Related Research Articles

Chiang Kai-shek, also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and romanized via Mandarin as Chiang Chieh-shih and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China between 1928 and 1975, first in mainland China until 1949 and then in Taiwan until his death.

Japan is an island country in East Asia, located in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south. Part of the Ring of Fire, Japan spans an archipelago of 6852 islands covering 377,975 square kilometers (145,937 sq mi); the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa. Tokyo is Japan's capital and largest city; other major cities include Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto.
Japanese is an East Asian language spoken by about 128 million people, primarily in Japan, where it is the national language. It is a member of the Japonic language family, and its relation to other languages, such as Korean, is debated. Japonic languages have been grouped with other language families such as Ainu, Austroasiatic, and the now-discredited Altaic, but none of these proposals has gained widespread acceptance.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. Neighbouring countries include the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast, and the Philippines to the south. The main island of Taiwan has an area of 35,808 square kilometres (13,826 sq mi), with mountain ranges dominating the eastern two-thirds and plains in the western third, where its highly urbanised population is concentrated. Taipei is the capital as well as the largest metropolitan area of Taiwan. Other major cities include New Taipei, Kaohsiung, Taichung, Tainan and Taoyuan. With 23.57 million inhabitants, Taiwan is among the most densely populated countries.

World War II, also known as the Second World War, was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. In a state of total war, directly involving more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries, the major participants threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. World War II was the deadliest conflict in human history, resulting in 70 to 85 million fatalities, with more civilians than military personnel killed. Tens of millions of people died due to genocides, premeditated death from starvation, massacres, and disease. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, including in strategic bombing of population centres, the development of nuclear weapons, and the only two uses of such in war.

Kanji are the adopted logographic Chinese characters that are used in the Japanese writing system. They are used alongside the Japanese syllabic scripts hiragana and katakana. The Japanese term kanji for the Chinese characters literally means "Han characters". It is written with the same characters as in Traditional Chinese to refer to the character writing system, hanzi (漢字).

The Russo-Japanese War was fought during 1904 and 1905 between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and Korea. The major theatres of operations were the Liaodong Peninsula and Mukden in Southern Manchuria and the seas around Korea, Japan and the Yellow Sea.
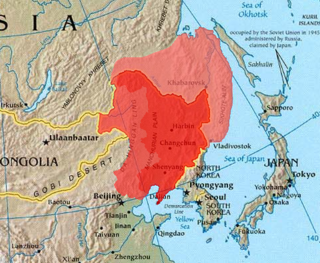
Manchuria is an exonym for several large overlapping historical and geographic regions in Northeast Asia. Depending on the context, it may refer to:

The Chinese Civil War was a civil war in China fought between the Kuomintang (KMT)-led government of the Republic of China (ROC) and the Communist Party of China (CPC) lasting intermittently between 1927 and 1949. The war is generally divided into two phases with an interlude: from August 1927 to 1937, the KMT-CPC Alliance collapsed during the Northern Expedition, and the Nationalists controlled most of China. From 1937 to 1945, hostilities were put on hold, and the Second United Front fought the Japanese invasion of China with eventual help from the Allies of World War II. The civil war resumed with the Japanese defeat, and the CPC gained the upper hand in the final phase of the war from 1945 to 1949, generally referred to as the Chinese Communist Revolution.

The Nanjing Massacre or the Rape of Nanjing was an episode of mass murder and mass rape committed by Imperial Japanese troops against the residents of Nanjing (Nanking), at that time the capital of China, during the Second Sino-Japanese War.

Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Northeast China and Inner Mongolia from 1932 until 1945. It was founded in 1932 after the Japanese invasion of Manchuria, and in 1934 it became a constitutional monarchy. Under the de facto control of Japan, it had limited international recognition.
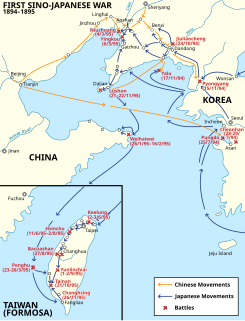
The First Sino-Japanese War was a conflict between the Qing dynasty of China and the Empire of Japan primarily over influence in Joseon Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the port of Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895.

