
Sophora is a genus of about 45 species of small trees and shrubs in the pea family Fabaceae. The species have a pantropical distribution. The generic name is derived from sophera, an Arabic name for a pea-flowered tree.

Viminaria juncea is the single species in the genus Viminaria endemic to Australia. The genus is in the pea family Fabaceae. It is colloquially known as native broom after its resemblance to the related European broom plants. The Noongar peoples know the plant as koweda.

Carmichaelia is a genus of 24 plant species belonging to Fabaceae, the legume family. All but one species are native to New Zealand; the exception, Carmichaelia exsul, is native to Lord Howe Island and presumably dispersed there from New Zealand.

Clianthus puniceus, common name kaka beak, is a species of flowering plant in the genus Clianthus of the legume family Fabaceae, native to New Zealand's North Island.

Grevillea juniperina, commonly known as juniper- or juniper-leaf grevillea or prickly spider-flower, is a plant of the family Proteaceae native to eastern New South Wales and southeastern Queensland in Australia. Scottish botanist Robert Brown described the species in 1810, and seven subspecies are recognised. One subspecies, G. j. juniperina, is restricted to Western Sydney and environs and is threatened by loss of habitat and housing development.

Damnamenia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asteraceae.

Pittosporum kirkii is a glabrous evergreen perennial shrub that reaches up to 5 metres (16 ft) in height and possesses distinctive coriaceous, fleshy, thick leaves. It is one of four shrubs endemic to New Zealand that frequently displays an epiphytic lifestyle. P. kirkii is commonly epiphytic, perched amongst nest epiphytes in the canopies of emergent or canopy trees in old-growth forest; however, it can be observed occasionally growing on the ground or over rocks. Kirk first observed P. kirkii on Great Barrier Island. It was described by Joseph Dalton Hooker from material collected by Thomas Kirk, possibly from the Thames Goldfields, and published in 1869. The initial brief description titled Pittosporum n. sp.? by Thomas Kirk was published in his paper on Great Barrier Island in 1868. This description along with herbarium specimens were sent to Dr. J. D Hooker at Kew Gardens in 1868, and he collaborated to name it after T. Kirk, by giving it the specific epithet kirkii within the publication that was otherwise written by Kirk.

Carmichaelia stevensonii, the cord broom or weeping broom, is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in the north east of the South Island of New Zealand. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Carmichaelia muritai, common name coastal tree broom, is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in the South Island of New Zealand.

Carmichaelia exsul is a flowering plant in the legume family. It is the only species of the genus Carmichaelia found in Australia. The specific epithet means an exile, with reference to it being the only species in its genus native outside New Zealand.

Fuchsia procumbens is a prostrate shrub that is endemic to coastal areas of the North Island of New Zealand. Common names include creeping fuchsia, climbing fuchsia or trailing fuchsia.

Carmichaelia petriei is a species of New Zealand broom in the genus Carmichaelia. It is endemic to New Zealand. C. petrieis is possibly a host plant for the critically endangered fungus weevil Cerius otagensis.

Dysphania pusilla, formerly Chenopodium pusillum, otherwise known as pygmy goosefoot or parahia in Māori, is a prostrate herb endemic to the north-eastern parts of South Island, New Zealand. Presumed extinct after 56 years without recorded observations, the species was rediscovered in 2015.

Dracophyllum arboreum, commonly known as Chatham Island grass tree and tarahinau (Moriori), is a species of tree in the heath family Ericaceae. Endemic to the Chatham Islands of New Zealand, it reaches a height of 18 m (60 ft) and has leaves that differ between the juvenile and adult forms.

Carmichaelia appressa is a species of pea in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in the South Island of New Zealand. Its conservation status (2018) is "At Risk - Naturally Uncommon" under the New Zealand Threat Classification System.
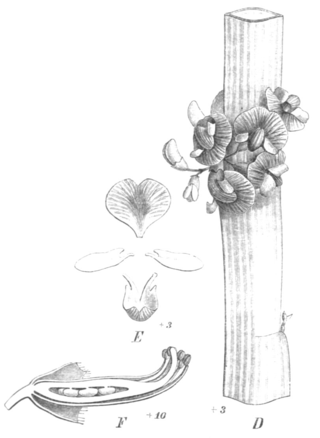
Carmichaelia australis, or common broom, is a species of pea in the family Fabaceae. It is native to New Zealand and found in both the North and South Islands. Its conservation status (2018) is "Not Threatened" under the New Zealand Threat Classification System.

Carmichaelia hollowayi is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found only in the South Island of New Zealand. Its conservation status (2018) is "Nationally Critical" under the New Zealand Threat Classification System.

Carmichaelia nana is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found in both the North and South Islands of New Zealand. Its conservation status in 2013 was assessed as "At Risk (declinining)" under the New Zealand Threat Classification System, but in 2018 its risk under the same system became "Threatened-Nationally Vulnerable".

Carmichaelia corrugata is a species of plant in the family Fabaceae. It is found only on the South Island of New Zealand.

Dracophyllum traversii, commonly known as mountain neinei, grass tree, and pineapple tree is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae. It is a deciduous tree endemic to New Zealand. It reaches a height of 0.2–13 m (0.66–42.65 ft) and has leaves which form tufts at the end of its branches. It has a lifespan of between 500 and 600 years.





















