Related Research Articles

The potato is a starchy root vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are tubers of the plant Solanum tuberosum, a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.

Lettuce is an annual plant of the family Asteraceae. It is most often grown as a leaf vegetable, but sometimes for its stem and seeds. Lettuce is most often used for salads, although it is also seen in other kinds of food, such as soups, sandwiches and wraps; it can also be grilled. One variety, celtuce, is grown for its stems, which are eaten either raw or cooked. In addition to its main use as a leafy green, it has also gathered religious and medicinal significance over centuries of human consumption. Europe and North America originally dominated the market for lettuce, but by the late 20th century the consumption of lettuce had spread throughout the world. As of 2021, world production of lettuce and chicory was 27 million tonnes, 53 percent of which came from China.

Alfalfa, also called lucerne, is a perennial flowering plant in the legume family Fabaceae. It is cultivated as an important forage crop in many countries around the world. It is used for grazing, hay, and silage, as well as a green manure and cover crop. The name alfalfa is used in North America. The name lucerne is more commonly used in the United Kingdom, South Africa, Australia, and New Zealand. The plant superficially resembles clover, especially while young, when trifoliate leaves comprising round leaflets predominate. Later in maturity, leaflets are elongated. It has clusters of small purple flowers followed by fruits spiralled in two to three turns containing 10–20 seeds. Alfalfa is native to warmer temperate climates. It has been cultivated as livestock fodder since at least the era of the ancient Greeks and Romans.

Rutabaga or Swede is a root vegetable, a form of Brassica napus. Other names include Swedish turnip, neep (Scots), and turnip. However, elsewhere, the name "turnip" usually refers to the related white turnip. The species Brassica napus originated as a hybrid between the cabbage and the turnip. Rutabaga roots are eaten as human food in various ways, and the leaves can be eaten as a leaf vegetable. The roots and tops are also used for livestock, fed directly in the winter or foraged in the field during the other seasons. Scotland, Northern and Western England, Wales, the Isle of Man, and Ireland had a tradition of carving the roots into Jack-o'-lanterns at Halloween.

The radish is a flowering plant in the mustard family, Brassicaceae. Its large taproot is commonly used as a root vegetable, although the entire plant is edible and its leaves are sometimes used as a leaf vegetable. Originally domesticated in Asia prior to Roman times, radishes are now grown and consumed throughout the world. The radish is sometimes considered to form a species complex with the wild radish, and instead given the trinomial name Raphanus raphanistrum subsp. sativus.

The British Agricultural Revolution, or Second Agricultural Revolution, was an unprecedented increase in agricultural production in Britain arising from increases in labor and land productivity between the mid-17th and late 19th centuries. Agricultural output grew faster than the population over the hundred-year period ending in 1770, and thereafter productivity remained among the highest in the world. This increase in the food supply contributed to the rapid growth of population in England and Wales, from 5.5 million in 1700 to over 9 million by 1801, though domestic production gave way increasingly to food imports in the 19th century as the population more than tripled to over 35 million.

Mangelwurzel or mangold wurzel, also called mangold, mangel beet, field beet, fodder beet and (archaic) root of scarcity, is a cultivated root vegetable. It is a variety of Beta vulgaris, the same species that also contains the red beet (beetroot) and sugar beet varieties. The cultivar group is named Crassa Group. Their large white, yellow or orange-yellow swollen roots were developed in the 18th century as a fodder crop for feeding livestock.

The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, precious metals, commodities, culture, human populations, technology, diseases, and ideas between the New World in the Western Hemisphere, and the Old World (Afro-Eurasia) in the Eastern Hemisphere, in the late 15th and following centuries. It is named after the Italian explorer Christopher Columbus and is related to the European colonization and global trade following his 1492 voyage. Some of the exchanges were purposeful while others were unintended. Communicable diseases of Old World origin resulted in an 80 to 95 percent reduction in the number of Indigenous peoples of the Americas from the 15th century onwards, most severely in the Caribbean. The cultures of both hemispheres were significantly impacted by the migration of people, both free and enslaved, from the Old World to the New. European colonists and African slaves replaced Indigenous populations across the Americas, to varying degrees. The number of Africans taken to the New World was far greater than the number of Europeans moving to the New World in the first three centuries after Columbus.

Agriculture began independently in different parts of the globe, and included a diverse range of taxa. At least eleven separate regions of the Old and New World were involved as independent centers of origin. The development of agriculture about 12,000 years ago changed the way humans lived. They switched from nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyles to permanent settlements and farming.

