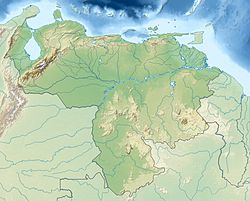
Angel Falls is a waterfall in Venezuela. It is the world's highest uninterrupted waterfall, with a height of 979 metres (3,212 ft) and a plunge of 807 m (2,648 ft). The waterfall drops over the edge of the Auyán-tepui mountain in the Canaima National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage site in the Gran Sabana region of Bolívar State. The height figure, 979 m (3,212 ft), mostly consists of the main plunge but also includes about 400 metres (1,300 ft) of sloped cascade and rapids below the drop and a 30-metre (98 ft) high plunge downstream of the talus rapids.

The genus Heliamphora contains 23 species of pitcher plants endemic to South America. The species are collectively known as sun pitchers, based on the mistaken notion that the heli of Heliamphora is from the Greek helios, meaning "sun". In fact, the name derives from helos, meaning marsh, so a more accurate translation of their scientific name would be marsh pitcher plants. Species in the genus Heliamphora are carnivorous plants that consist of a modified leaf form that is fused into a tubular shape. They have evolved mechanisms to attract, trap, and kill insects; and control the amount of water in the pitcher. At least one species produces its own proteolytic enzymes that allows it to digest its prey without the help of symbiotic bacteria.

William Henry Phelps Jr. was a Venezuelan ornithologist and businessman.

Heliamphora heterodoxa is a species of marsh pitcher plant native to Gran Sabana and the plateau of Ptari Tepui in Venezuela. It was first discovered in 1951 upon Ptari Tepui. This Heliamphora is closely related to H. glabra and the latter was for a long time considered a form of H. heterodoxa. It is one of four Heliamphora taxa formally described by Julian A. Steyermark.

Heliamphora minor is a species of marsh pitcher plant endemic to Auyán-tepui in Venezuela. As the name suggests, it is one of the smallest species in the genus. It is closely related to H. ciliata and H. pulchella.
Oreophrynella huberi is a species of toad in the family Bufonidae. It is endemic to Venezuela. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist montane forests and swamps.

Upuigma-tepui, also known as El Castillo, is a tepui in Bolívar state, Venezuela. A relatively isolated peak, both it and nearby Angasima-tepui lie just south of the vast Chimantá Massif, from which they are separated by the Río Aparurén valley. Upuigma-tepui is situated entirely within the bounds of Canaima National Park.
Heliamphora ciliata is a species of Marsh Pitcher Plant endemic to Venezuela. It is restricted to a small number of swampy meadows in the uplands of Gran Sabana. In this habitat it is sympatric with a species of Stegolepis (Rapateaceae). Unusually for the genus, H. ciliata is a submontane plant, growing at an elevation of only 900 m.

Kukenán, also known as Matawi, is a tepui in Guayana Region, Venezuela. It is 2,680 metres (8,790 ft) high and about 3 km (1.9 mi) long. Kukenan Falls, which is 674 m (2,211 ft) high, is located at the south end of the tepui.
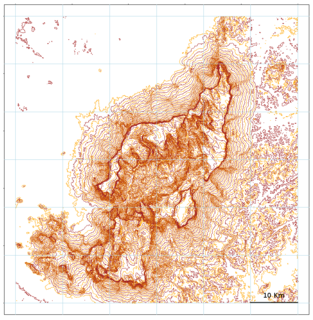
Cerro de la Neblina, also known as Serra da Neblina in Brazil and Sierra de la Neblina in Venezuela, is a sandstone massif located in the northern Amazon Basin. It is a tilted, heavily eroded plateau, with a deep canyon in its central portion, drained by the Baria River.

The natural range of the carnivorous plant genus Heliamphora is restricted to the southern Venezuelan states of Amazonas and Bolívar, and to adjacent portions of northern Brazil and western Guyana, an area corresponding to the western part of the Guayana Shield. These plants are largely confined to the summits and foothills of the sandstone table-top mountains of the region, known as tepuis.

Cerro Duida, also known as Cerro Yennamadi, is a very large tepui in Amazonas state, Venezuela. It has an uneven and heavily inclined plateau, rising from highs of around 1,300–1,400 metres (4,300–4,600 ft) in the north and east to a maximum of 2,358 metres (7,736 ft) on its southwestern rim. It has a summit area of 1,089 km2 (420 sq mi) and an estimated slope area of 715 km2 (276 sq mi). At its foot lies the small settlement of La Esmeralda, from which the mountain can be climbed.

Cerro El Sol, also known as Wei- or Uei-tepui, is a small tepui in Bolívar state, Venezuela. It is situated off the northern flank of Auyán-tepui, just northwest of the similarly small Cerro La Luna, and forms part of the Auyán Massif. Both it and Cerro La Luna emerge near the end of a long forested ridge leading from Auyán-tepui. Cerro El Sol has an elevation of around 1,750 metres (5,740 ft) and a summit area of 0.6 km2 (0.23 sq mi).

Uei-tepui, also known as Wei-tepui, Cerro El Sol or Serra do Sol is a tepui on the border between Brazil and Venezuela. It may be considered the southernmost member of the Eastern Tepuis chain.

Los Testigos, also known as the Aparamán range, is a mountain chain in Bolívar, Venezuela. It consists of four rather small tepuis, forming a bridge between the giant Auyán-tepui to the west and Ptari-tepui to the east. The four major peaks of Los Testigos are : Aparamán-tepui (2,100 m), Murisipán-tepui (2,350 m), Tereke-yurén-tepui (1,900 m), and Kamarkawarai-tepui (2,400 m), the latter three sharing a common slope area. There however remains some confusion in the literature regarding the names of these peaks.

Uaipán-tepui, also spelled Waipán, is a tepui in Bolívar state, Venezuela. It is a southern satellite peak of the vast Auyán Massif, with a maximum elevation of around 1,950 metres (6,400 ft). Its mostly forested summit plateau has an area of 2.5 km2 (0.97 sq mi). The mountain's slope area has been estimated at 60 km2 (23 sq mi).

Ptari-tepui, also spelled Pu-tari and sometimes called Cerro Budare or Cerro del Budare, is a tepui in Bolívar state, Venezuela. Lying near the centre of the Sierra de Lema, it has a maximum elevation of around 2,400 metres (7,900 ft) above sea level. Its mostly bare summit plateau has an area of 1.25 km2 (0.48 sq mi). Though generally flat, distinctive erosional rock formations are found on the more dissected eastern edge of the summit.

Cerro Aracamuni is a tepui in Amazonas state, Venezuela. Part of the Neblina–Aracamuni Massif, it lies north of Cerro Avispa and the vast complex of Cerro de la Neblina. Cerro Aracamuni and Cerro Avispa share a common slope area; they have a combined summit area of 238 km2 (92 sq mi) and an estimated combined slope area of 658 km2 (254 sq mi). Both of these cerro-plateaus have a maximum elevation of around 1,600 metres (5,200 ft).

Cerro Avispa is a tepui in Amazonas state, Venezuela. Part of the Neblina–Aracamuni Massif, it lies south of Cerro Aracamuni and north of Cerro de la Neblina. Cerro Avispa and Cerro Aracamuni have a combined summit area of 238 km2 (92 sq mi) and an estimated combined slope area of 658 km2 (254 sq mi). Both of these cerro-plateaus have a maximum elevation of around 1,600 metres (5,200 ft).