
The carob is a flowering evergreen tree or shrub in the Caesalpinioideae sub-family of the legume family, Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated for its edible fruit, which takes the form of seed pods, and as an ornamental tree in gardens and landscapes. The carob tree is native to the Mediterranean region and the Middle East. Portugal is the largest producer of carob, followed by Italy and Morocco.
Magnolia guatemalensis is a tree found in the highlands and mountains of Guatemala, Chiapas, El Salvador, and Honduras. It is considered an indicator species of the cloud forest.

Alnus jorullensis, commonly known as Mexican alder, is an evergreen or semi-evergreen alder, native to eastern and southern Mexico, Guatemala, and Honduras. Although previously reported from the Andes, further collections showed these to be the similar species A. acuminata, commonly found in South America.

Prosopis alba is a South American tree species that grows in central Argentina, the Gran Chaco ecoregion, and part of the Argentine Mesopotamia, as well as Bolivia, Chile, Paraguay, and Peru. It is known as algarrobo blanco in Spanish. Spanish settlers gave it that name because of its similarity to the European carob tree. Other common names come from Guaraní, including ibopé and igopé.

Ceratonia is small genus of flowering trees in the pea family, Fabaceae, endemic to the Mediterranean region and the Middle East. Its best known member is the carob tree, which is cultivated for its edible pods and has been widely introduced to regions with similar climates. The genus was long considered monotypic, but a second species, Ceratonia oreothauma, was identified in 1979 from Oman and Somalia. The genus is in subfamily Caesalpinioideae and tribe Umtizieae.
Agathis robusta subsp. nesophila, the New Guinea kauri, is a subspecies of conifer native to the highlands of Papua New Guinea. It grows in the Eastern Highlands and Owen Stanley Range of eastern New Guinea and the highlands of New Britain at elevations of 900–1980 m. Although long known, it has only relatively recently (1980) been described as a subspecies of Agathis robusta. It is also known by the synonym Agathis spathulata. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Podocarpus matudae is a species of conifer in the family Podocarpaceae. It is found in Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras and Mexico.

Cratoxylum formosum is a species of flowering plant in the Hypericaceae family. Its commercial name in timber production is "mampat".
Damburneya roberto-andinoi is a species of plant in the family Lauraceae. It is endemic to Honduras. It is a tree growing up to 15 meters tall.

Chisocheton cumingianus is a tree in the family Meliaceae. The tree is named for the English naturalist Hugh Cuming. Habitat is rain forests from sea-level to 1,300 metres (4,300 ft) elevation. C. cumingianus is found from India and tropical China through Indochina and throughout Malaysia. In the Philippines, the seeds of C. cumingianus are used to make a non-drying oil either for traditional medicine or as fuel for oil lamps.
Planchonella reticulata is a flowering plant in the sapodilla family, Sapotaceae. It is a shrub or tree endemic to east-central New Caledonia. The specific epithet refers to the reticulate venation on the leaves.

Gaultheria fragrantissima is a species of flowering plant native to southern and southeastern Asia. It is commonly known as fragrant wintergreen or dhasingre.
Hanak's dwarf bat or Hanak's pipistrelle is a species of bat only found in Cyrenaica, Libya and Crete, Greece.

The Somali montane xeric shrublands is a desert and xeric scrubland ecoregion in Somalia. The ecoregion lies in the rugged Karkaar Mountains, which run parallel and close to Somalia's northern coast on the Gulf of Aden, and follows coast from Cape Guardafui south to Eyl on the Arabian Sea.

The Southwestern Arabian foothills savanna, also known as the Southwestern Arabian Escarpment shrublands and woodlands, is a desert and xeric shrubland ecoregion of the southern Arabian Peninsula, covering portions of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Oman.

Acer skutchii, often called the cloud forest sugar maple, Guatemalan maple, Mexican sugar maple, Skutch maple, or álamo plateado is a species of flowering plant in the genus Acer, native to Mexico and Guatemala.
Maytenus umbellata is a species of plant in the family Celastraceae. Common names include Buxo-da-rocha and Madeira shrubby bittersweet. It is endemic to Madeira.
Analavelona, also known as Analavelona Massif, is a mountain in southwestern Madagascar. The massif is home to an enclave of montane subhumid forest, which is considered a sacred forest by the local people and notable for its biodiversity.
Magnolia sororum is a species of flowering plant in the family Magnoliaceae. It is commonly known as vaco. It is native to the mountain forests of Costa Rica and western Panama, and may range into Nicaragua.
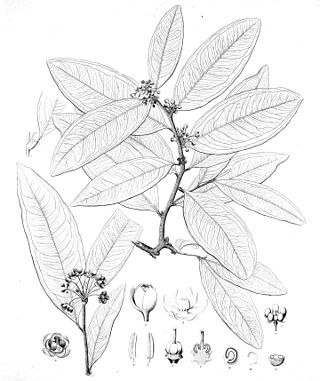
Brackenridgea nitida is a species of flowering plant in family Ochnaceae. It is a shrub or tree native to Fiji and Queensland.











