
Pluteus cervinus, commonly known as the deer shield, deer mushroom, or fawn mushroom, is a species of fungus in the order Agaricales. Fruit bodies are agaricoid (mushroom-shaped). Pluteus cervinus is saprotrophic and fruit bodies are found on rotten logs, roots, tree stumps, sawdust, and other wood waste. The species is common in Europe and eastern North America, but rare and possibly introduced in western North America.

Pluteus is a large genus of fungi with over 300 species. They are wood rotting saprobes with pink spore prints and gills that are free from the stem.

Pluteus salicinus is a European psychedelic mushroom that grows on wood. It is an edible mushroom after parboiling.

Pluteus leoninus, commonly known as lion shield, can occasionally be found growing on dead wood in Europe and North Africa. The underside of the cap is typical of the genus Pluteus — the gills are pale, soon becoming pink when the spores ripen. But the upper surface is a bright tawny or olivaceous yellow. The species name leoninus refers to this cap colour.

Melanoleuca is a poorly known genus of saprotrophic mushrooms traditionally classified in the family Tricholomataceae. Most are small to medium sized, white, brown, ocher or gray with a cylindrical to subcylindrical stipe and white to pale yellowish gills. The basidiospores are ellipsoid and ornamented with amyloid warts. Melanoleuca is considered a difficult group to study due to their macroscopic similarities among species and the need of a thorough microscopic analysis to separate species. DNA studies have determined that this genus is closely related to Amanita and Pluteus and that it does not belong to the family Tricholomataceae.

The Hydnangiaceae are a family of fungi in the mushroom order Agaricales. Widespread in temperate and tropical regions throughout the world, the family contains about 30 species in four genera. Species in the Hydnangiaceae form ectomycorrhizal relationships with various species of trees in both coniferous and deciduous forests.

Mycena cinerella, commonly known as the mealy bonnet, is an inedible species of mushroom in the family Mycenaceae. It is found in Europe and the United States, where it grows in groups on fallen leaves and needles under pine and Douglas fir. The small grayish mushrooms have caps that are up to 1.5 cm (0.6 in) wide atop stipes that are 5 cm (2.0 in) long and 2.5 mm (0.10 in) thick. Its gills are grayish-white and adnate, with a "tooth" that runs slightly down the stipe. The fungus has both two- and four-spored basidia. As its common name suggests, it smells mealy.

Mycena stylobates, commonly known as the bulbous bonnet, is a species of inedible mushroom in the family Mycenaceae. Found in North America and Europe, it produces small whitish to gray fruit bodies with bell-shaped caps that are up to 15 mm (0.6 in) in diameter. The distinguishing characteristic of the mushroom is the fragile stipe, which is seated on a flat disk marked with distinct grooves, and fringed with a row of bristles. The mushrooms grow in small troops on leaves and other debris of deciduous and coniferous trees. The mushroom's spores are white in deposit, smooth, and ellipsoid-shaped with dimensions of 6–10 by 3.5–4.5 μm. In the development of the fruit body, the preliminary stipe and cap structures appear at the same time within the primordium, and hyphae originating from the stipe form a cover over the developing structures. The mycelia of the mushroom is believed to have bioluminescent properties.

Volvopluteus is a genus of small to medium-sized or big saprotrophic mushrooms growing worldwide. The genus has been segregated from Volvariella with which it shares some morphological characteristics such as the presence of a volva and a pink to pink-brown spore print. Phylogenetic analyses of DNA data have shown that Volvopluteus is closely related to Pluteus and both genera currently are classified in the family Pluteaceae, while Volvariella is not closely related to either genus and its position in the Agaricales is still uncertain.

Psathyrella ammophila is a species of fungus in the family Psathyrellaceae and is found throughout Europe. Commonly known as the dune brittlestem, this agaric primarily grows on sand dunes near marram grass, feeding saprotrophically on the decaying roots. The season of growth is generally May to November.

Pluteus nevadensis is a species of fungus in the agaric family Pluteaceae. Described as new to science in 2010, the species is known only from subtropical and pine forests in Mexico, where it grows on rotting pine and oak wood. Fruit bodies (mushrooms) have red-orange caps up to 3.8 cm (1.5 in) in diameter with a shape ranging from conic, convex, or flattened, depending on their age. The silky yellow stems are up to 4.5 cm (1.8 in) long. It is similar in appearance to Pluteus aurantiorugosus, with which it shares an orange- or scarlet-colored cap and a yellow stem. P. nevadensis can be distinguished from this and other superficially similar Pluteus species by differences in microscopic characteristics.

