Heliamphora tatei is a species of marsh pitcher plant endemic to Cerro Duida, Cerro Huachamacari and Cerro Marahuaca in Venezuela. It is closely related to H. macdonaldae, H. neblinae, and H. parva, and all three have in the past been considered forms or varieties of H. tatei. Like H. tatei, these species are noted for their stem-forming growth habit.
"Cochranella" duidaeana is a species of frog in the family Centrolenidae. It is endemic to Cerro Duida, Venezuela. The generic placement of this species within the subfamily Centroleninae is uncertain.
Anomaloglossus shrevei is a species of frog in the Aromobatidae family. It is endemic to Venezuela where it is only known from the Cerro Marahuaca and Cerro Duida, two adjacent tepuis. These frogs live near streams in tropical rainforest. It is not a common species but the population may be presently stable and is protected by Parque Nacional Duida-Marahuaca.

The Monte Duida tree frog is a species of frog in the family Hylidae. It is endemic to Venezuela and only known from the Cerro Duida, its type locality in the Amazonas state of southern Venezuela. Its natural habitat is montane tepui vegetation, specifically forest and shrubs adjacent to rivers, streams, and peat bogs. No significant threats to this species occurring in the Duida-Marahuaca National Park are known.
Dischidodactylus colonnelloi is a species of frog in the family Craugastoridae. It is endemic to Venezuela and only know from its type locality, Cerro Marahuaca, in the Amazonas State. The holotype was collected by G. Colonnello, hence the specific name colonnelloi.

Dischidodactylus duidensis is a species of frog in the family Craugastoridae. It is endemic to Venezuela and only known from its type locality, Cerro Duida. It was formally described in 1968 by Juan A. Rivero, even though the type series was collected 40 years earlier by George Henry Hamilton Tate.
Stefania goini is a species of frog in the family Hemiphractidae. It is endemic to Amazonas, Venezuela, and known from Cerro Duida and the nearby Cerro Huachamacari. Its natural habitats are streams on the tops of tepuis. It usually occurs on rocks.
Stefania marahuaquensis is a species of frog in the family Hemiphractidae. It is endemic to Venezuela and known from Cerro Duida and Cerro Marahuaca, both in Amazonas State. Its occurs on rocks along the forested margins of small streams at elevations of 340–1,200 m (1,120–3,940 ft) asl. The range is within the Duida–Marahuaca National Park, and no major threats to this species have been identified.

Cerro Marahuaca, also spelled Marahuaka, is a tepui in Amazonas state, Venezuela. It has an elevation of 2,832 metres (9,291 ft) above sea level and is the second-highest mountain of the entire Guayana Shield. Cerro Marahuaca shares a common base with the much larger Cerro Duida and together they form the Duida–Marahuaca Massif. Both tepuis are located entirely within the bounds of Duida–Marahuaca National Park.
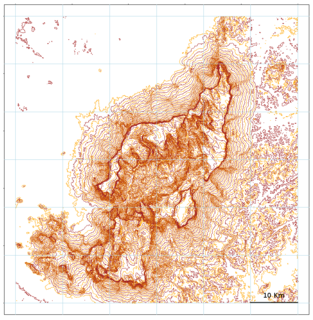
Cerro de la Neblina, also known as Serra da Neblina in Brazil and Sierra de la Neblina in Venezuela, is a sandstone massif located in the northern Amazon Basin. It is a tilted, heavily eroded plateau, with a deep canyon in its central portion, drained by the Baria River.

The natural range of the carnivorous plant genus Heliamphora is restricted to the southern Venezuelan states of Amazonas and Bolívar, and to adjacent portions of northern Brazil and western Guyana, an area corresponding to the western part of the Guayana Shield. These plants are largely confined to the summits and foothills of the sandstone table-top mountains of the region, known as tepuis.

Cerro Petaca is a large forested ridge in Amazonas state, Venezuela. It lies just west of the two high plateaus of Cerro Marahuaca and northeast of the massive Cerro Duida. The ridge reaches a height of at least 2,700 metres (8,900 ft) above sea level. Part of the Duida–Marahuaca Massif, it is entirely within the bounds of Duida–Marahuaca National Park.

Cerro La Luna is a small tepui in Bolívar state, Venezuela. It is situated off the northern flank of Auyán-tepui, just southeast of the similarly small Cerro El Sol, and forms part of the Auyán Massif. Both it and Cerro El Sol emerge near the end of a long forested ridge leading from Auyán-tepui. Cerro La Luna has an elevation of around 1,650 metres (5,410 ft) and a summit area of 0.2 km2 (0.077 sq mi).

Cerro El Sol, also known as Wei- or Uei-tepui, is a small tepui in Bolívar state, Venezuela. It is situated off the northern flank of Auyán-tepui, just northwest of the similarly small Cerro La Luna, and forms part of the Auyán Massif. Both it and Cerro La Luna emerge near the end of a long forested ridge leading from Auyán-tepui. Cerro El Sol has an elevation of around 1,750 metres (5,740 ft) and a summit area of 0.6 km2 (0.23 sq mi).

Ptari-tepui, also spelled Pu-tari and sometimes called Cerro Budare or Cerro del Budare, is a tepui in Bolívar state, Venezuela. Lying near the centre of the Sierra de Lema, it has a maximum elevation of around 2,400 metres (7,900 ft) above sea level. Its mostly bare summit plateau has an area of 1.25 km2 (0.48 sq mi). Though generally flat, distinctive erosional rock formations are found on the more dissected eastern edge of the summit.

Cerro Aracamuni is a tepui in Amazonas state, Venezuela. Part of the Neblina–Aracamuni Massif, it lies north of Cerro Avispa and the vast complex of Cerro de la Neblina. Cerro Aracamuni and Cerro Avispa share a common slope area; they have a combined summit area of 238 km2 (92 sq mi) and an estimated combined slope area of 658 km2 (254 sq mi). Both of these cerro-plateaus have a maximum elevation of around 1,600 metres (5,200 ft).

Cerro Avispa is a tepui in Amazonas state, Venezuela. Part of the Neblina–Aracamuni Massif, it lies south of Cerro Aracamuni and north of Cerro de la Neblina. Cerro Avispa and Cerro Aracamuni have a combined summit area of 238 km2 (92 sq mi) and an estimated combined slope area of 658 km2 (254 sq mi). Both of these cerro-plateaus have a maximum elevation of around 1,600 metres (5,200 ft).

Duida–Marahuaca National Park is a protected area in Amazonas state, Venezuela. It has an area of 210,000 ha, and includes the Duida–Marahuaca Massif.

The Alto Orinoco-Casiquiare Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO biosphere reserve in the Venezuelan Amazon biome.