Canada is one of the largest agricultural producers and exporters in the world. As with other developed nations, the proportion of the population agriculture employed and agricultural GDP as a percentage of the national GDP fell dramatically over the 20th century, but it remains an important element of the Canadian economy. A wide range of agriculture is practised in Canada, from sprawling wheat fields of the prairies to summer produce of the Okanagan valley. In the federal government, overview of Canadian agriculture is the responsibility of the Department of Agriculture and Agri-Food.
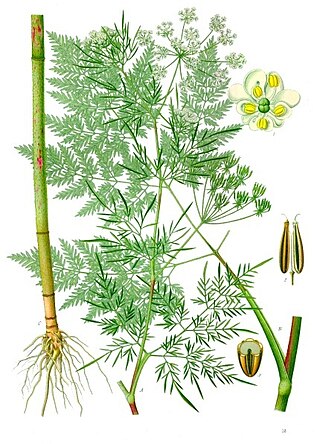
Chaerophyllum bulbosum is a species of flowering plant from the carrot family and known by several common names, including turnip-rooted chervil, tuberous-rooted chervil, bulbous chervil, and parsnip chervil. It is native to Europe and Western Asia. It was a popular vegetable in the 19th century.

Amflora is a genetically modified potato cultivar developed by BASF Plant Science. "Amflora" potato plants produce pure amylopectin starch that is processed to waxy potato starch. It was approved for industrial applications in the European Union on 2 March 2010 by the European Commission. In January 2012, the potato was withdrawn from the market in the EU.
Agriculture in the Southwest United States is very important economically in that region.

The potato was the first domesticated vegetable in the region of modern-day southern Peru and extreme northwestern Bolivia between 8000 and 5000 BC. Cultivation of potatoes in South America may go back 10,000 years, but tubers do not preserve well in the archaeological record, making identification difficult. The earliest archaeologically verified potato tuber remains have been found at the coastal site of Ancón, dating to 2500 BC. Aside from actual remains, the potato is also found in the Peruvian archaeological record as a design influence of ceramic pottery, often in the shape of vessels. The potato has since spread around the world and has become a staple crop in most countries.

In North Korea, the cultivation of potatoes is an important aspect to the livelihood of the country's population. The crop was introduced into the country in the early 1800s. Since the famine of the 1990s, a potato revolution has taken place. Over ten years, the area of potato cultivation in North Korea quadrupled to 200,000 hectares and per capita consumption increased from 16 to 60 kilograms per year.

A staple food, food staple, or simply staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for an individual or a population group, supplying a large fraction of energy needs and generally forming a significant proportion of the intake of other nutrients as well. For humans, a staple food of a specific society may be eaten as often as every day or every meal, and most people live on a diet based on just a small variety of food staples. Specific staples vary from place to place, but typically are inexpensive or readily available foods that supply one or more of the macronutrients and micronutrients needed for survival and health: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, and vitamins. Typical examples include grains, seeds, nuts and root vegetables. Among them, cereals, legumes and tubers account for about 90% of the world's food calorie intake.

China is the world's largest producer of potatoes, generating more than 22 percent of global potato production. The potato is the only crop that can be grown in all regions of China, although cultivation predominantly takes place in the northern and southern regions of the country.
Will Bonsall is an American author, seed saver and veganic farmer who lives in Maine. He is a regular speaker about seed saving, organic farming and veganic farming.

Nigeria is one of the largest producers of potatoes in Africa. The potato was introduced to the country in the 19th century by Christian missionaries and is largely cultivated in the central region of the country in Plateau State.

The cultivation of potatoes is a major part of the agricultural industry of Algeria. The country was the 17th-largest producer of potatoes in the world in 2018. Production is centred on two regions: the Mediterranean coast and the desert around El Oued. Growing conditions in the coast are broadly conventional in earth furrows while at El Oued centre pivot irrigation predominates, with the potatoes grown in sand. Only an insignificant minority of the crop is factory-processed.
References
- ↑ Bouchier, Frank; Marsh, Stephen. "Potato Seed Catalogue 2005". Irish Seed Saver Association. Archived from the original on 2012-12-16. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ↑ /Potato Varieties of Historical Interest in Ireland Archived 2013-06-21 at the Wayback Machine Irish Government website Retrieved 2012-06-04