Pluteus phaeocyanopus is an agaric fungus in the family Pluteaceae. Described as a new species in 2010, it has only been collected from California, where it grows singularly or in groups on the decaying wood of oak. The fruit body has a smooth brown cap measuring 2–4 cm (0.8–1.6 in) in diameter. The stipe is 2–5 cm (0.8–2.0 in) long by 0.4–0.8 cm (0.16–0.31 in) thick, and roughly equal in width throughout. It is whitish but becomes grayish-green near the base. The thin and fragile gills are free from attachment to the stipe, close to somewhat distantly placed, and interspersed with several tiers of lamellulae. The flesh has no distinctive taste or odor. The spores are spherical or nearly so and measure 6.2–8.4 by 5.7–7.9 μm.

Tricholoma vernaticum is an agaric fungus of the genus Tricholoma native to the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. The fungus was originally described in 1976 as a species of Armillaria when that genus was more inclusive; it received its current name twenty years later. The stout fruit bodies (mushrooms) have moist white to grayish caps, a membranous ring on the stipe, and an odor resembling cucumbers. Mycorrhizal with conifers, the fungus fruits in the spring or early summer, with its mushrooms appearing on the ground singly or in groups at high elevations, often at the edge of melting snowbanks. The edibility of the mushroom is unknown, but it has a strong unpleasant odor and a mealy taste.

Volvopluteus earlei is a species of mushroom in the family Pluteaceae. It was originally described in 1911 by American mycologist William Alphonso Murrill as Volvariopsis earlei, based on collections made in a Cuban banana field. The fungus was later shuffled to the genera Volvaria and Volvariella before molecular studies placed it in Volvopluteus, a genus newly described in 2011.

Volvopluteus michiganensis is a species of mushroom in the family Pluteaceae. It was originally described under the name Pluteus michiganensis but molecular studies have placed it in the Volvopluteus, a genus described in 2011. The cap of this mushroom is about 7–9 cm (2.8–3.5 in) in diameter, gray, and has a cracked margin that is sticky when fresh. The gills start out as white but they soon turn pink. The stipe is white and has a volva at the base. Microscopical features and DNA sequence data are of great importance for separating this taxon from related species. V. michiganensis is a saprotrophic fungus that was originally described as growing on sawdust. It has only been reported from Michigan (US) and the Dominican Republic.
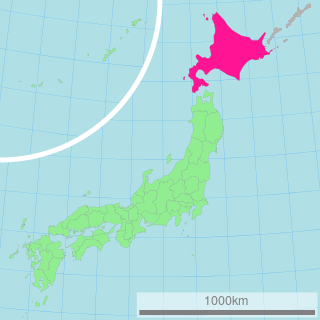
Volvopluteus asiaticus is a species of mushroom in the Pluteaceae family. The cap of this mushroom is about 70–90 mm (2.8–3.5 in) in diameter, greyish brown to brown. The gills start out white but they soon turn pink. The stipe is white and has a volva at the base. Microscopical features and DNA sequence data are of great importance for separating this taxon from related species. V. asiaticus is a saprotrophic fungus that was originally described as growing on the ground, in the humus layer. It is only known from Hokkaido (Japan).

Flammulaster erinaceellus is a species of fungus in the agaric family Tubariaceae. It was first described in 1876 as Agaricus detersibilis by Charles Horton Peck. Roy Watling transferred it to Flammulaster in 1967. The fruit body has a hemispherical to convex cap 1–2.5 cm (0.4–1.0 in) in diameter that is covered with small, erect, brownish scales that can be readily rubbed off. The gills have an adnexed attachment to the stipe. The stipe is up to 2.5 cm (1.0 in) long and 2 mm thick. It is either hollow, or stuffed with a pith-like mycelium. The spores measure 7.5–9 by 4–5 μm. Fruiting occurs on logs in the woods.

Pluteus americanus is a North American and Russian psychedelic mushroom that grows on hardwoods.

Pluteus exilis is a species of agaric fungus in the family Pluteaceae. It was described as new to science by mycologist Rolf Singer in 1989, from specimens collected in Muir Woods, California.

Pluteus microspermus is a saprotrophic, mushroom-like (agaricoid) fungi in the Section Pluteus. It is often confused with Pluteus concentricus, a species endemic to New Zealand because P. concentricus also has concentric ridges on its cap (pileus). P. microspermus and P. concentricus can be differentiated by microscopy as the spores are different sizes. P. concentricus also has rougher material on its stipe.




















