI) converts phytoene directly to lycopene by an all-trans pathway.
9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.51, nine-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase, NCED, AtNCED3, PvNCED1, VP14) is an enzyme in the biosynthesis of abscisic acid (ABA), with systematic name 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid 11,12-dioxygenase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
8'-apo-beta-carotenoid 14',13'-cleaving dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.67) is an enzyme with systematic name 8'-apo-beta-carotenol:O2 oxidoreductase (14',13'-cleaving). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
9-cis-beta-carotene 9',10'-cleaving dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.68, CCD7 (gene), MAX3 (gene), NCED7 (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 9-cis-beta-carotene:O2 oxidoreductase (9',10'-cleaving). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
All-trans-10'-apo-beta-carotenal 13,14-cleaving dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.70, CCD8 (gene), MAX4 (gene), NCED8 (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name all-trans-10'-apo-beta-carotenal:O2 oxidoreductase (13,14-cleaving). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Carotenoid-9',10'-cleaving dioxygenase (EC 1.13.11.71, BCO2 (gene), beta-carotene 9',10'-monooxygenase (misleading)) is an enzyme with systematic name all-trans-beta-carotene:O2 oxidoreductase (9',10'-cleaving). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Beta-carotene 3-hydroxylase (EC 1.14.13.129, beta-carotene 3,3'-monooxygenase, CrtZ) is an enzyme with systematic name beta-carotene,NADH:oxygen 3-oxidoreductase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
All-trans-8'-apo-beta-carotenal 15,15'-oxygenase (EC 1.14.99.41, Diox1, ACO, 8'-apo-beta-carotenal 15,15'-oxygenase) is an enzyme with systematic name all-trans-8'-apo-beta-carotenal:oxygen 15,15'-oxidoreductase (bond-cleaving). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Very-long-chain 3-oxoacyl-CoA synthase (EC 2.3.1.199, very-long-chain 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase, very-long-chain beta-ketoacyl-CoA synthase, condensing enzyme, CUT1 (gene), CERS6 (gene), FAE1 (gene), KCS (gene), ELO (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name malonyl-CoA:very-long-chain acyl-CoA malonyltransferase (decarboxylating and thioester-hydrolysing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Ditrans,polycis-polyprenyl diphosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name (2E,6E)-farnesyl-diphosphate:isopentenyl-diphosphate cistransferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Beta-carotene isomerase is an enzyme with systematic name beta-carotene 9-cis-all-trans isomerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Lupeol synthase is an enzyme with systematic name (3S)-2,3-epoxy-2,3-dihydrosqualene mutase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Strigolactones are a group of chemical compounds produced by roots of plants. Due to their mechanism of action, these molecules have been classified as plant hormones or phytohormones. So far, strigolactones have been identified to be responsible for three different physiological processes: First, they promote the germination of parasitic organisms that grow in the host plant's roots, such as Strigalutea and other plants of the genus Striga. Second, strigolactones are fundamental for the recognition of the plant by symbiotic fungi, especially arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, because they establish a mutualistic association with these plants, and provide phosphate and other soil nutrients. Third, strigolactones have been identified as branching inhibition hormones in plants; when present, these compounds prevent excess bud growing in stem terminals, stopping the branching mechanism in plants.







