
The Tethys OceanTEETH-iss, TETH-, also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean during much of the Mesozoic Era and early Cenozoic Era, located between the ancient continents of Gondwana and Laurasia, before the opening of the Indian and Atlantic oceans during the Cretaceous Period.
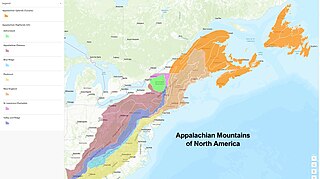
The geology of the Appalachians dates back more than 1.1 billion years to the Mesoproterozoic era when two continental cratons collided to form the supercontinent Rodinia, 500 million years prior to the later development of the range during the formation of the supercontinent Pangea. The rocks exposed in today's Appalachian Mountains reveal elongate belts of folded and thrust faulted marine sedimentary rocks, volcanic rocks and slivers of ancient ocean floor – strong evidence that these rocks were deformed during plate collision. The birth of the Appalachian ranges marks the first of several mountain building plate collisions that culminated in the construction of the supercontinent Pangea with the Appalachians and neighboring Anti-Atlas mountains near the center. These mountain ranges likely once reached elevations similar to those of the Alps and the Rocky Mountains before they were eroded.

An evaporite is a water-soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as ocean deposits, and non-marine, which are found in standing bodies of water such as lakes. Evaporites are considered sedimentary rocks and are formed by chemical sediments.

The Taconic orogeny was a mountain building period that ended 440 million years ago and affected most of modern-day New England. A great mountain chain formed from eastern Canada down through what is now the Piedmont of the East coast of the United States. As the mountain chain eroded in the Silurian and Devonian periods, sediments from the mountain chain spread throughout the present-day Appalachians and midcontinental North America.

The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building era recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Mountains, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly 490–390 million years ago (Ma). It was caused by the closure of the Iapetus Ocean when the continents and terranes of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia collided.

The geological history of the Earth follows the major geological events in Earth's past based on the geological time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed about 4.54 billion years ago by accretion from the solar nebula, a disk-shaped mass of dust and gas left over from the formation of the Sun, which also created the rest of the Solar System.
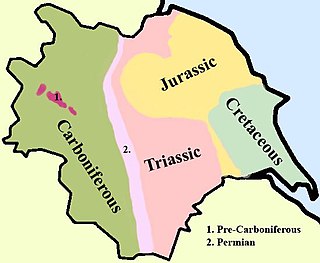
The Geology of Yorkshire in northern England shows a very close relationship between the major topographical areas and the geological period in which their rocks were formed. The rocks of the Pennine chain of hills in the west are of Carboniferous origin whilst those of the central vale are Permo-Triassic. The North York Moors in the north-east of the county are Jurassic in age while the Yorkshire Wolds to the south east are Cretaceous chalk uplands. The plain of Holderness and the Humberhead levels both owe their present form to the Quaternary ice ages. The strata become gradually younger from west to east.

West Virginia's geologic history stretches back into the Precambrian, and includes several periods of mountain building and erosion. At times, much of what is now West Virginia was covered by swamps, marshlands, and shallow seas, accounting for the wide variety of sedimentary rocks found in the state, as well as its wealth of coal and natural gas deposits. West Virginia has had no active volcanism for hundreds of millions of years, and does not experience large earthquakes, although smaller tremors are associated with the Rome Trough, which passes through the western part of the state.
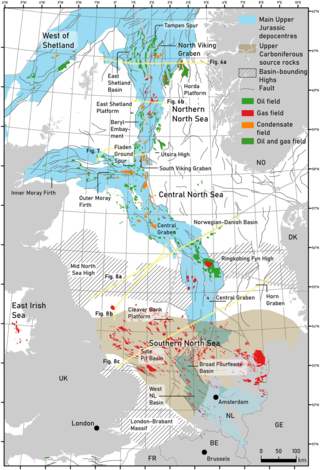
The geology of the North Sea describes the geological features such as channels, trenches, and ridges today and the geological history, plate tectonics, and geological events that created them.

The Iapetus Suture is one of several major geological faults caused by the collision of several ancient land masses forming a suture. It represents in part the remains of what was once the Iapetus Ocean. Iapetus was the father of Atlas in Greek mythology, making his an appropriate name for what used to be called the 'Proto-Atlantic Ocean'. When the Atlantic Ocean opened, in the Cretaceous period, it took a slightly different line from that of the Iapetus suture, with some originally Laurentian rocks being left behind in north-west Europe and other, Avalonian, rocks remaining as part of Newfoundland.

The Black River Group is a geologic group that covers three sedimentary basins in the Eastern and Midwestern United States. These include the Appalachian Basin, Illinois Basin and the Michigan Basin. It dates back to the Late Ordovician period. It is roughly equivalent to the Platteville Group in Illinois. In Kentucky and Tennessee it is also known as the High Bridge Group. In areas where this Geologic Unit thins it is also called the Black River Formation (undifferentiated). One example of this is over the Cincinnati Arch & Findley Arch. Large parts of the Black River have been dolomized (where the parent limestone CaCO3 has been turned into dolomite CaMg(CO3)2.) This happed when there was interaction of hot saline brine and the limestone. This created hydrothermal dolomites that in some areas serve as petroleum reservoirs.
The Vernon Formation is a geologic formation in the Appalachian Basin. It is the lowest unit of the Salina Group. It is made up of red and green shales, siltstone, dolomite, anhydrite and halite. It is made up of three distinct units starting at the bottom (oldest) A, B and C units. These units correspond to units of the same name in its parent group the Salina.