The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) was a military conflict that was primarily waged between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. In China, the war is known as the War of Resistance against Japanese Aggression, or as the oriental theatre of the World Anti-Fascist War, the latter term originating from Mao Zedong's wartime alliance with Stalin. The war made up the Chinese theater of the wider Pacific Theater of the Second World War. The beginning of the war is conventionally dated to the Marco Polo Bridge Incident 7 July 1937, when a dispute between Japanese and Chinese troops in Peking escalated into a full-scale invasion. This full-scale war between the Chinese and the Empire of Japan is often regarded as the beginning of World War II in Asia. In 2017 the Ministry of Education in the People's Republic of China decreed that the term "eight-year war" in all textbooks should be replaced by “fourteen-year war", with a revised starting date of 18 September 1931 provided by the Japanese invasion of Manchuria. According to historian Rana Mitter, historians in China are unhappy with the blanket revision, and the Republic of China did not consider itself to be continuously at war with Japan over these six years.

Chinese characters, also called Hanzi, are logograms developed for the writing of Chinese. They have been adapted to write other Asian languages, and remain a key component of the Japanese writing system where they are known as kanji. Chinese characters are the oldest continuously used system of writing in the world. By virtue of their widespread current use in East Asia, and historic use throughout the Sinosphere, Chinese characters are among the most widely adopted writing systems in the world by number of users.

The Empire of Japan was a historical nation-state that existed from the Meiji Restoration in 1868 until the enactment of the post-World War II 1947 constitution and subsequent formation of modern Japan. It encompassed the Japanese archipelago and several colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories.

Unit 731, also known as Detachment 731, the 731 Regiment, Manshu Detachment 731, The Kamo Detachment, Ishii Unit, Ishii Detachment or the Ishii Company, was a covert biological and chemical warfare research and development unit of the Imperial Japanese Army that undertook lethal human experimentation during the Second Sino-Japanese War (1937–1945) of World War II. It was responsible for some of the most notorious war crimes carried out by Imperial Japan. Unit 731 was based at the Pingfang district of Harbin, the largest gas chamber in the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo, and had active branch offices throughout China and Southeast Asia.

The Pacific War, sometimes called the Asia–Pacific War, was the theater of World War II that was fought in Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Indian Ocean, and Oceania. It was geographically the largest theater of the war, including the vast Pacific Ocean theater, the South West Pacific theater, the South-East Asian theater, the Second Sino-Japanese War, and the Soviet–Japanese War.

East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Hong Kong, Japan, Macau, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. The East Asian states of China, North Korea, South Korea and Taiwan are all unrecognized by at least one other East Asian state due to severe ongoing political tensions in the region, specifically the division of Korea and the political status of Taiwan. Hong Kong and Macau, two small coastal quasi-dependent territories located in the south of China, are officially highly autonomous but are under de jure Chinese sovereignty. North Asia borders East Asia's north, Southeast Asia the south, South Asia the southwest and Central Asia the west. To the east is the Pacific Ocean and to the southeast is Micronesia. Countries such as Singapore and Vietnam are also considered a part of the East Asian cultural sphere due to its cultural, religious, and ethnic similarities.

The Republic of China (ROC), commonly known as China, was a sovereign state based in mainland China between 1912 and 1949, prior to the relocation of its government to the island of Taiwan. At a population of 541 million in 1949, it was the world's most populous country. Covering 11.4 million square kilometers, it consisted of 35 provinces, 1 special administrative region, 2 regions, 12 special municipalities, 14 leagues, and 4 special banners. This period is sometimes referred to as the Republican Era or the Mainland Period.
The year of 2020 featured many film releases. This is an overview of events, including award ceremonies, festivals, a list of country-specific films released, and notable deaths. The year was greatly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, and numerous films originally scheduled for theatrical release were postponed to 2021 or later in the year, or were released on video on demand or on streaming services throughout 2020, as a result.
References
- ↑ "GlobIZ search". Global Information System on Pyraloidea. Retrieved 2011-10-11.
| This Pyraustinae-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |