
Ceropegia is a genus of plants within the family Apocynaceae, native to Africa, southern Asia, and Australia. It was named by Carl Linnaeus, who first described this genus in volume 1 of his Species plantarum, which appeared in 1753. Linnaeus thought that the flowers looked like a fountain of wax. From this the scientific name was derived: kērós meaning wax and pēgḗ meaning fountain. They have many common names including lantern flower, parasol flower, parachute flower, bushman’s pipe, string of hearts, snake creeper, wine-glass vine, rosary vine, and necklace vine.

Alstroemeriaceae is a family of flowering plants, with 254 known species in four genera, almost entirely native to the Americas, from Central America to southern South America. One species of Luzuriaga occurs in New Zealand, and the genus Drymophila is endemic to south-eastern Australia.

Limonium is a genus of 120 flowering plant species. Members are also known as sea-lavender, statice, caspia or marsh-rosemary. Despite their common names, species are not related to the lavenders or to rosemary. They are instead in Plumbaginaceae, the plumbago or leadwort family. The generic name is from the Latin līmōnion, used by Pliny for a wild plant and is ultimately derived from the Ancient Greek leimon.

Delonix regia is a species of flowering plant in the bean family Fabaceae, subfamily Caesalpinioideae native to Madagascar. It is noted for its fern-like leaves and flamboyant display of orange-red flowers over summer. In many tropical parts of the world it is grown as an ornamental tree and in English it is given the name royal poinciana, flamboyant, flame of the forest, or flame tree.

Jacaranda mimosifolia is a sub-tropical tree native to south-central South America that has been widely planted elsewhere because of its attractive and long-lasting violet-colored flowers. It is also known as the jacaranda, blue jacaranda, black poui, or fern tree. Older sources call it J. acutifolia, but it is nowadays more usually classified as J. mimosifolia. In scientific usage, the name "jacaranda" refers to the genus Jacaranda, which has many other members, but in horticultural and everyday usage, it nearly always means the blue jacaranda.

Sherardia is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the family Rubiaceae. The genus contains only one species, viz. Sherardia arvensis or (blue) field madder, which is widespread across most of Europe and northern Africa as well as southwest and central Asia and Macaronesia. It is also reportedly naturalized in Australia, New Zealand, Taiwan, Kerguelen, Ethiopia, Sudan, southern Africa, Mexico, Costa Rica, South America, Bermuda, Cuba, Haiti and much of Canada and the United States.

Phoenix canariensis is a species of flowering plant in the palm family Arecaceae, native to the Canary Islands. It is a relative of Phoenix dactylifera, the true date palm. It is the natural symbol of the Canary Islands, together with the canary Serinus canaria. Mature P. canariensis are often used in ornamental landscaping and are collected and transplanted to their new planting location. A Canary Island date palm with 10 m (30 ft) of trunk is approximately 60 years of age.

Ceropegia woodii is a flowering plant in the genus Ceropegia (Apocynaceae), native to South Africa, Swaziland, and Zimbabwe. It is sometimes treated as a subspecies of the related Ceropegia linearis, as C. linearis subsp. woodii. Common names include chain of hearts, collar of hearts, string of hearts, rosary vine, hearts-on-a-string, and sweetheart vine.
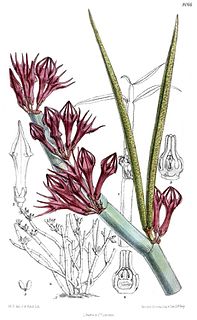
Ceropegia fusca is a flowering plant in the genus Ceropegia (Apocynaceae). It is endemic to the Canary Islands, where it grows on Tenerife, Gran Canaria, and La Palma in the Tabaibal-Cardonal zone at up to about 600 m altitude.

Ceropegia stapeliiformis is a flowering plant in the genus Ceropegia (Apocynaceae), native to South Africa and Swaziland. Common names include serpent ceropegia, snake creeper, and slangkambro.

Euphorbia atropurpurea, called tabaiba majorera or tabaiba roja in Spanish, is a shrub in the family Euphorbiaceae native to Tenerife in the Canary Islands. It can reach 2 metres in height, and grows in ravines, and on slopes and terraces.

Phillyrea is a genus of two species of flowering plants in the family Oleaceae, native to the Mediterranean region, and naturalized in the Canary Islands and Madeira.

Acacia dealbata, the silver wattle, blue wattle or mimosa, is a species of flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae, native to southeastern Australia in New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, and the Australian Capital Territory and widely introduced in Mediterranean, warm temperate, and highland tropical landscapes.

Kleinia neriifolia, known in Spanish as verode or berode, is a species of flowering plant in the daisy family (Asteraceae). It is endemic to the Canary Islands. It was formerly named Senecio kleinia.

Pancratium illyricum is a species of bulbous plant native to Corsica, Sardinia and the Capraia Islands of Tuscany.

Ocotea foetens, commonly called til or stinkwood is a species of tree in the family Lauraceae. It is evergreen and grows up to 40 m tall. It is a common constituent of the laurisilva forests of Madeira and the Canary Islands. Leaf fossils of this species are known from the Mio-Pleistocene of Madeira Island.

Sideroxylon mirmulans, commonly known as marmulano, is a species of flowering plants in the family Sapotaceae. It is endemic to the Madeira Islands (Portugal). It is threatened by habitat loss.

Agapanthus praecox is a popular garden plant around the world, especially in Mediterranean climates. It is native of Natal and Cape of Good Hope in South Africa, local names include agapant, bloulelie, isicakathi and ubani. Most of the cultivated plants of the genus Agapanthus are hybrids or cultivars of this species. It is divided into three subspecies: subsp.praecox, subsp. orientalis and subsp. minimus.

Argyranthemum frutescens, known as Paris daisy, marguerite or marguerite daisy, is a perennial plant known for its flowers. It is native to the Canary Islands. Hybrids derived from this species are widely cultivated as ornamental plants in private gardens and public parks in many countries, and have naturalized in Italy and southern California. There are many cultivars, but the most common has white petals.

Clethra arborea, commonly known as the lily-of-the-valley-tree, is a flowering plant in the genus Clethra. It is found in Macaronesia where it is native to Madeira, extinct in the Canary Islands, and considered an introduced species in the Azores. In Madeira its natural habitat is laurisilva forest.




