The North Sea basin is located in northern Europe and lies between the United Kingdom, and Norway just north of The Netherlands and can be divided into many sub-basins. The Southern North Sea basin is the largest gas producing basin in the UK continental shelf, with production coming from the lower Permian sandstones which are sealed by the upper Zechstein salt. The evolution of the North Sea basin occurred through multiple stages throughout the geologic timeline. First the creation of the Sub-Cambrian peneplain, followed by the Caledonian Orogeny in the late Silurian and early Devonian. Rift phases occurred in the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic which allowed the opening of the northeastern Atlantic. Differential uplift occurred in the late Paleogene and Neogene. The geology of the Southern North Sea basin has a complex history of basinal subsidence that had occurred in the Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic. Uplift events occurred which were then followed by crustal extension which allowed rocks to become folded and faulted late in the Paleozoic. Tectonic movements allowed for halokinesis to occur with more uplift in the Mesozoic followed by a major phase of inversion occurred in the Cenozoic affecting many basins in northwestern Europe. The overall saucer-shaped geometry of the southern North Sea Basin indicates that the major faults have not been actively controlling sediment distribution.

The Precordillera terrane of western Argentina is a large mountain range located southeast of the main Andes mountain range. The evolution of the Precordillera is noted for its unique formation history compared to the region nearby. The Cambrian-Ordovian sedimentology in the Precordillera terrane has its source neither from old Andes nor nearby country rock, but shares similar characteristics with the Grenville orogeny of eastern North America. This indicates a rift-drift history of the Precordillera in the early Paleozoic. The Precordillera is a moving micro-continent which started from the southeast part of the ancient continent Laurentia. The separation of the Precordillera started around the early Cambrian. The mass collided with Gondwana around Late Ordovician period. Different models and thinking of rift-drift process and the time of occurrence have been proposed. This page focuses on the evidence of drifting found in the stratigraphical record of the Precordillera, as well as exhibiting models of how the Precordillera drifted to Gondwana.
The geology of Morocco formed beginning up to two billion years ago, in the Paleoproterozoic and potentially even earlier. It was affected by the Pan-African orogeny, although the later Hercynian orogeny produced fewer changes and left the Maseta Domain, a large area of remnant Paleozoic massifs. During the Paleozoic, extensive sedimentary deposits preserved marine fossils. Throughout the Mesozoic, the rifting apart of Pangaea to form the Atlantic Ocean created basins and fault blocks, which were blanketed in terrestrial and marine sediments—particularly as a major marine transgression flooded much of the region. In the Cenozoic, a microcontinent covered in sedimentary rocks from the Triassic and Cretaceous collided with northern Morocco, forming the Rif region. Morocco has extensive phosphate and salt reserves, as well as resources such as lead, zinc, copper and silver.
The geology of Virginia began to form 1.8 billion years ago and potentially even earlier. The oldest rocks in the state were metamorphosed during the Grenville orogeny, a mountain building event beginning 1.2 billion years ago in the Proterozoic, which obscured older rocks. Throughout the Proterozoic and Paleozoic, Virginia experienced igneous intrusions, carbonate and sandstone deposition, and a series of other mountain building events which defined the terrain of the inland parts of the state. The closing of the Iapetus Ocean, to form the supercontinent Pangaea added additional small landmasses, some of which are now hidden beneath thick Atlantic Coastal Plain sediments. The region subsequently experienced the rifting open of the Atlantic Ocean in the Mesozoic, the development of the Coastal Plain, isolated volcanism and a series of marine transgressions that flooded much of the area. Virginia has extensive coal, deposits of oil and natural gas, as well as deposits of other minerals and metals, including vermiculite, kyanite and uranium.
The geology of Ohio formed beginning more than one billion years ago in the Proterozoic eon of the Precambrian. The igneous and metamorphic crystalline basement rock is poorly understood except through deep boreholes and does not outcrop at the surface. The basement rock is divided between the Grenville Province and Superior Province. When the Grenville Province crust collided with Proto-North America, it launched the Grenville orogeny, a major mountain building event. The Grenville mountains eroded, filling in rift basins and Ohio was flooded and periodically exposed as dry land throughout the Paleozoic. In addition to marine carbonates such as limestone and dolomite, large deposits of shale and sandstone formed as subsequent mountain building events such as the Taconic orogeny and Acadian orogeny led to additional sediment deposition. Ohio transitioned to dryland conditions in the Pennsylvanian, forming large coal swamps and the region has been dryland ever since. Until the Pleistocene glaciations erased these features, the landscape was cut with deep stream valleys, which scoured away hundreds of meters of rock leaving little trace of geologic history in the Mesozoic and Cenozoic.

The geology of the State of New York is made up of ancient Precambrian crystalline basement rock, forming the Adirondack Mountains and the bedrock of much of the state. These rocks experienced numerous deformations during mountain building events and much of the region was flooded by shallow seas depositing thick sequences of sedimentary rock during the Paleozoic. Fewer rocks have deposited since the Mesozoic as several kilometers of rock have eroded into the continental shelf and Atlantic coastal plain, although volcanic and sedimentary rocks in the Newark Basin are a prominent fossil-bearing feature near New York City from the Mesozoic rifting of the supercontinent Pangea.
The Bertie Group or Bertie Limestone, also referred to as the Bertie Dolomite and the Bertie Formation, is an upper Silurian geologic group and Lagerstätte in southern Ontario, Canada, and western New York State, United States. Details of the type locality and of stratigraphic nomenclature for this unit as used by the U.S. Geological Survey are available on-line at the National Geologic Map Database. The formation comprises dolomites, limestones and shales and reaches a thickness of 495 feet (151 m) in the subsurface, while in outcrop the group can be 60 feet (18 m) thick.

The Salina Group or Salina Formation is a Late Silurian-age, Stratigraphic unit of sedimentary rock that is found in Northeastern and Midwestern North America. Named for its Halite beds, the phrase "Salina Group" was first used as a descriptive term by James D. Dana in 1863.













